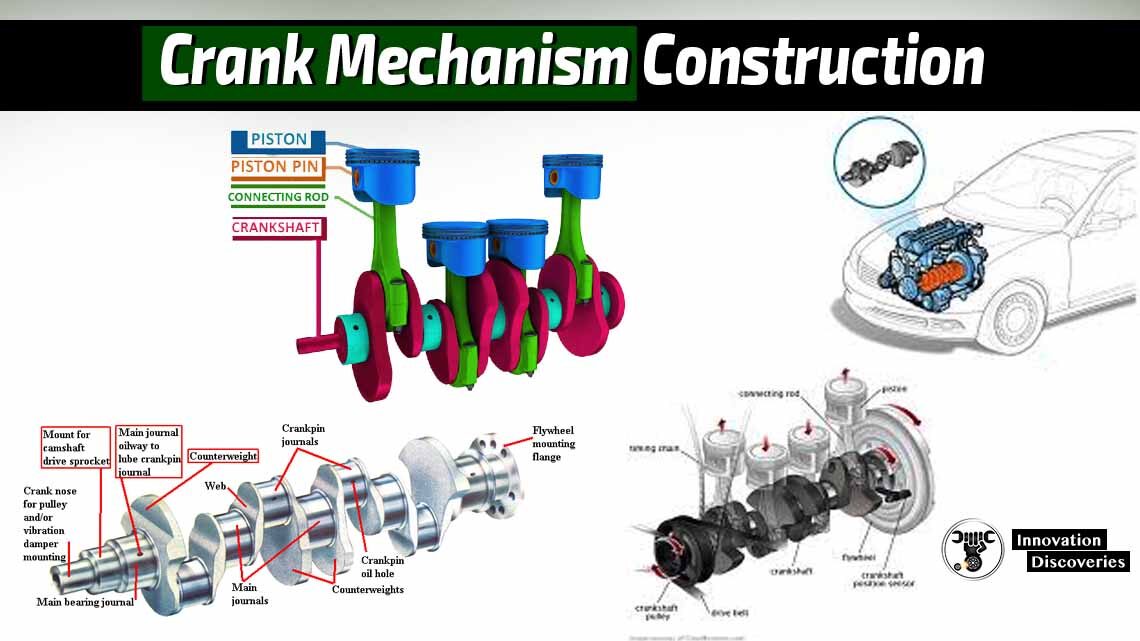
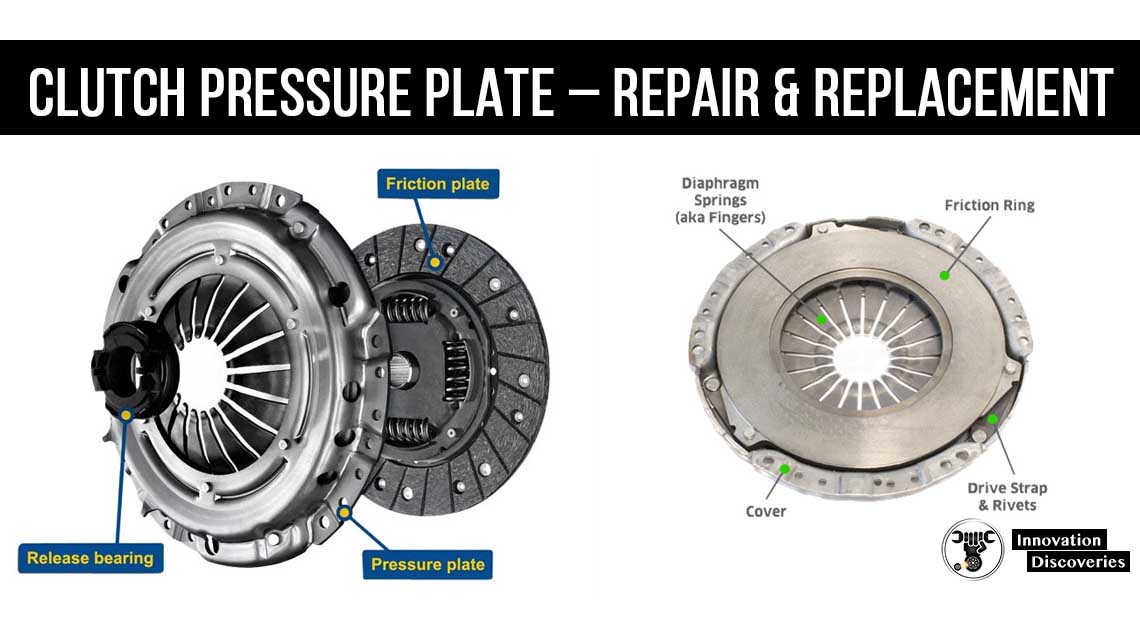
What is a flywheel? What does it do?
