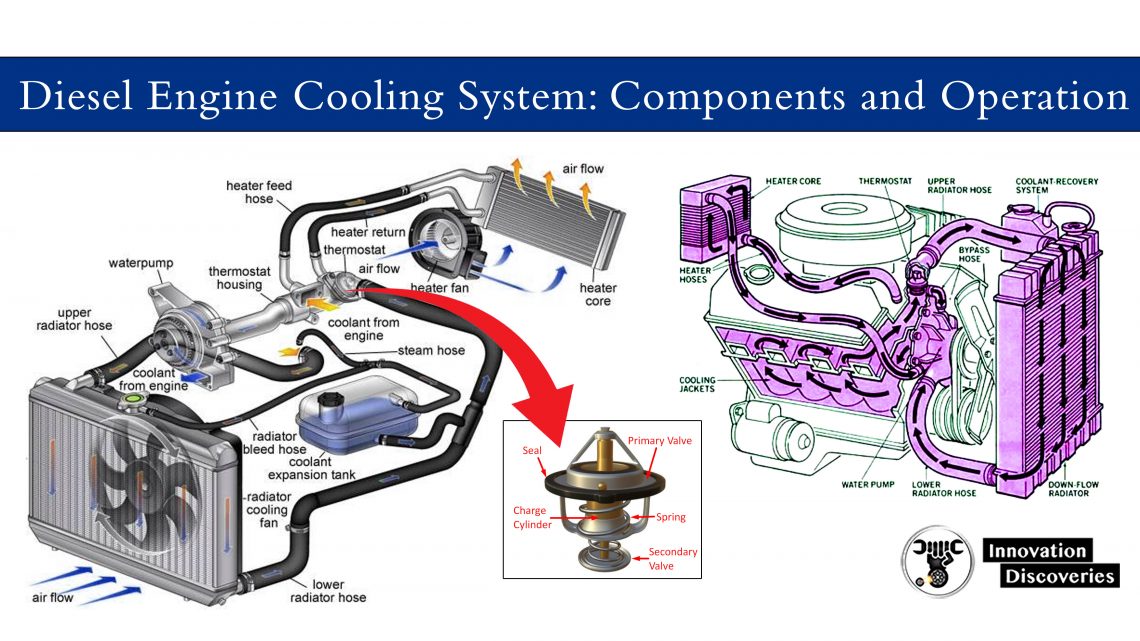
Introduction
In the world of automotive performance and longevity, one often-overlooked component plays a crucial role in maintaining engine health and efficiency: the engine oil cooler.
While it might not be as flashy as a turbocharger or a high-performance exhaust system, an oil cooler can significantly enhance your vehicle’s performance and lifespan, especially under demanding conditions.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore why adding an engine oil cooler to your vehicle is a smart decision, how it works, whether your car needs one, the types available, how to choose the right aftermarket oil cooler, installation procedures, and essential maintenance tips.
Why You Should Add an Engine Oil Cooler
Your engine operates within a delicate balance of temperature and pressure, and maintaining proper lubrication is essential to prevent premature wear and tear.
An engine oil cooler helps dissipate heat from the engine oil, ensuring it stays within optimal temperature ranges. By keeping the oil temperature in check, an oil cooler prevents thermal breakdown and maintains proper viscosity, resulting in improved engine performance and longevity.
How an Oil Cooler Works
At its core, an oil cooler functions as a heat exchanger, transferring heat from the engine oil to the surrounding air or coolant.
Whether it’s air-to-oil or liquid-to-oil cooling, the principle remains the same: as the oil flows through the cooler’s tubes or fins, heat is transferred away, effectively lowering the oil temperature and maintaining its lubricating properties.
Does Your Car Need an Oil Cooler?
While not every vehicle requires an oil cooler, certain conditions warrant its addition. If you frequently tow heavy loads, engage in performance driving, or live in hot climates, an oil cooler can be immensely beneficial.
These scenarios subject the engine to increased stress and heat, making proper oil cooling essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Types of Engine Oil Coolers
Engine oil coolers come in various types, each with its own advantages:
1. Air-to-Oil Coolers:
Air-to-Oil Coolers are a popular choice for many vehicle owners seeking efficient engine oil cooling. Operating on a straightforward principle, these coolers utilize the airflow generated by the vehicle’s movement or through an integrated fan to dissipate heat from the engine oil.
How Air-to-Oil Coolers Work
In an air-to-oil cooler setup, the engine oil circulates through a network of tubes or fins, which are exposed to the incoming airflow.
As the vehicle moves forward or the fan operates, ambient air passes over these tubes or fins, carrying away the heat absorbed by the engine oil.
This process effectively lowers the temperature of the oil, ensuring it remains within optimal operating conditions.
Advantages of Air-to-Oil Coolers
- Simplicity: Air-to-oil coolers are relatively simple in design and installation, making them accessible for a wide range of vehicles.
