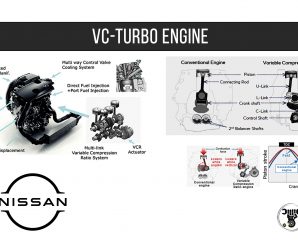
Advertisement The VC-Turbo engine utilizes a multi-link system that continuously varies piston top dead center (TDC)? bottom dead center (BDC) positions, allowing free control of the compression ratio critical factor of power and efficiency, on-demand. This makes it the world’s …
Tag: Otto cycle
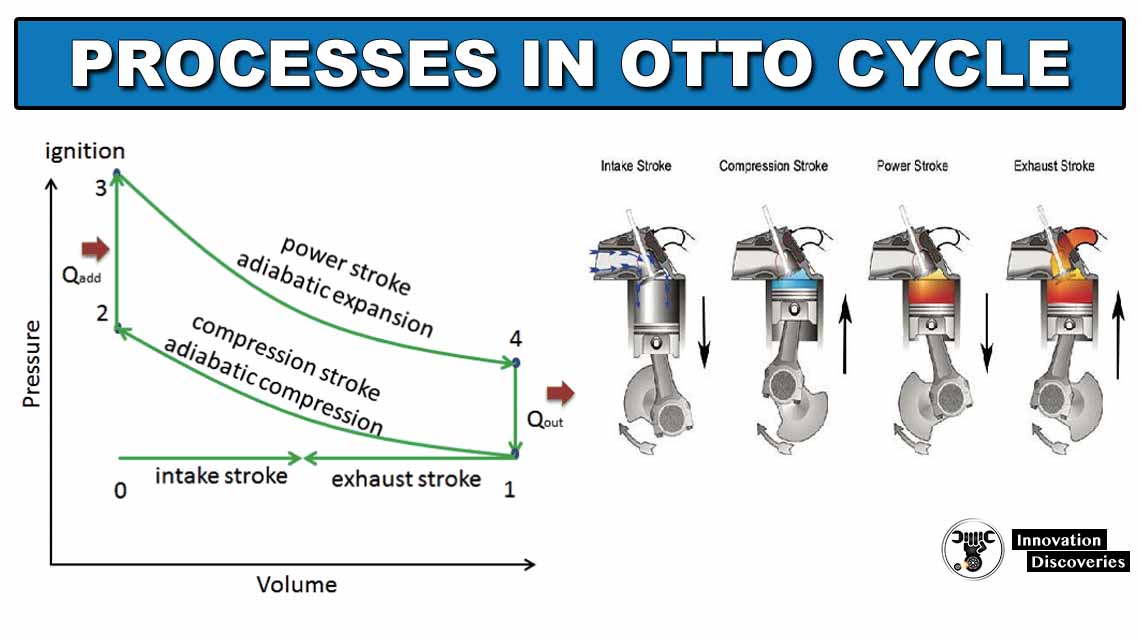
Advertisement How Otto cycle works? Otto Cycle is the hypothetical thermodynamic cycle Which depicts the working of a starter motor. This kind of start motors is the most well-known Sort of motors utilized in vehicles. Today we will endeavour to …