Introduction:
The K-Jetronic fuel injection system, also known as Continuous Injection System (CIS), was developed by Bosch and introduced in the 1970s. It became widely used in a variety of vehicles during that time and remained in production until the late 1980s.
The K-Jetronic system is a mechanical fuel injection system that relies on air-flow measurement to regulate fuel supply and metering. It consists of several key components working together to ensure efficient and precise fuel delivery to the engine.
The 3 main functional areas of a K-Jetronic are:
1. Air-flow measurement:
The K-Jetronic system determines the amount of air entering the engine to calculate the appropriate fuel mixture. This is achieved through an air-flow sensor, which measures the volume of air passing through the intake system and sends signals to the fuel system accordingly.
2. Fuel supply:
The fuel supply system in K-Jetronic comprises several components that work together to provide a steady flow of fuel to the engine. These components include an electric fuel pump, a fuel accumulator, a fuel filter, a pressure regulator, and a fuel injection valve.
3. Fuel metering:
Once the air-flow measurement is determined, the K-Jetronic system regulates the amount of fuel delivered to the engine. Fuel metering is controlled by the fuel distributor, which distributes the fuel to individual injection valves based on signals from the air-flow sensor. This ensures the correct fuel-to-air ratio for optimal combustion.
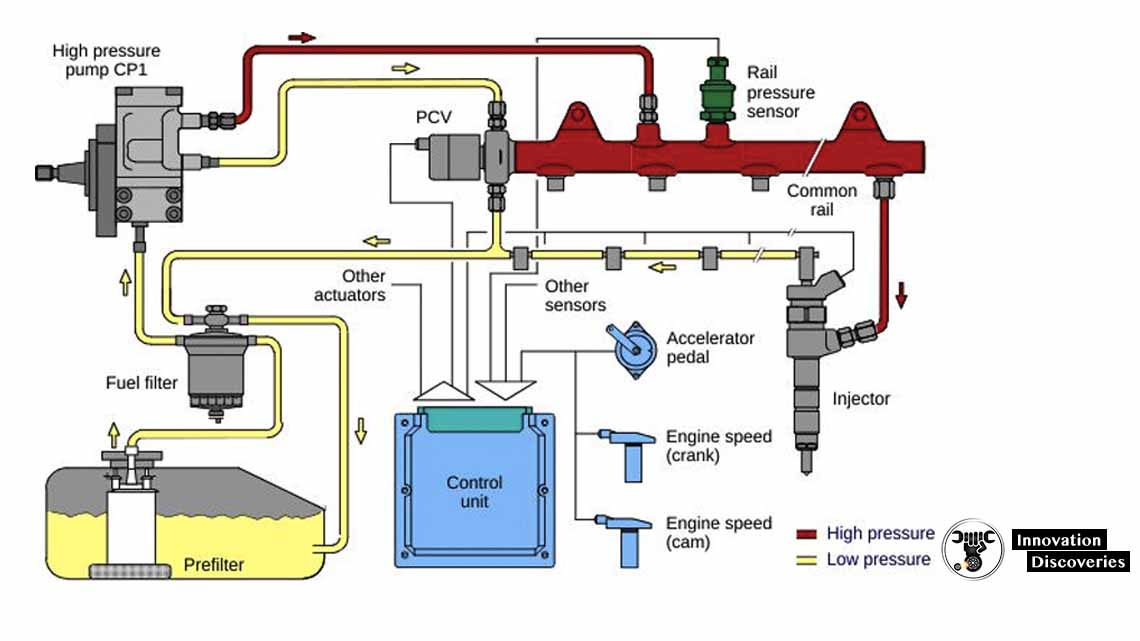
FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM:
The fuel supply system consists of the following parts:
- Electric fuel pump
- Fuel accumulator
- Fuel filter
- Pressure regulator
- Fuel distributor
- Injection Valves
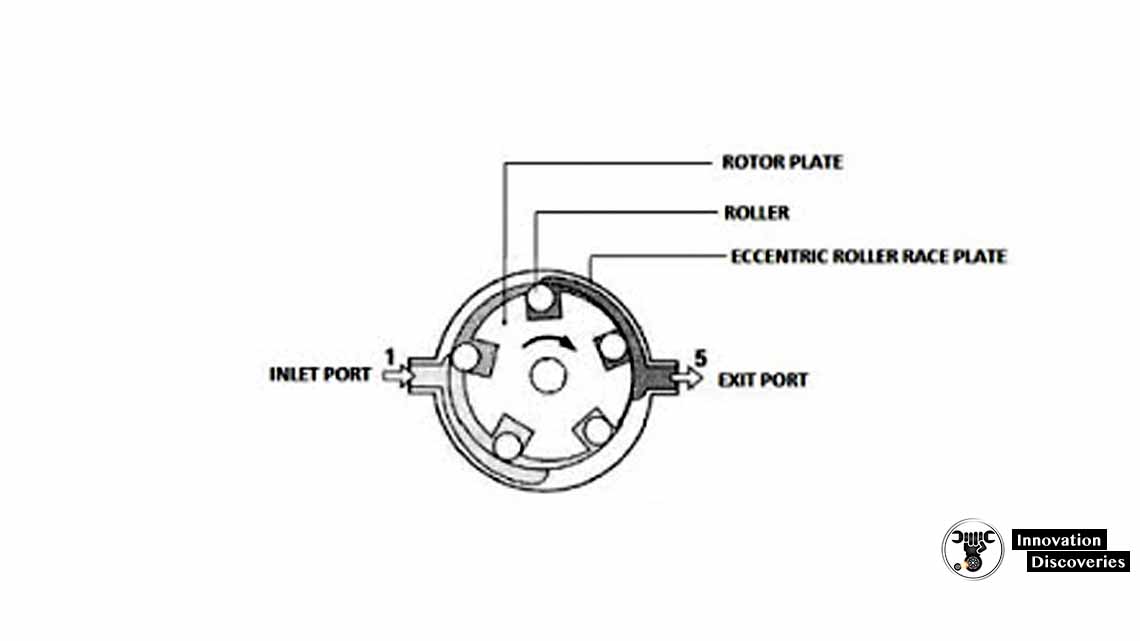
Electric Fuel Pump:
The electric fuel pump in the K-Jetronic system is responsible for drawing fuel from the tank and delivering it to the fuel injection system. It is typically located near the fuel tank and is driven by an electric motor. The pump maintains a constant fuel pressure within the system.
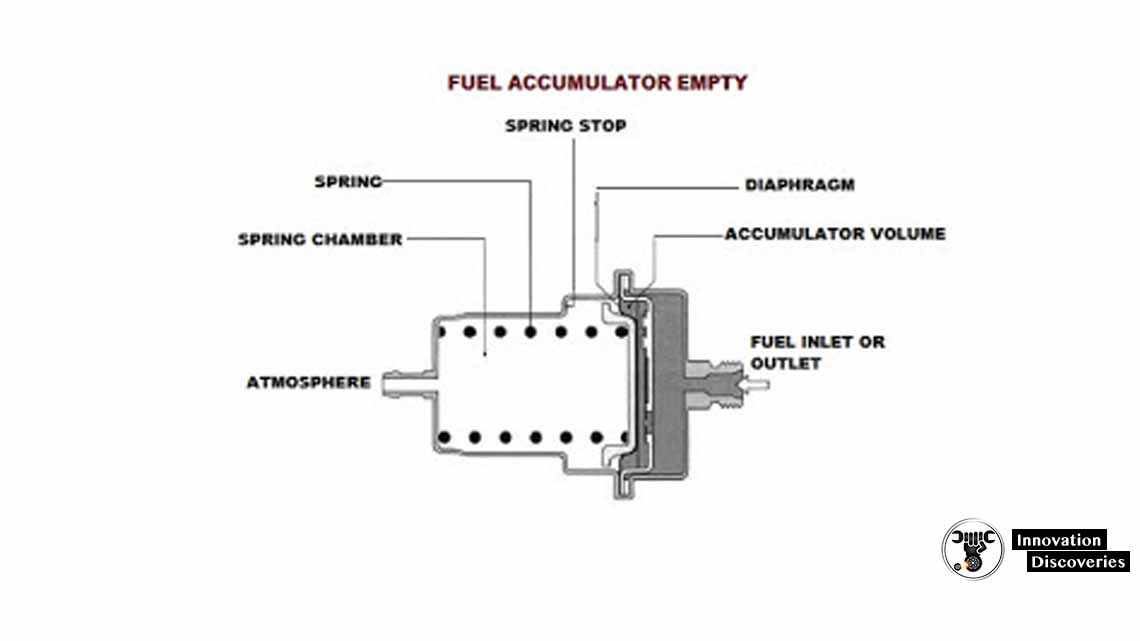