- No Additional Fluids: Unlike liquid-to-oil coolers, air-to-oil coolers don’t require additional fluids, simplifying maintenance and reducing the risk of leaks.
- Efficiency: With the constant airflow generated by the vehicle’s movement or through a dedicated fan, air-to-oil coolers can efficiently dissipate heat from the engine oil, helping to maintain consistent oil temperatures.
- Compact Size: Air-to-oil coolers are often compact in size, making them suitable for installation in tight spaces within the vehicle’s engine bay or behind the bumper.
Applications of Air-to-Oil Coolers
Air-to-oil coolers are commonly used in various applications, including:
- Performance Vehicles: High-performance cars often benefit from air-to-oil coolers to maintain oil temperature stability during aggressive driving.
- Towing and Hauling: Vehicles used for towing heavy loads or hauling cargo can experience increased engine oil temperatures, making air-to-oil coolers a valuable addition to prevent overheating.
- Hot Climates: In regions with hot climates, air-to-oil coolers help ensure that engine oil remains at optimal temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal breakdown and engine damage.
Installation Considerations
When installing an air-to-oil cooler, it’s crucial to position it in an area where it can receive sufficient airflow.
This may involve mounting the cooler in front of the vehicle’s radiator or behind the bumper, depending on available space and airflow dynamics.
Additionally, ensuring proper airflow through the cooler’s fins or tubes is essential for optimal cooling efficiency.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance of air-to-oil coolers involves inspecting for any signs of damage or blockages and cleaning the cooler as needed to remove dirt, debris, and other contaminants that can hinder airflow.
It’s also important to monitor oil temperatures and ensure that the cooler is operating effectively under varying driving conditions.
In conclusion, air-to-oil coolers offer an efficient and practical solution for maintaining optimal engine oil temperatures in a wide range of applications.
By leveraging the vehicle’s airflow or incorporating a dedicated fan, these coolers effectively dissipate heat from the engine oil, enhancing engine performance and longevity.
Whether you’re driving a high-performance vehicle, towing heavy loads, or operating in hot climates, an air-to-oil cooler can be a valuable addition to your vehicle’s cooling system.
2. Liquid-to-Oil Coolers:
Liquid-to-Oil Coolers are another effective option for engine oil cooling, particularly in applications where additional cooling capacity is needed or where ambient airflow is limited.
Unlike air-to-oil coolers, which rely on ambient air for heat dissipation, liquid-to-oil coolers use a separate coolant, such as water or engine coolant, to transfer heat away from the engine oil.
How Liquid-to-Oil Coolers Work
In a liquid-to-oil cooling system, the engine oil circulates through a heat exchanger, typically a radiator-like component, where it comes into contact with a separate coolant.
As the coolant absorbs heat from the engine oil, it carries the heat away to be dissipated elsewhere in the vehicle’s cooling system, often through the main radiator.
This process effectively lowers the temperature of the engine oil, ensuring optimal operating conditions.
Advantages of Liquid-to-Oil Coolers
- Enhanced Cooling Capacity: Liquid-to-oil coolers can provide greater cooling capacity compared to air-to-oil coolers, making them suitable for high-performance applications or situations where additional cooling is necessary.
- Efficient Heat Transfer: By utilizing a separate coolant, liquid-to-oil coolers can achieve efficient heat transfer, even in environments where ambient airflow is limited or insufficient for effective cooling.
- Temperature Regulation: Liquid-to-oil coolers allow for precise temperature regulation of the engine oil by adjusting the flow rate or temperature of the coolant, ensuring consistent oil temperatures under varying driving conditions.
- Versatility: Liquid-to-oil coolers can be integrated into the vehicle’s existing cooling system, allowing for seamless operation and compatibility with other cooling components.
Applications of Liquid-to-Oil Coolers
Liquid-to-oil coolers find applications in various scenarios, including:
- High-Performance Vehicles: Performance cars with high-output engines benefit from the enhanced cooling capacity and precise temperature regulation provided by liquid-to-oil coolers, ensuring optimal engine performance during spirited driving.
- Heavy-Duty Use: Vehicles used for towing heavy loads or hauling cargo may require additional cooling capacity to prevent overheating, making liquid-to-oil coolers a valuable addition to the cooling system.
- Limited Airflow Environments: In situations where ambient airflow is limited, such as off-road or low-speed driving, liquid-to-oil coolers offer an effective cooling solution that doesn’t rely on external airflow.
Installation Considerations
Installing a liquid-to-oil cooler involves integrating it into the vehicle’s existing cooling system, typically in-line with the engine oil circuit.
Mounting locations may vary depending on available space and routing considerations, but it’s essential to ensure proper coolant flow and compatibility with other cooling components.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance of liquid-to-oil coolers includes inspecting for leaks, checking coolant levels and quality, and ensuring proper coolant flow through the cooler.
