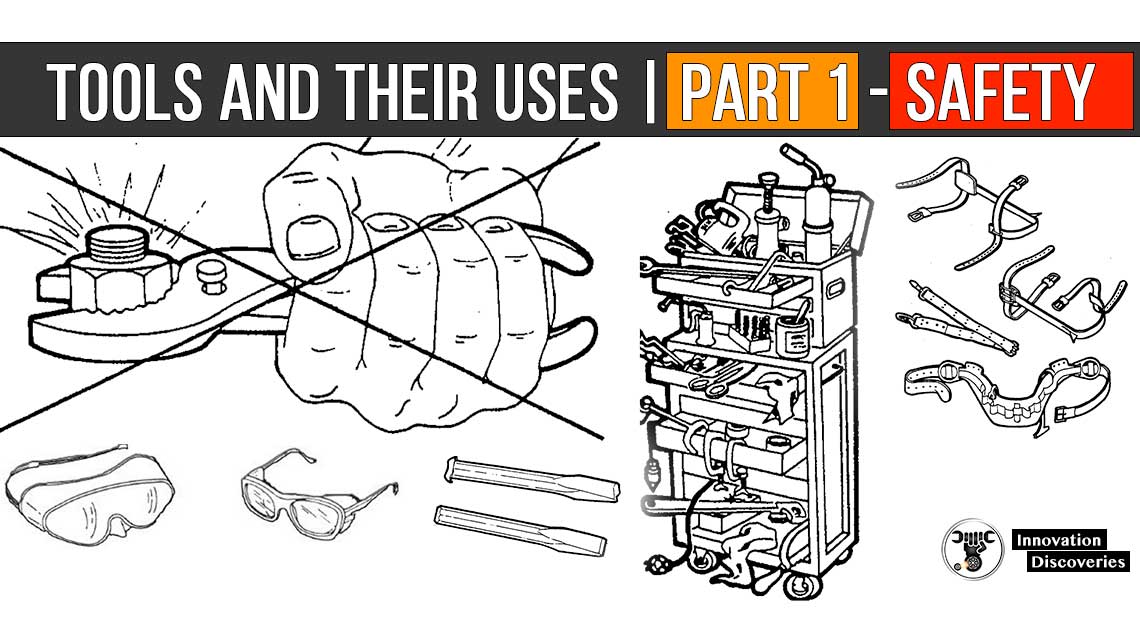
No matter how small the job, safety must be practiced at INDEX at all times.
A tool may be efficient, essential, time-saving, or even convenient; but it is also dangerous.
When Item Page using any hand tool you must use it correctly, following the methods prescribed in this manual.
You must also be alert for any conditions that might endanger yourself or fellow workers. Take the time necessary to acquaint yourself with the safety guidelines in this article(chapter).
Remember, you are the most important part of safety procedures.
SAFETY RULES (GENERAL)
There will undoubtedly be a safety program to follow for the shop or area in which you will be working.
The following general safety rules are furnished as a guide.
- SUPPORT your local safety program and take an active part in safety meetings.
- INSPECT tools and equipment for safe conditions before starting work.
- ADVISE your supervisor promptly of any unsafe conditions or practices.
- LEARN the safe way to do your job before you start.
- THINK safety, and ACT safety at all times.
- OBEY safety rules and regulations-they are for your protection.
- WEAR proper clothing and protective equipment.
- CONDUCT yourself properly at all times-horseplay is prohibited.
- OPERATE only the equipment you are authorized to use.
- REPORT any injury immediately to your supervisor.
In addition to the above, other good tool habits will help you perform your work more efficiently as well as safely.
TOOL HABITS
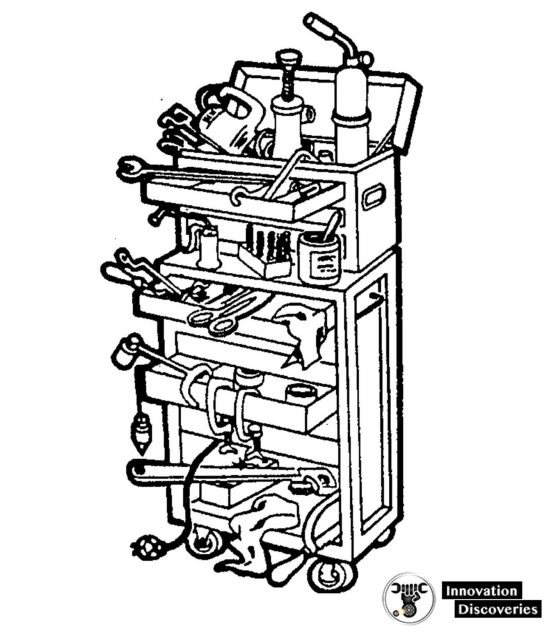
“A place for everything and everything in its place” is just common sense.
You cannot do an efficient, fast repair job if you have to stop and look around for each tool that you need.
The following rules, if applied, will make your job easier.
KEEP EACH TOOL IN ITS PROPER STORAGE PLACE.