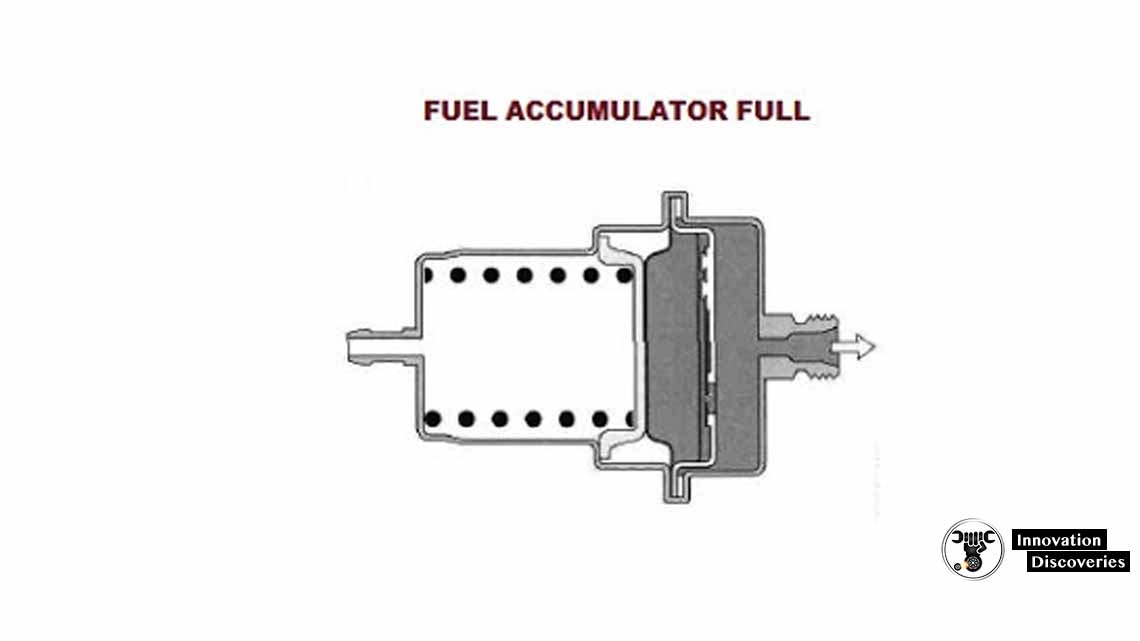
Fuel Accumulator:
The fuel accumulator is a component that stores a certain amount of fuel under pressure. It helps maintain a constant and consistent fuel pressure in the system, even when the engine is not running. The accumulator ensures immediate fuel availability upon engine start-up and prevents pressure fluctuations during operation.
Fuel Filter:
The fuel filter is an essential component that removes impurities and contaminants from the fuel before it reaches the fuel injection system. It prevents these particles from entering the delicate components of the system, such as the fuel injectors and fuel distributor, ensuring their proper functioning and longevity.
Pressure Regulator:
The pressure regulator is responsible for maintaining a constant fuel pressure within the K-Jetronic system. It controls the amount of fuel returning to the fuel tank, adjusting the pressure as necessary to ensure consistent fuel delivery. The pressure regulator helps maintain the desired fuel-to-air ratio and prevents excessive pressure buildup.
