
We see the words “drop forged” stamped on so many tools. It makes us wonder what it is! 🤔
Why do manufacturers want you to know that a tool is drop forged? 🤔
Striking a piece of hot metal with a hammer is forging, and blacksmiths have been doing this for centuries.
As blacksmiths experimented with new techniques, they learned that complex shapes could be created by hammering metal into a die.
The die contains the shape of the finished product.
Modern manufacturers use either a falling hammer or a powered hammer to do the hammering (rather than doing it by hand) and usually use dies on both sides of the piece. This is drop forging.
Drop forging is a metal shaping process, the metal to be formed is first heated then shaped by forcing it into the contours of a die, this force can be in excess of 2000 tons.
The drop forging process can be performed with the material at various temperatures;
Hot Forging
- During hot forging, the metals are heated to above their recrystallization temperature.
- The main benefit of this hot forging is that work hardening is prevented due to the recrystallization of the metal as it begins to cool.
Cold Forging
- Cold Forging is generally performed with metal at room temperature below the recrystallization temperature. Also, Cold forging typically work hardens the metal.
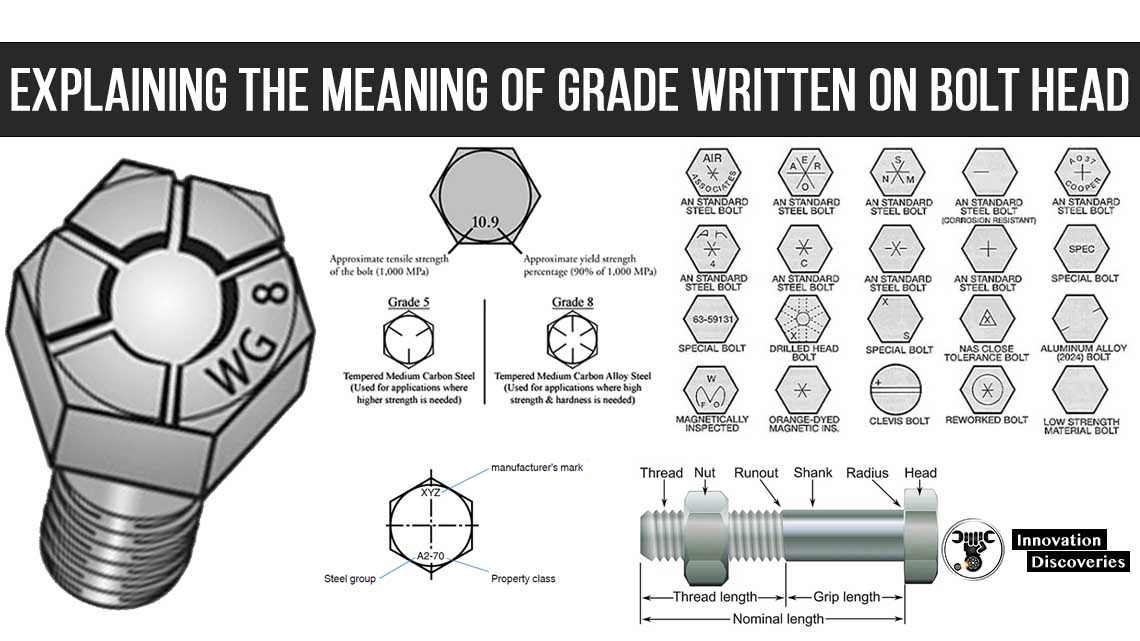
READ: EXPLAINING THE MEANING OF GRADE WRITTEN ON BOLT HEAD
The reason why manufacturers want you to know that a tool is drop forged is that this tells you something about the strength and durability of the tool.
The other two ways to make a tool would be casting it from molten metal or machining it (cutting material away) from a larger block of metal.
The advantage of forging is that it improves the strength of the metal by aligning and stretching the grain structure.
A forged part will normally be stronger than a casting or a machined piece.
