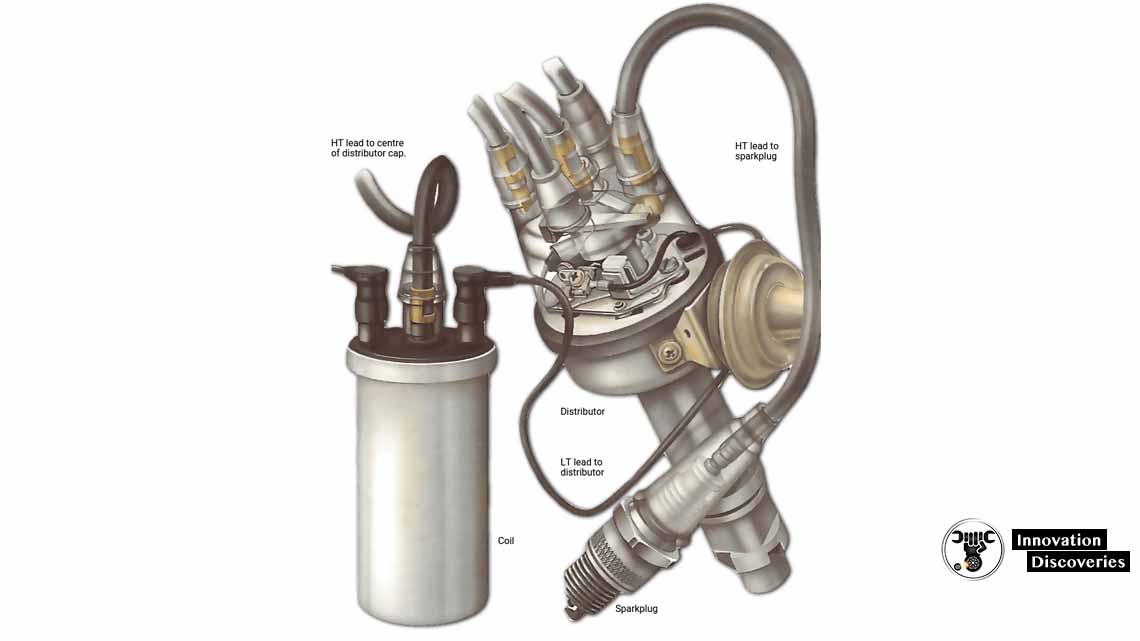
The high-tension (HT) or secondary circuit carries high-voltage electricity.
It runs from the secondary winding of the coil
Through the distributor to the plugs. Any of these can break down and cause ignition failure.
Do not touch any part of the HT circuit with,
Bare hands when the ignition is switched on. Work with pliers and screwdrivers that have thickly insulated plastic handles. Take care not to touch any metal parts of the tools.
Also, read – How the ignition system works
Since HT-circuit checks involve using the car’s own HT leads,
Begin by testing the leads to make sure that they are sound.
Testing the coil secondary winding
To check the secondary winding,
Take off the distributor cap and detach the central HT lead
Remove or push back the cap from the end of the
HT leads to expose the core connection.
Remove a lead from one of the sparkplugs, then switch on the ignition.
Grip the detached central HT lead with insulated pliers,
And hold its exposed end against the plug terminal. Flick open the contact-breaker points with a small insulated screwdriver.
A strong spark between the end of the HT lead and the plug terminal shows
That both the coil and condenser are in order.
An alternative test can be made by taking off all the plug leads to
Prevent the engine from starting (number the leads to avoid later confusion).
Remove one of the plugs and reconnect it to a lead.
Touch it against the engine and watch for a strong spark
When a helper turns the starter switch.
If either test produces only a weak spark, and the HT leads are sound,
Suspect a faulty condenser. Check by fitting another condenser that you know to be serviceable.
Check the condenser connections. If the spark is no better, or if the first test gave no spark, the coil is faulty. Replace it if necessary.
It is possible for the rotor arm to short circuit to the top of the contact-breaker cam. Detach the central HT lead from the distributor cap and hold it with insulated pliers. Switch on the ignition. Hold the exposed metal end of the lead about in. (3 mm) from the rotor-arm tip.
Flick the points open. There should be no spark or a feeble spark from static discharge. A strong spark means a short circuit.
Clean the cam and rotor arm of dirt and grease. If the trouble persists, examine the rotor
Arm for cracks and replace it if necessary.
SEE MORE:
- Magneto Ignition System – Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, and Disadvantages with Application
- The engine – how it drives its ancillary parts
Testing the high-tension leads
HT cable is made with a carbon core in two resistances,
So, that leads to different lengths can have equal resistance.
Resistance per foot or meter is usually marked on the lead.
Detach each lead in turn. Take off the plug cap if it is removable.
Measure the lead and work out its resistance,
Then measure actual resistance with an ohmmeter or multimeter.
If the reading is higher than the figure you worked out,
Or if it is more than 25,000 ohms, replace the whole set of leads.
Some leads have a copper core with small resistance.
Interference is suppressed by plug caps with 5,000 – 10,000 ohms resistance.
Check the caps with an ohmmeter.