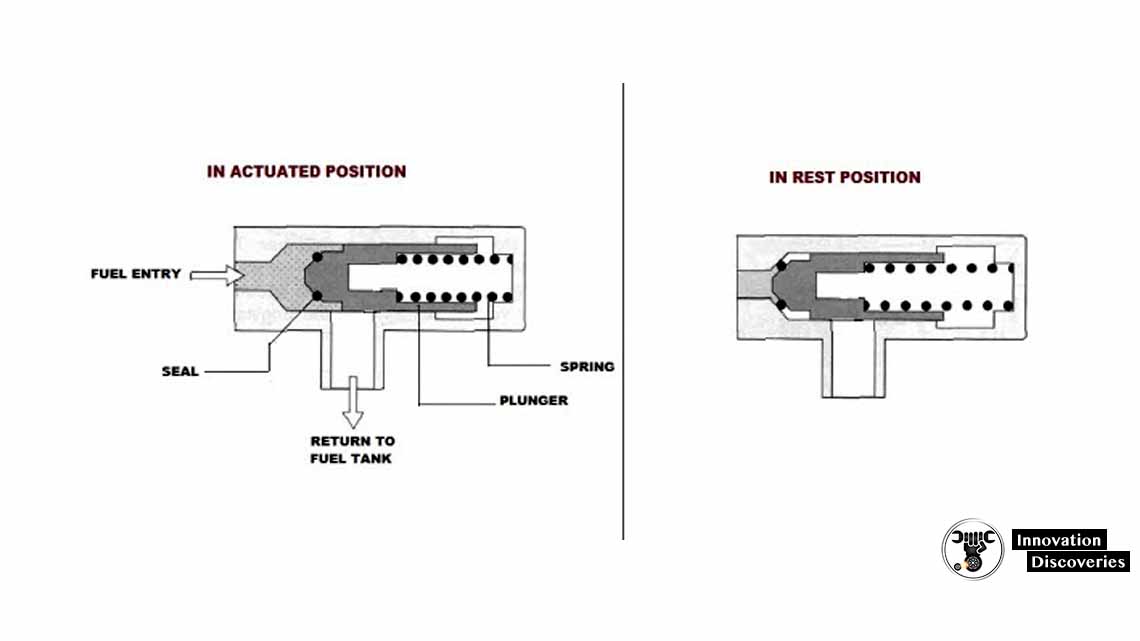
Fuel Injection Valve:
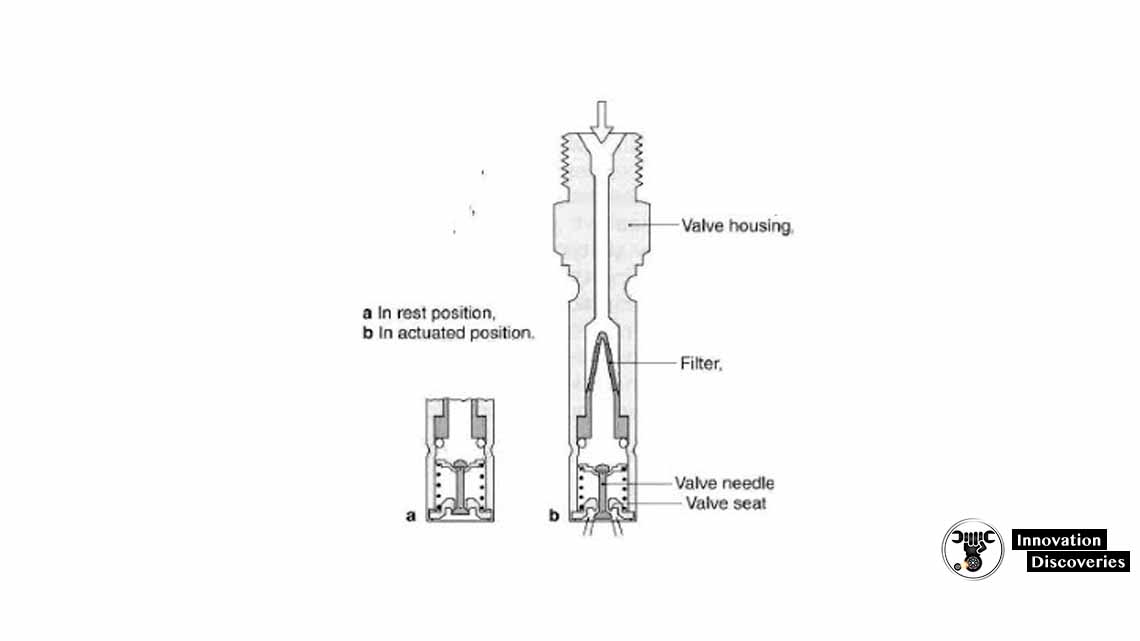
The fuel injection valve, also known as the fuel injector, delivers pressurized fuel into the intake manifold or directly into the combustion chamber.