A flywheel is a mechanical component in a vehicle’s transmission system that is responsible for providing inertia to the engine’s crankshaft, which helps to maintain a steady rotational speed. It is usually made of cast iron or steel and mounted on the engine’s crankshaft.
The flywheel stores kinetic energy and releases it to the engine during power strokes, ensuring that the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. It also helps to reduce engine vibration and improve the longevity of the vehicle’s transmission system.
In more detail, the flywheel is a rotating component that is connected to the engine’s crankshaft. It works by storing energy in the form of rotational kinetic energy, which is created by the engine’s pistons during the power stroke. The stored energy in the flywheel is then released during the engine’s compression stroke, which helps to maintain a smooth and steady rotation of the engine’s crankshaft.
The flywheel also serves as a damper, which helps to reduce engine vibration and provides a more comfortable driving experience. The mass of the flywheel absorbs any small variations in torque output from the engine, which helps to reduce the effects of any fluctuations in the engine’s output.
Flywheels are typically made of cast iron or steel, as these materials provide the necessary strength and durability to withstand the stresses and forces created by the engine. They are mounted on the engine’s crankshaft using bolts or pins and are located in the transmission housing of the vehicle.
In summary, the flywheel is an important component in a vehicle’s transmission system that helps to ensure a smooth and efficient operation of the engine. Its primary function is to store and release energy to maintain a steady rotational speed of the engine’s crankshaft and to reduce engine vibration.
Types of Components
Discs used for this purpose are typically constructed from steel, cast iron, or aluminum. The greater rotational inertia of the disc is more efficient in reducing high fluctuations in speed. The two main types of flywheels are single-mass and dual-mass flywheels.
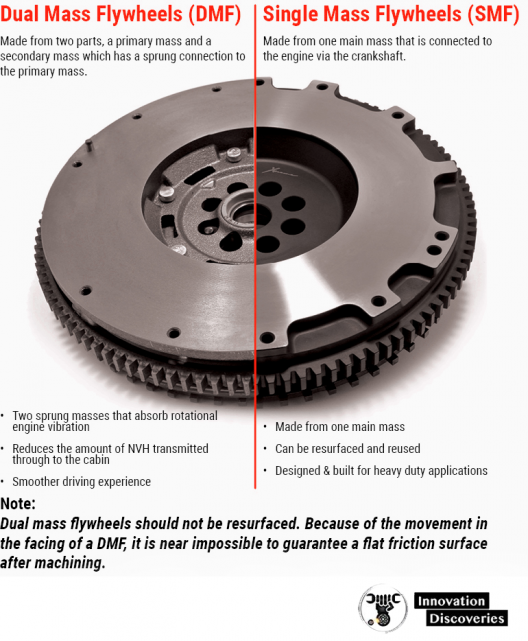
Single mass flywheels:
Single-mass flywheels are the most common type of flywheel used in vehicles with manual transmissions. They consist of a solid disc made of cast iron or steel, which is bolted directly to the engine’s crankshaft. The clutch assembly is mounted on the flywheel, and the pressure plate, clutch disc, and throw-out bearing are all attached to the clutch assembly.
Single-mass flywheels are generally simpler and more reliable than dual-mass flywheels, as they have fewer moving parts and are less susceptible to failure. They also tend to be lighter than dual-mass flywheels, which can provide a more responsive driving experience and improved fuel efficiency.
