Casting and forging are both industrial processes of metal forming and shaping. The different processes are used in different conditions.
The main difference between casting and forging is that the metal is compulsory to heat and convert into a liquid stage in casting but in forging metal is converted into the desired shape by applying pressure with or without applying heat.
If the metal is preheated into forging it does not convert into the liquid stage. But before differentiate between both terms; you have to know about what is casting and what is forging.
Casting and forging are both industrial processes of metal forming and shaping. The different processes are used in different conditions.
The main difference between casting and forging is that the metal is compulsory to heat and convert into a liquid stage in casting but in forging metal is converted into the desired shape by applying pressure with or without applying heat.
If the metal is preheated into forging it does not convert into the liquid stage. But before differentiate between both terms; you have to know about what is casting and what is forging.
What is casting?
Casting is a process in which metal is heated until the molten stage and pour this liquid metal into a mold or cavity where it allows solidifying. This process converts the metal into the desired shape. It is useful to make a complex structure. Most of the industrial structure’s parts are like lathe machine bed, milling machine bed make the big base of other machinery parts, IC engine components, etc. are made by this process.Advantages of Casting
- This process can form a very large structure which is impossible to form by other processes.
- It can make any complex and unsymmetrical structure.
- The structure formed by this process has high compressive strength.
- It can attain a wide range of properties.
- This process can attain high accuracy.
What is forging?