The number of injectors corresponds to the number of cylinders in the engine. The injection valve opens and closes to precisely control the amount of fuel injected into the engine, based on signals received from the fuel distributor.
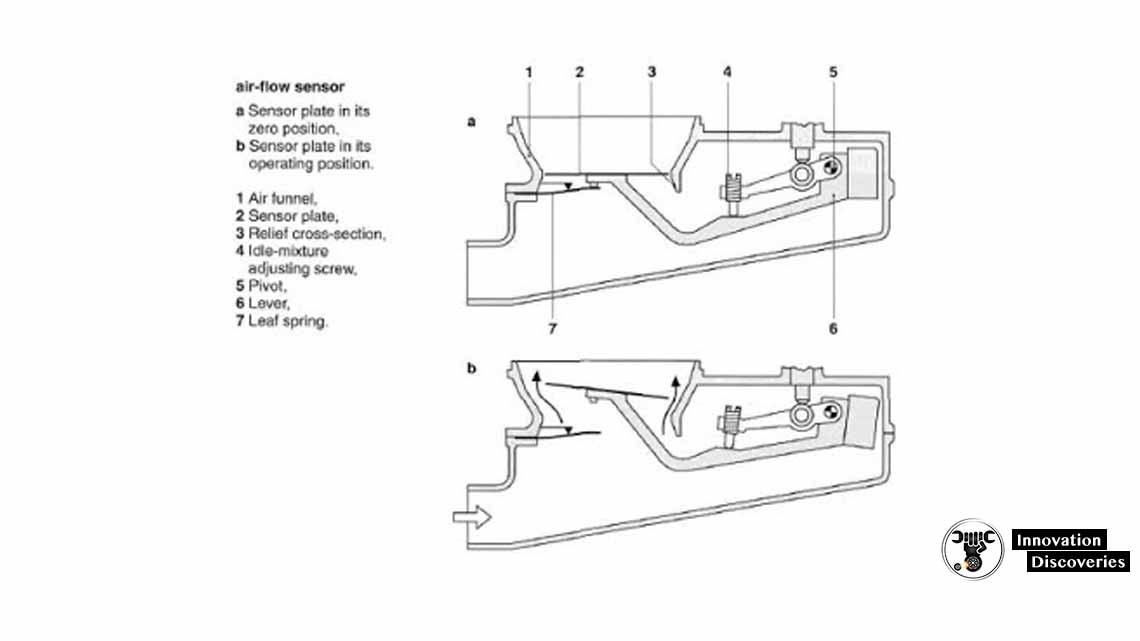
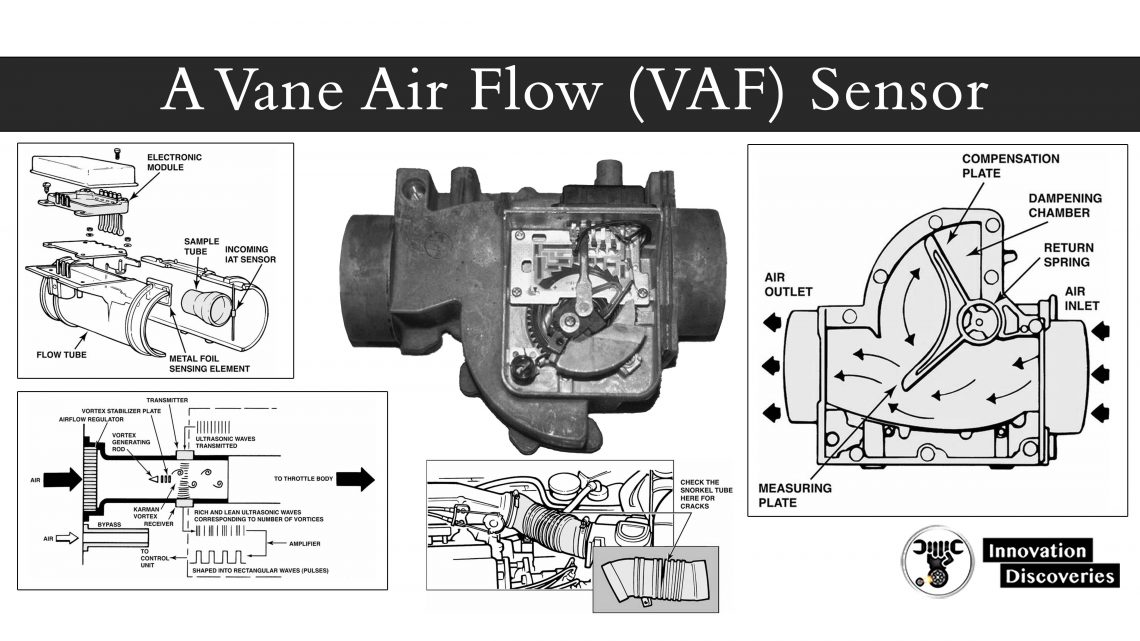
AIR-FLOW SENSOR:
The air-flow sensor in the K-Jetronic system measures the volume of air entering the engine. It typically consists of a vane or flap that moves in response to the air flow, generating signals that are used to regulate the fuel supply.