However, single-mass flywheels can be more prone to clutch chatter, which is a vibration that occurs when the clutch is engaged. This is caused by the solid design of the flywheel, which can create more transmission of engine vibrations in the transmission system.
Overall, single-mass flywheels are a popular choice for vehicles with manual transmissions due to their simplicity, reliability, and lighter weight. They are generally more suitable for high-performance applications and can provide a more responsive and engaging driving experience.
Dual mass flywheels:
Dual mass flywheels (DMFs) are a more complex type of flywheel that is commonly used in modern vehicles with manual transmissions. They consist of two flywheels, one inner and one outer, which are connected by a series of springs or dampers. The inner flywheel is bolted to the engine’s crankshaft, while the outer flywheel is connected to the clutch assembly.
DMFs are designed to reduce engine vibration and improve the comfort of the driver and passengers. They work by isolating the transmission system from the engine’s vibrations, which helps to reduce noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) levels.
The springs or dampers in the DMF allow the inner and outer flywheels to move independently of each other, which absorbs any small variations in torque output from the engine and prevents them from being transmitted to the transmission system.
DMFs are generally more expensive and complex than single-mass flywheels, and they require more maintenance. They are also more prone to failure due to their more complicated design, and they can be difficult to repair or replace.
However, they are a popular choice for vehicles that require a smoother and more comfortable driving experience, such as luxury cars and commercial vehicles.
Overall, dual-mass flywheels are a more advanced type of flywheel that can provide a smoother and more comfortable driving experience. They are ideal for vehicles that prioritize driver and passenger comfort over performance, and they can help to reduce NVH levels and improve fuel efficiency.
What causes flywheel damage?
Flywheels can become damaged due to a variety of factors, including improper maintenance, engine condition, and driving habits, as well as overheating.
Improper Maintenance
Improper maintenance is one of the most common causes of flywheel damage. Failure to maintain the flywheel and other components of the transmission system can lead to premature wear and tear, which can cause the flywheel to fail. This can include issues such as worn or damaged clutch components, contaminated clutch fluid, or insufficient lubrication.
Engine condition and driving habits
Engine conditions and driving habits can also contribute to flywheel damage. Vehicles that are frequently driven aggressively or used for towing heavy loads can place a significant amount of stress on the flywheel and other transmission components. This can cause the flywheel to become worn or damaged over time, particularly if the vehicle is frequently driven in stop-and-go traffic or hilly terrain.
Overheating
Overheating is another common cause of flywheel damage. When the engine becomes overheated, the flywheel can become warped or distorted, which can affect its ability to function properly. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including a malfunctioning cooling system, a clogged radiator, or a damaged water pump.
Symptoms of a faulty flywheel
A faulty flywheel can exhibit several symptoms, which can indicate that it requires repair or replacement. Some of the most common symptoms of a faulty flywheel include:
1. A burning smell:
If the flywheel is damaged or worn, it can cause excessive heat and friction in the clutch system, which can lead to a burning smell. This can indicate that the flywheel is overheating and needs to be replaced.
2. Difficulty changing gears:
If the flywheel is damaged or worn, it can affect the ability of the clutch system to engage and disengage properly. This can make it difficult or impossible to shift gears, particularly when starting or stopping the vehicle.
3. A vibrating clutch pedal:
A damaged or worn flywheel can cause the clutch pedal to vibrate or shake when it is engaged. This can be felt through the pedal and can be a sign that the flywheel is warped or out of balance.
4. Clutch chatter:
Clutch chatter is a vibration or juddering that can occur when the clutch is engaged. This can be caused by a damaged or worn flywheel, which can affect the smooth engagement of the clutch system.
Can you drive with a faulty flywheel?
It is generally not recommended to drive with a faulty flywheel as it can cause further damage to the vehicle and make it unsafe to drive.
A faulty flywheel can affect the performance of the clutch system and cause symptoms such as difficulty changing gears, clutch chatter, a vibrating clutch pedal, and a burning smell. These symptoms can make the vehicle difficult to drive and compromise its safety. In addition, a faulty flywheel can cause further damage to the transmission system if left unaddressed, which can result in more costly repairs.
