Introduction:
Submarines have long fascinated us with their ability to navigate beneath the ocean’s surface, exploring the depths and performing vital missions. But have you ever wondered how these remarkable machines work?
In this article, we will delve into the principles and design of submarines, unraveling the secrets behind their operations and exploring the engineering marvels that enable them to dive and resurface.
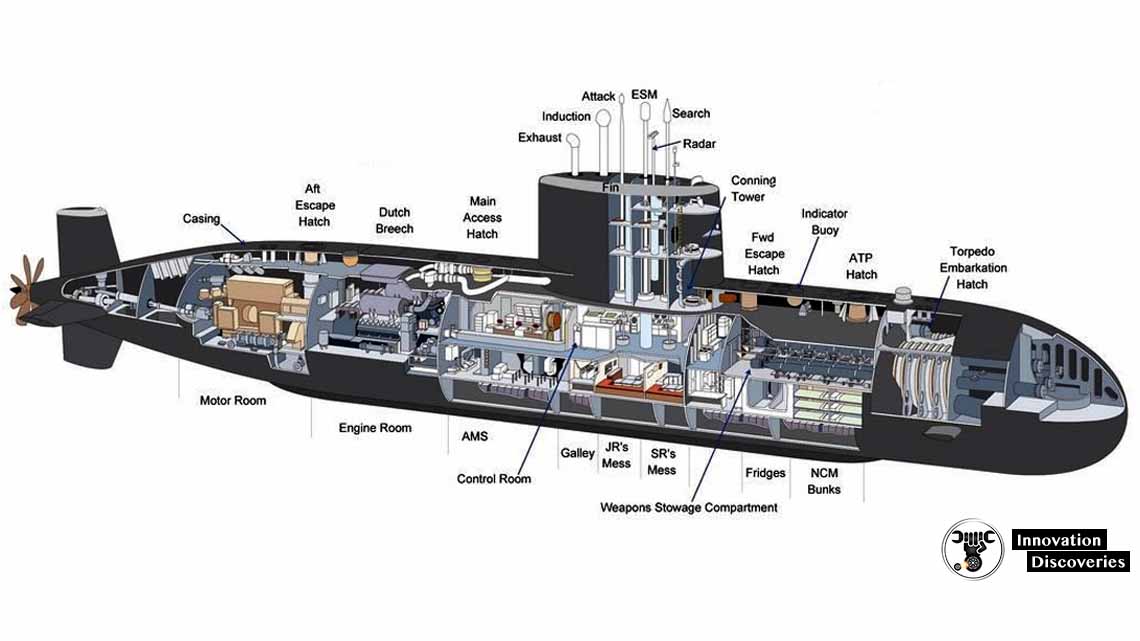
Working & Design Principles of submarines
1. Buoyancy and Ballast Systems:
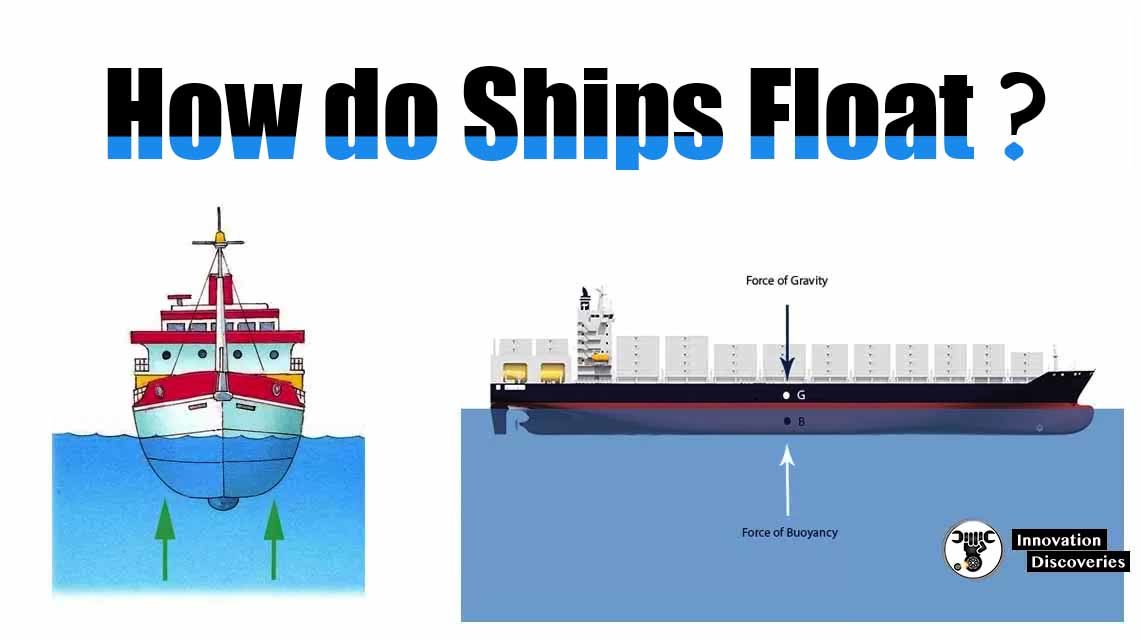
At the heart of a submarine’s ability to submerge and resurface lies the principle of buoyancy. By adjusting its overall density, a submarine can control its position in the water. The ballast tanks, located strategically throughout the vessel, are used to control buoyancy.