The position of the vane determines the fuel mixture, as more air requires more fuel for an optimal ratio.
FUEL DISTRIBUTOR:
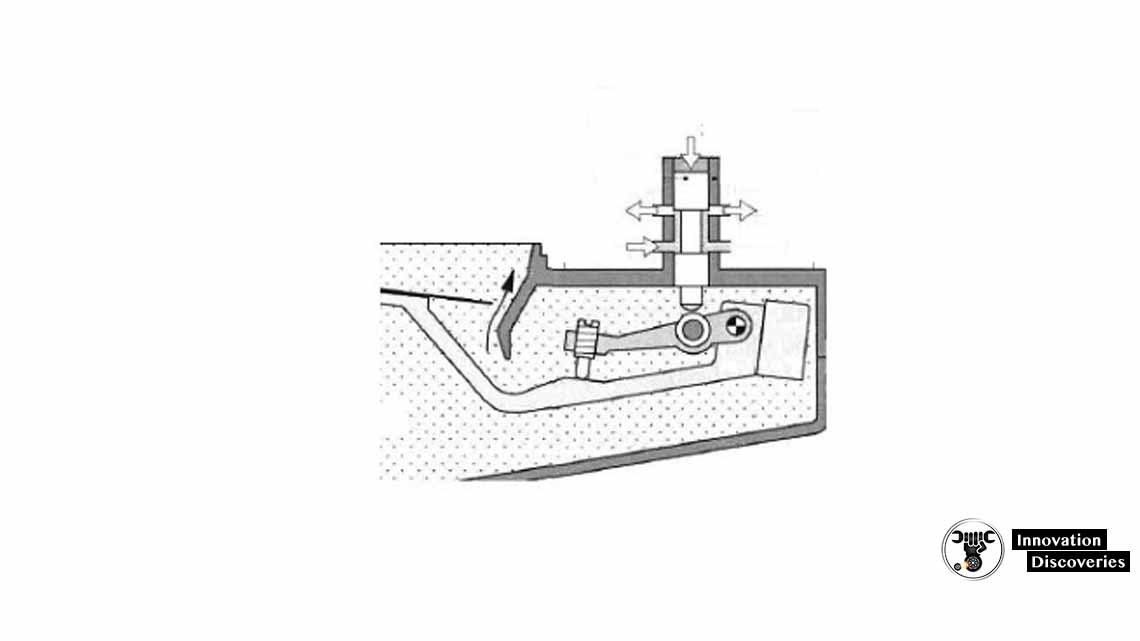
The fuel distributor is a crucial component in the K-Jetronic system responsible for distributing the pressurized fuel to individual injectors. It ensures that each cylinder receives the correct amount of fuel based on signals received from the air-flow sensor.