If you suspect that your flywheel is faulty, it is important to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible. The mechanic can diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate course of action, which may include repair or replacement of the flywheel. Driving with a faulty flywheel can be dangerous and should be avoided until the issue has been resolved.
Is it possible to have it repaired?
In some cases, a faulty flywheel can be repaired, while in other cases, it may need to be replaced. The type and extent of the damage to the flywheel will determine whether it can be repaired or not.
For example, if the flywheel has only minor damage, such as surface wear or scoring, it may be possible to resurface or refinish it. This involves machining the surface of the flywheel to remove any imperfections and restore it to its original condition. However, if the flywheel is severely damaged, such as being warped or cracked, it may need to be replaced.
In addition, the type of flywheel can also affect whether it can be repaired or not. Single-mass flywheels are generally easier to repair than dual-mass flywheels, which are more complex and have more components that can fail.
If you suspect that your flywheel is faulty, it is important to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic. The mechanic can diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate course of action, which may include repair or replacement of the flywheel.
Don’t try to repair a bad flywheel yourself.
Correct, it is not recommended to attempt to repair a faulty flywheel yourself. Repairing or replacing a flywheel requires specialized knowledge, tools, and equipment, and should only be performed by a qualified mechanic.
Attempting to repair a flywheel yourself can be dangerous and can cause further damage to the vehicle. A faulty flywheel can affect the performance of the clutch system, and attempting to repair it without the proper knowledge and equipment can result in an improperly functioning clutch system, which can compromise the safety of the vehicle.
In addition, flywheels are often made of heavy materials and can be difficult to handle. Attempting to remove or repair a flywheel without the proper equipment or techniques can result in injury or damage to the vehicle.
If you suspect that your flywheel is faulty, it is important to have it inspected by a qualified mechanic. The mechanic can diagnose the problem and recommend the appropriate course of action, which may include repair or replacement of the flywheel. By leaving the repair or replacement of the flywheel to a professional, you can ensure that your vehicle is repaired properly and safely.
Discover More:
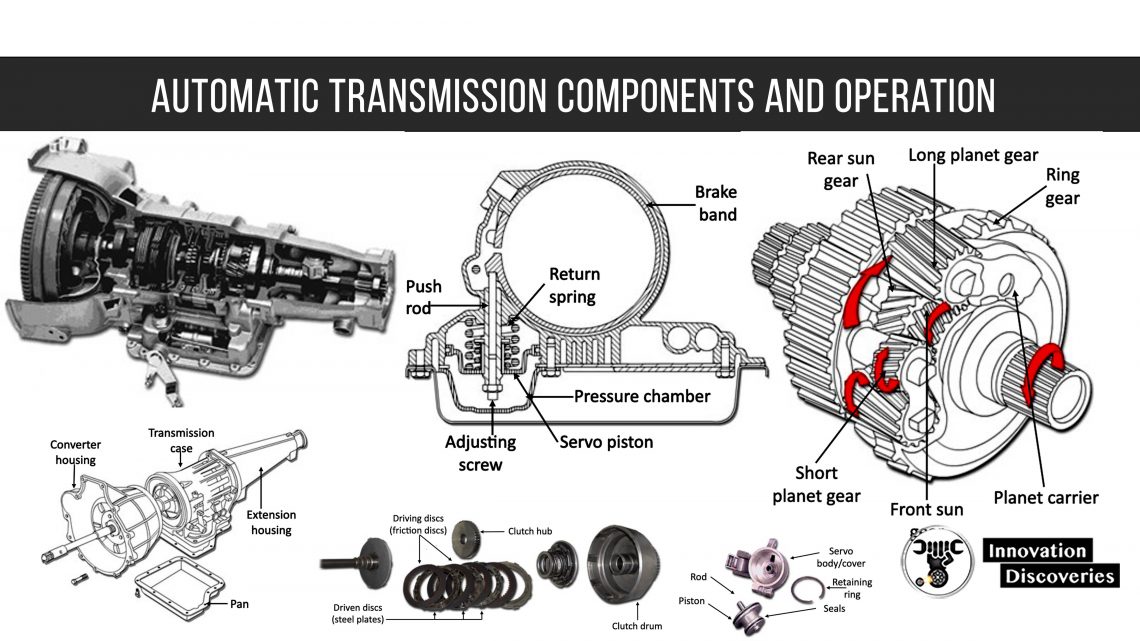
See More:
- 4 Common Symptoms of Automatic Transmission Problems
- How To Do Automatic Transmission Service Yourself?