When the tanks are flooded with water, the submarine’s density increases, causing it to sink. Conversely, when the tanks are emptied of water and filled with air, the submarine becomes less dense, allowing it to rise to the surface.
Also, read: What Is Sonar? How Does It Work?
2. Propulsion Systems:
Submarines employ various propulsion systems to navigate underwater. The most common propulsion method is through the use of electric motors powered by large battery banks. These motors drive the submarine’s propellers, enabling it to move silently and efficiently underwater. For longer dives and higher speeds, submarines often switch to diesel engines or nuclear reactors, which generate electricity to power the motors and recharge the batteries.
3. Pressure Hull and Ballistic Tanks:
A submarine’s pressure hull is a critical component that protects the crew and equipment from the immense pressure of the deep sea. Typically made of strong steel or titanium alloys, the pressure hull withstands the external water pressure and provides a habitable environment inside.
Additionally, ballistic tanks, located within the hull, allow the crew to adjust the submarine’s depth. By flooding or venting these tanks, the submarine can achieve neutral buoyancy or control its ascent or descent.
4. Navigation and Sonar Systems:
Submarines rely on advanced navigation and sonar systems to maneuver safely underwater and detect potential obstacles, as well as other vessels or threats. Sonar, which stands for Sound Navigation and Ranging, uses sound waves to navigate and locate targets. Submarines emit sound pulses and analyze the reflected signals to determine distances and directions. Additionally, navigation systems utilize GPS and inertial navigation technology to ensure accurate positioning and course corrections.
5. Life Support and Crew Accommodations:
Sustaining life within a submarine requires careful design and engineering. Submarines are equipped with systems to generate breathable air, remove carbon dioxide, and recycle water for drinking and other necessities. Crew accommodations include sleeping quarters, mess areas, and facilities for personal hygiene. Submarines are designed to provide a safe and comfortable environment for the crew during long deployments beneath the surface.
The Engine’s Role in Submarine Propulsion
Engine:
One of the key components of a submarine is the engine, which provides the necessary power for propulsion and various onboard systems. Submarine engines can vary depending on the type of submarine and its intended use. Here are two common types of engines found in submarines:
– Diesel Engines:
Diesel engines are commonly used in non-nuclear submarines. These engines burn diesel fuel to generate mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy using generators. The electrical power is used to operate electric motors that drive the submarine’s propellers. Diesel engines are efficient and reliable, making them suitable for shorter underwater missions.
– Nuclear Reactors:
Nuclear-powered submarines, also known as nuclear submarines, utilize nuclear reactors as their power source. These reactors generate heat through controlled nuclear fission reactions, producing high-pressure steam. The steam is then used to drive turbines connected to electric generators, which provide electrical power for propulsion and other systems. Nuclear reactors offer significant advantages in terms of endurance and underwater performance, allowing submarines to stay submerged for extended periods without the need for frequent resurfacing.
Both diesel engines and nuclear reactors have their distinct advantages and considerations. Diesel engines are quieter and more suitable for covert operations, while nuclear reactors offer greater endurance and power for long-range missions. The choice of engine depends on factors such as the submarine’s mission requirements, operational range, and desired performance characteristics.
Engine maintenance and operation are critical in submarines, as they operate in a challenging and often hostile environment. The crew works diligently to ensure proper maintenance, monitoring fuel levels, cooling systems, and other parameters to optimize engine performance and ensure the safety and effectiveness of the submarine.
In conclusion, the engine is a vital component of a submarine, providing the power needed for propulsion and the operation of various systems. Whether it’s a diesel engine or a nuclear reactor, the engine plays a crucial role in the submarine’s capabilities, endurance, and overall mission success.
Also, read: What Is Sonar? How Does It Work?
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website





One Comment