On the other hand, forging is the process of converting metal into the desired shape by applying pressure and with or without heat. When the metal is heated before applying pressure the process is called hot forging. In forging metal is heated before below critical temperature or below the molten stage. Rolling, pressing, Wire drawing, etc. is various types of forging. All sheets, small components, wires, etc are formed by this process.Advantages of Forging:
It produces tougher product compare to other. The product made by forging has a high impact or tensile strength.The tabular form of Difference between Forging vs Casting.
| S. No. | Casting | Forging |
| 1 | The metal is heated until it converts into molten stage. | The metal is heated below recrystallization temperature. |
| 2 | The product produce by it have high compressive strength compare to forging. | It has low compressive strength. |
| 3 | It has low fatigue strength. | It has high fatigue strength |
| 4 | Imperfection or directional defecates does not improve in casting. | Directional defect are refined in forging. |
| 5 | It is less reliable or has low strength. | It is high reliable. |
| 6 | It is costly sometime and has high lead time. | It has low lead time and cheap compare to casting. |
| 7 | The product has low tensile strength. | This produces high tensile strength. |
| 8 | It required a secondary finishing operation. | It does not require a secondary operation. |
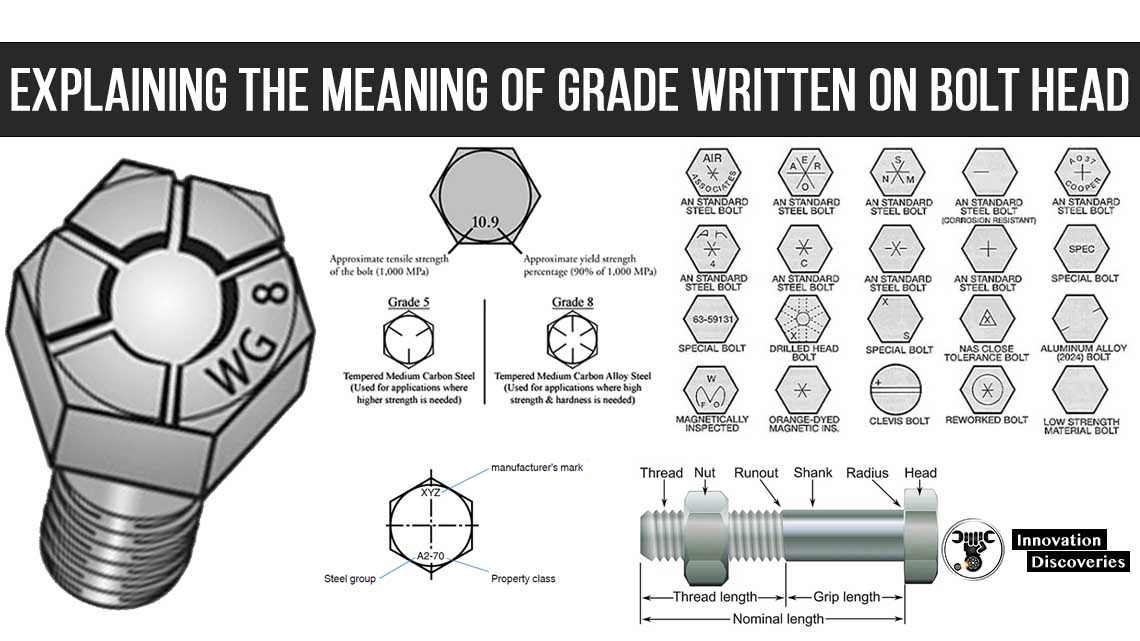
EXPLAINING THE MEANING OF GRADE WRITTEN ON BOLT HEAD
Check Out Why do Tools Have DROP FORGED Stamped On Them

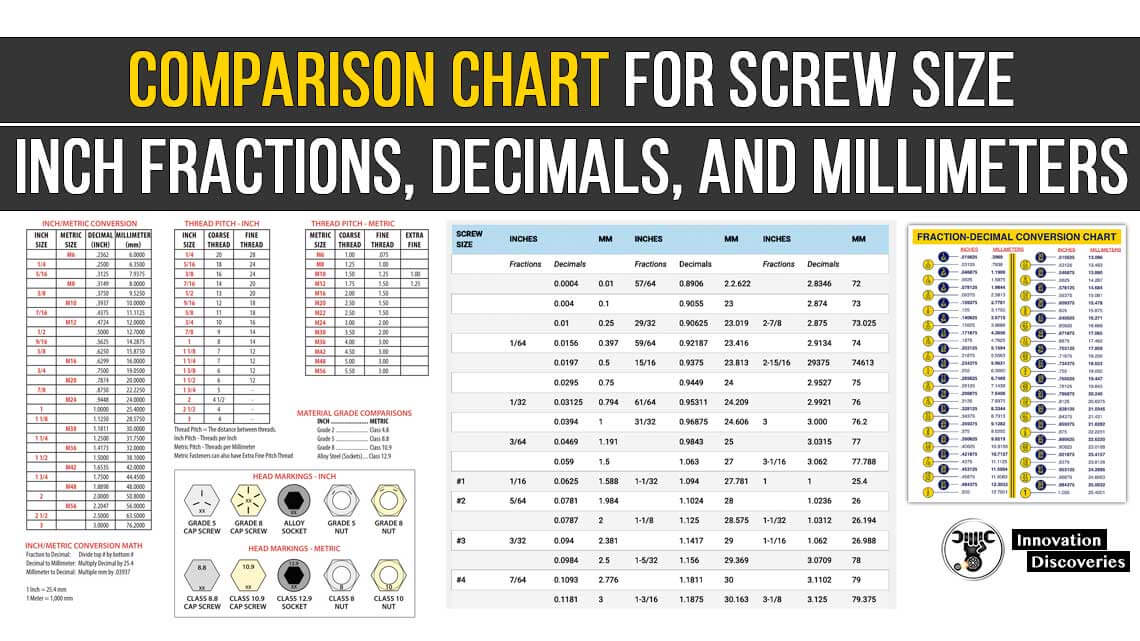
Comparison Chart for Screw Size, Inch Fractions, Decimals, and Millimeters
Tools and Their Uses | Part 1 – SAFETY
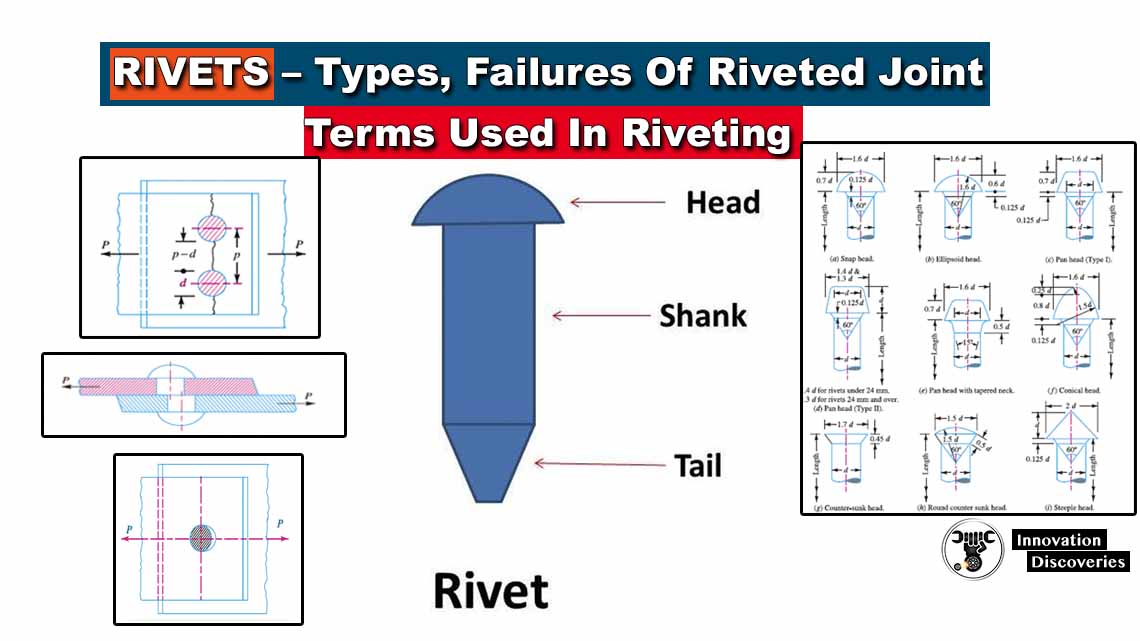
Rivets – Types, Failures Of Riveted Joint, Terms Used In Riveting
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website