Additionally, periodic cleaning of the cooler’s fins or tubes is necessary to remove any debris or contaminants that may impede heat transfer.
In conclusion, liquid-to-oil coolers offer an effective solution for maintaining optimal engine oil temperatures in a wide range of applications.
Whether you’re driving a high-performance vehicle, towing heavy loads, or operating in environments with limited airflow, a liquid-to-oil cooler can provide enhanced cooling capacity and precise temperature regulation to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity.
3. Thermostatic Oil Coolers:
Thermostatic Oil Coolers represent a sophisticated solution to engine oil cooling, offering precise temperature regulation and efficient cooling performance.
Unlike conventional oil coolers, which operate continuously, thermostatic oil coolers incorporate a built-in thermostat that regulates the flow of oil through the cooler based on temperature conditions.
This intelligent design ensures that the engine oil remains within optimal temperature ranges, providing both effective cooling and energy efficiency.
How Thermostatic Oil Coolers Work
The key feature of thermostatic oil coolers is the inclusion of a thermostat mechanism within the cooler assembly.
This thermostat monitors the temperature of the engine oil and adjusts the flow of oil through the cooler accordingly. When the engine oil temperature exceeds a certain threshold, the thermostat opens, allowing oil to flow through the cooler and undergo cooling.
Conversely, when the oil temperature falls below the set threshold, the thermostat closes, restricting the flow of oil through the cooler to conserve energy and maintain optimal operating conditions.
Advantages of Thermostatic Oil Coolers
- Precise Temperature Regulation: Thermostatic oil coolers ensure that the engine oil remains within optimal temperature ranges, preventing both overheating and excessive cooling, which can compromise engine performance and efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency: By regulating the flow of oil based on temperature conditions, thermostatic oil coolers operate only when necessary, conserving energy and reducing unnecessary cooling during periods of lower oil temperatures.
- Improved Engine Performance: By maintaining consistent oil temperatures, thermostatic oil coolers help optimize engine performance and longevity, reducing the risk of thermal breakdown and ensuring proper lubrication under varying driving conditions.
- Enhanced Cooling Control: Thermostatic oil coolers offer greater control over cooling performance, allowing for precise adjustment of the thermostat settings to accommodate specific driving environments and performance requirements.
Applications of Thermostatic Oil Coolers
Thermostatic oil coolers find applications in various automotive scenarios, including:
- Performance Driving: High-performance vehicles benefit from the precise temperature regulation provided by thermostatic oil coolers, ensuring optimal engine performance during aggressive driving maneuvers.
- Towing and Hauling: Vehicles used for towing heavy loads or hauling cargo can experience increased engine oil temperatures, making thermostatic oil coolers a valuable addition to prevent overheating and maintain lubrication efficiency.
- Cold Weather Operation: In colder climates, thermostatic oil coolers help reduce warm-up times and improve engine efficiency by restricting oil flow through the cooler until the engine reaches operating temperature.
Installation Considerations
Installing a thermostatic oil cooler involves integrating it into the vehicle’s existing cooling system, typically in-line with the engine oil circuit.
Mounting locations and routing considerations may vary depending on the vehicle’s layout and available space, but it’s essential to ensure proper installation and alignment of the thermostat mechanism for optimal performance.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance of thermostatic oil coolers includes periodic inspection of the thermostat mechanism for proper operation, checking for leaks, and ensuring that coolant levels and quality are within recommended specifications.
Additionally, cleaning the cooler’s fins or tubes as needed to remove debris and contaminants is essential for maintaining cooling efficiency.
In conclusion, thermostatic oil coolers offer a sophisticated and efficient solution for maintaining optimal engine oil temperatures in a wide range of driving conditions.
By incorporating a built-in thermostat mechanism, these coolers provide precise temperature regulation, energy efficiency, and enhanced cooling control, ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity for performance vehicles, towing applications, and cold weather operation alike.
Choosing an Aftermarket Engine Oil Cooler
When selecting an aftermarket oil cooler, consider factors such as cooling capacity, compatibility, ease of installation, and quality.
Opt for reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality cooling components to ensure reliability and performance.
Installing an Oil Cooler
Installation procedures may vary depending on your vehicle’s make and model, but generally involve mounting the cooler in a location with adequate airflow.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully or consult a professional mechanic for assistance to ensure proper installation and functionality.
Oil Cooler Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of your oil cooler. Inspect it regularly for damage or leaks, clean it as needed to remove dirt and debris, and adhere to the manufacturer’s recommendations for filter replacement and other maintenance tasks.
In conclusion, adding an engine oil cooler to your vehicle can provide a host of benefits, including improved cooling efficiency, consistent oil temperature, enhanced engine performance, protection against overheating, and extended engine life.
By understanding how oil coolers work and following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can make an informed decision about adding one to your vehicle and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with optimal engine health and performance.
Discover More:

Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website