- Automatic Transmission Valve Body Functions And Failure Symptoms
- Detecting 6 Common Automatic Transmission Problems
- Continuously Variable Transmission : Advantages and Disadvantages
Read: 5 CAUSES OF TRANSMISSION FLUID LEAKS AND REPAIR COST

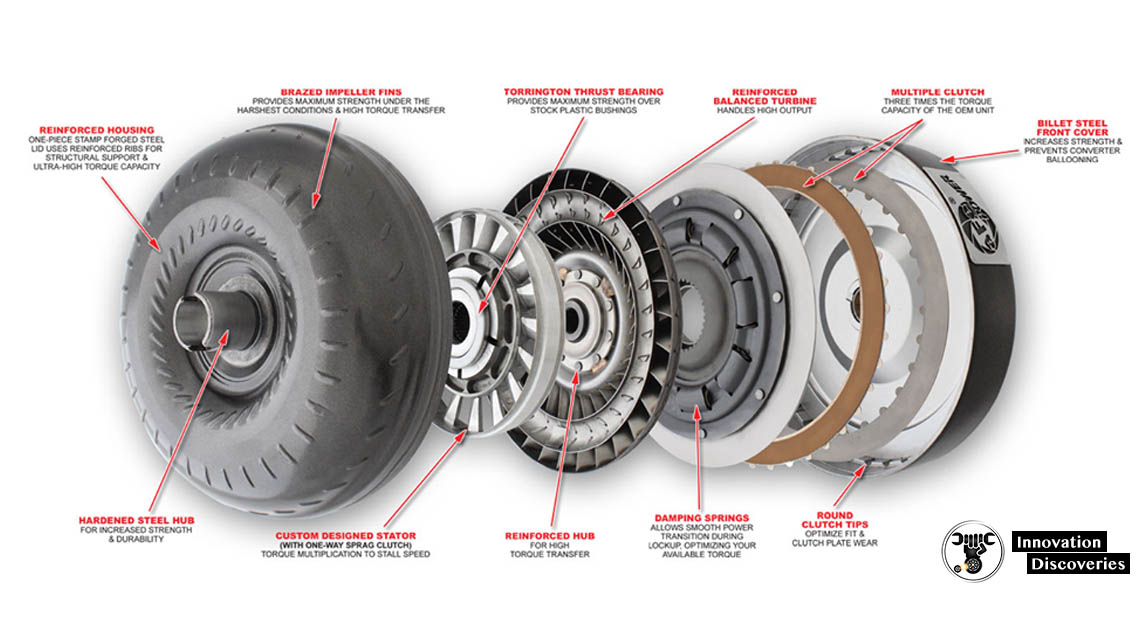
TORQUE CONVERTER: FUNCTIONS, PARTS, WORKING PRINCIPLES, AND TYPES
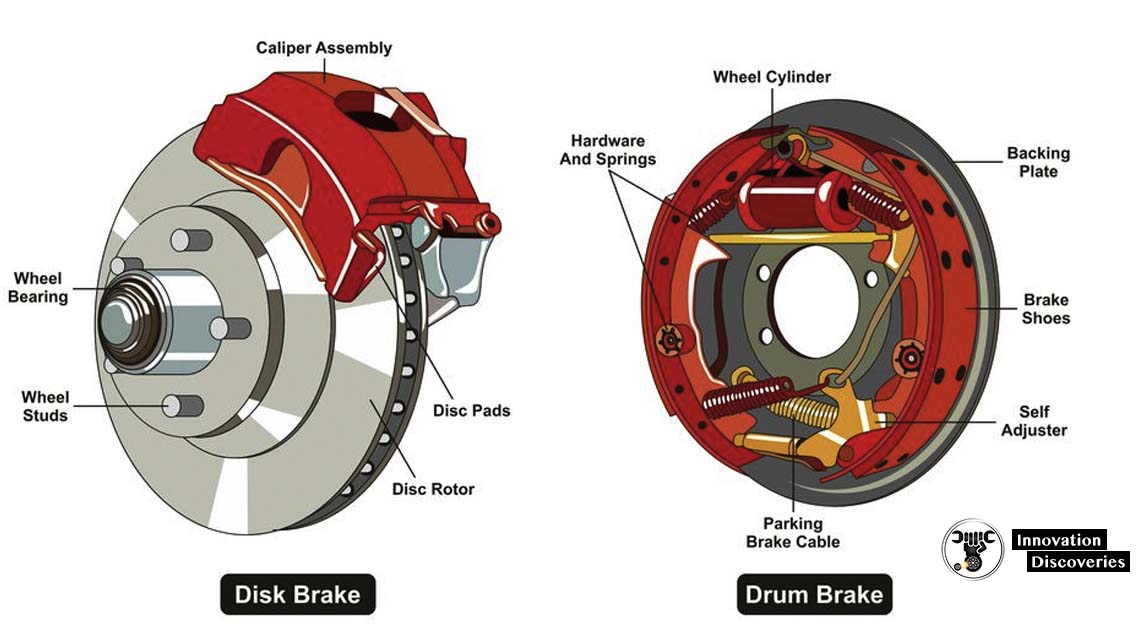