The fuel distributor regulates fuel flow by using a rotary valve or other mechanisms, ensuring precise fuel metering for each cylinder.
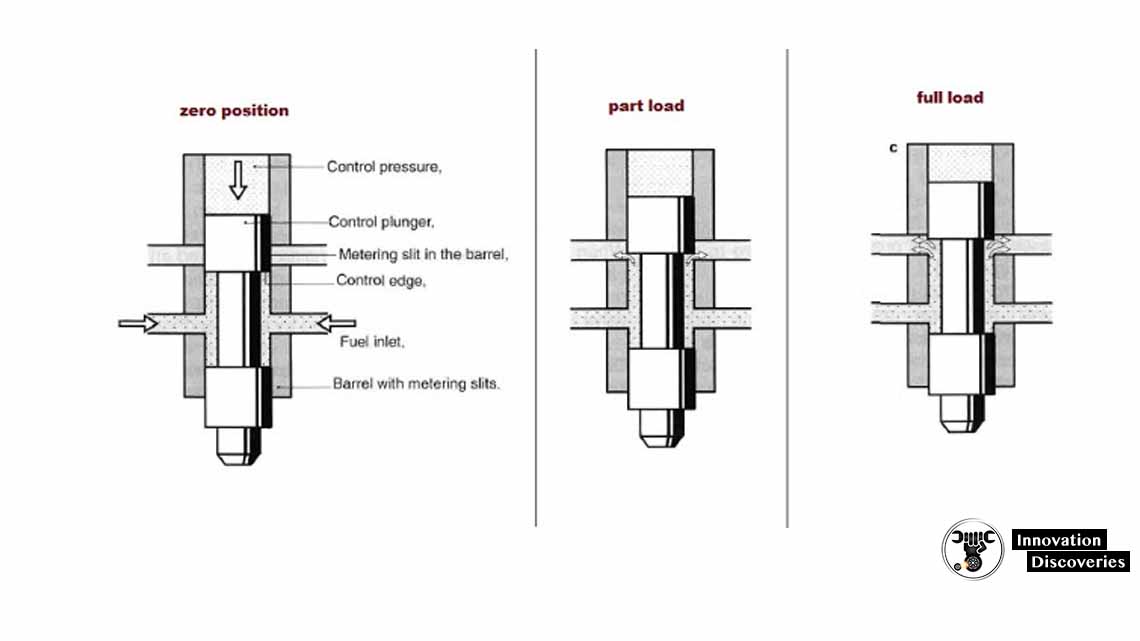
Conclusion:
The K-Jetronic fuel injection system revolutionized fuel delivery in vehicles during its time. With its mechanical design and reliance on air-flow measurement, it provided reliable and efficient fuel supply to engines.
The system’s three main functional areas, air-flow measurement, fuel supply, and fuel metering, worked together to ensure optimal combustion and engine performance. The components within the fuel supply system, such as the electric fuel pump, fuel accumulator, fuel filter, pressure regulator, and fuel injection valve, played crucial roles in maintaining steady fuel flow and pressure.
The air-flow sensor accurately measured the volume of air entering the engine, while the fuel distributor ensured precise fuel distribution to individual injectors.
Although the K-Jetronic system has been replaced by more advanced electronic fuel injection systems, its design and principles laid the foundation for future developments in fuel injection technology.
Read More:
- Carburetor Vs Fuel Injection: Which One Is The Better Option?
- FUEL SYSTEM: COMPONENTS, WORKING PRINCIPLES, SYMPTOMS AND EMISSION CONTROLS
- INJECTION SYSTEM: COMPONENTS, TYPES AND WORKING PRINCIPLES
- How Do Hydrogen Engines Function?
- FIRING ORDER: ITS PURPOSE AND ORDER IN DIFFERENT NUMBERS OF CYLINDERS
DISCOVER MORE

ECU CHIP TUNE | IGNITION TIMING | INCREASE HORSEPOWER
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website



3 Comments