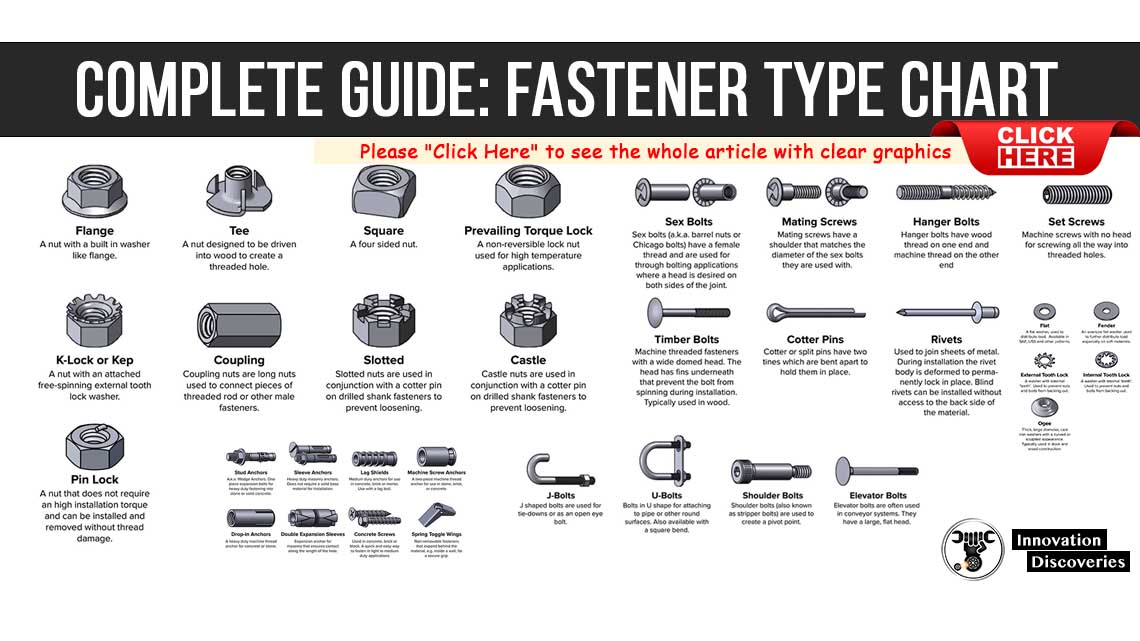
READ: Complete Guide: Fastener Type Chart
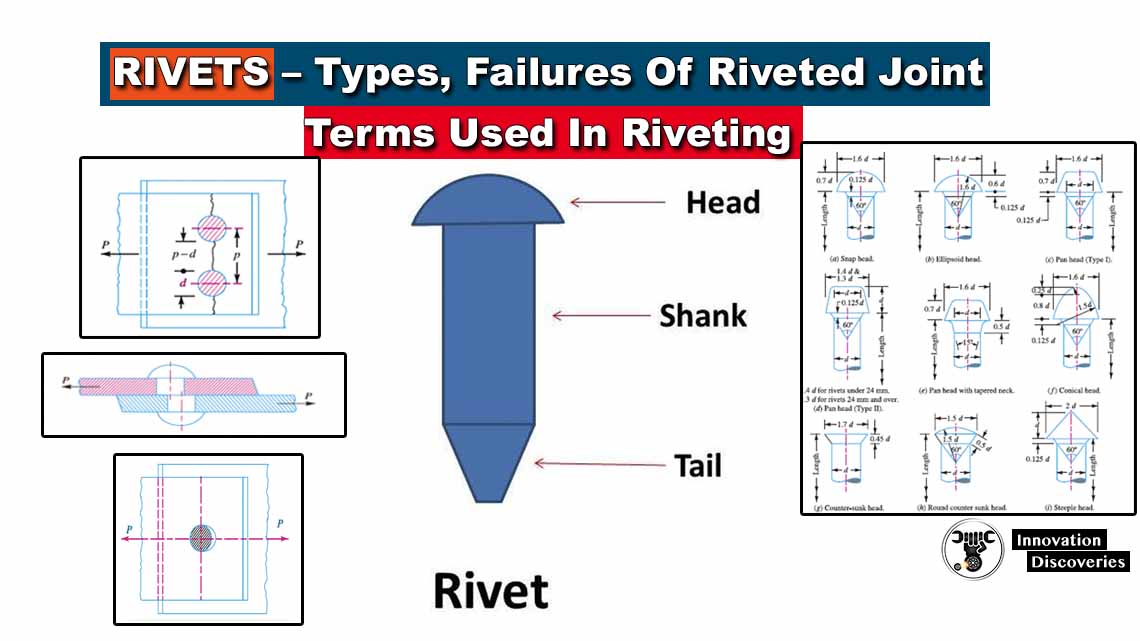
READ: Rivets – Types, Failures Of Riveted Joint, Terms Used In Riveting
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website




One Comment