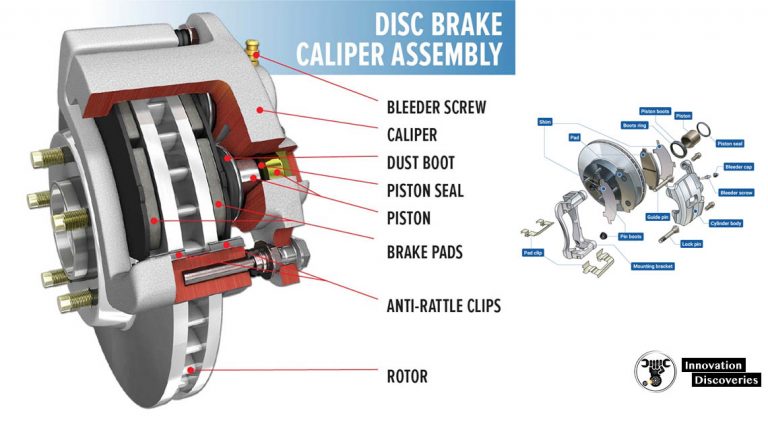
DISC BRAKES: CONSTRUCTION, WORKING PRINCIPLE, TYPES, AND ROTOR MATERIALS
Brake rotors of disc brakes rotate with the wheels, and brake pads, which are fitted to the brake calipers, clamp-on these rotors to stop or decelerate the wheels. The brake pads pushing against the rotors generate friction, which transforms kinetic energy into thermal energy. The thermal energy generates heat, but this heat can be effectively diffused as the main components are exposed to the atmosphere. This heat-dissipating property decreases brake fade, the phenomenon in which the heat affects the braking performance. Another advantage of disc brake is its resistance to water fade, which occurs when the water on the brakes significantly reduces the braking force. When the vehicle is in motion, the rotor spins at high speeds and this rotational motion discharges the water from the rotors themselves, resulting in stable braking force. CONSTRUCTION The brake rotor (disc) which rotates with the wheel, is clamped by brake pads (friction material) fitted to the caliper from both … Continue reading DISC BRAKES: CONSTRUCTION, WORKING PRINCIPLE, TYPES, AND ROTOR MATERIALS