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DRUM BRAKE AND DISC BRAKE
CONVERT DRUM BRAKES TO DISC BRAKES IN 3 STEPS!
WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN BRAKE SHOES AND BRAKE PADS?
Read: HOW DOES AN OIL SUMP WORK IN YOUR CAR?
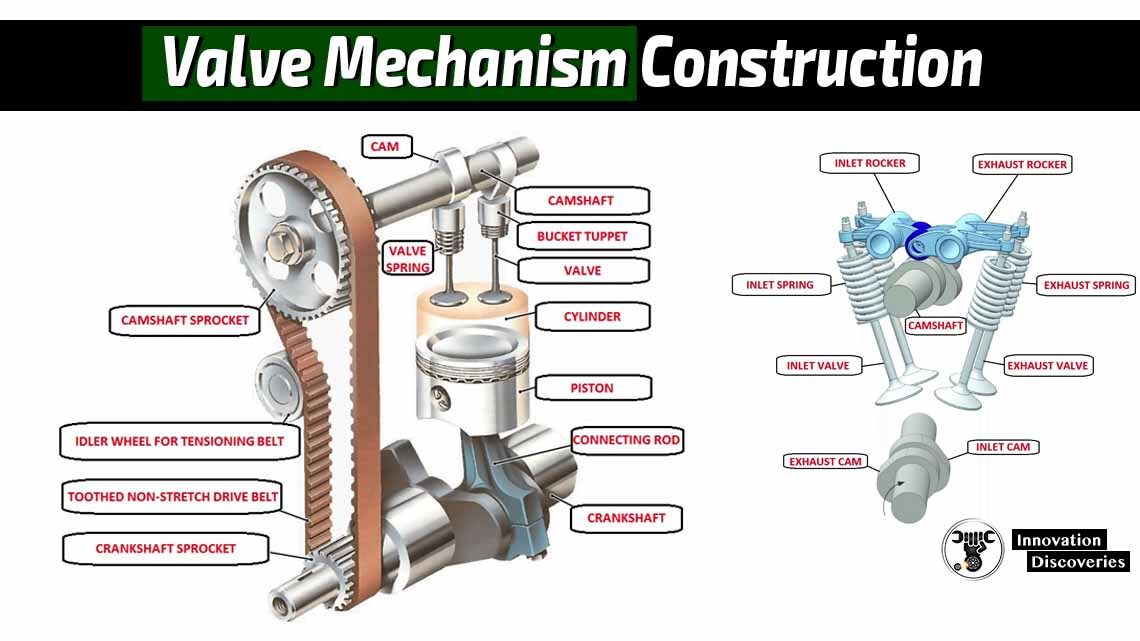
Download: VALVE SELECTION HANDBOOK | PDF
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website