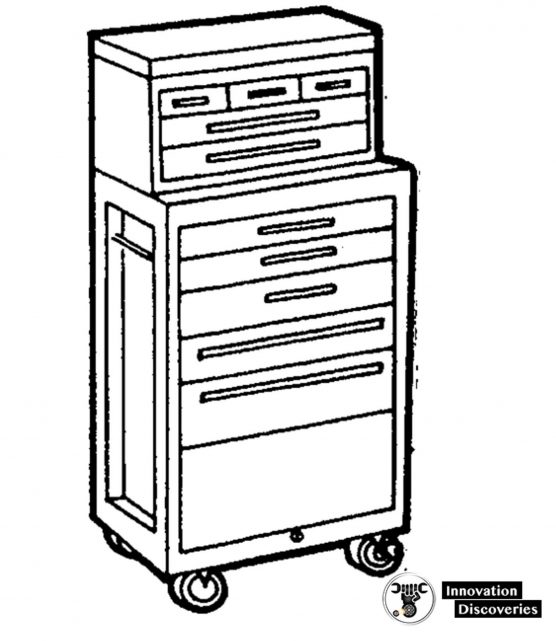
A tool is useless if you cannot find it. If you return each tool to its proper place, you will know where it is when you need it.
KEEP YOUR TOOLS WITHIN EASY REACH AND WHERE THEY CANNOT FALL ON THE FLOOR OR MACHINERY.

Avoid placing tools anywhere above machinery or electrical apparatus. Serious damage will result if the tool falls into the machinery after the equipment is turned on or running.
KEEP YOUR TOOLS IN GOOD CONDITION
Also, keep them free of rust, nicks, burrs, and breaks.
KEEP YOUR TOOLSET COMPLETE
If you are issued a toolbox, each tool should be placed in it when not in use.
If possible, the box should be locked and stored in a designated area. Keep an inventory list in the box and check it after each job.
This will help you to keep track of your tools.
USE EACH TOOL ONLY ON THE JOB FOR WHICH IT WAS DESIGNED.
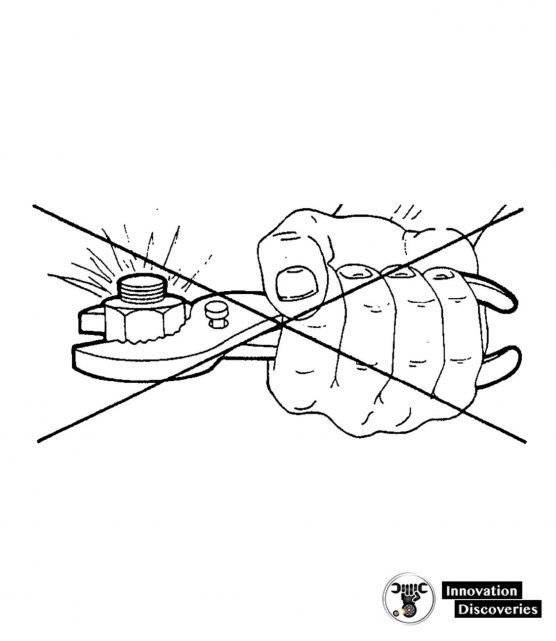
If you use the wrong tool to adjust, the result will probably be unsatisfactory.
For example, if you use a socket wrench that is too big, you will round off the corners of the wrench or nut.
If this rounded wrench or nut is not replaced immediately, the safety of your equipment may be endangered in an emergency.
NOTE – Return broken tools to section chief.
NEVER USE DAMAGED TOOLS
Notify your supervisor of broken or damaged tools.
A battered screwdriver may slip and spoil the screw slot or cause painful injury to the user.
A gage strained out of shape will result in inaccurate measurements.
Remember, a worker’s efficiency is often a direct result of the condition of the tools being used.
Workers are often judged by the manner in which they handle and care for their tools.
You should care for hand tools the same way you care for personal property. Always keep hand tools clean and free from dirt, grease, and foreign matter.
After use, return tools promptly to their proper places in the toolbox.
Improve your own efficiency by organizing your tools so that those used most frequently can be reached easily without sorting through the entire contents of the box.
Avoid accumulating unnecessary items.
SAFETY RULES (POWER TOOLS)
Safety is a very important factor in the use of power tools and cannot be overemphasized.
By observing the following safety guidelines, you can ensure maximum benefits from the tools you use and reduce to a minimum the chances of serious injury.
- Never operate any power equipment unless you are completely familiar with its controls and features.
- Inspect all portable power tools before using them. See that they are clean and in good condition.
- Make sure there is plenty of light in the work area.
- Never work with power tools in dark areas where you cannot see clearly.
- Before connecting a power tool to a power source, be sure the tool switch is in the “OFF” position.
- When operating a power tool, give it your FULL and UNDIVIDED ATTENTION.
- DO NOT DISTRACT OR IN ANY WAY DISTURB another person while they are operating a power tool.
- Never try to clear a jammed power tool until it is disconnected from the power source.
- After using a power tool, turn off the power, disconnect the power source, wait for all movement of the tool to stop, and then remove all waste and scraps from the work area.
- Store the tool in its proper place.
- Never plug the power cord of a portable electric tool into a power source before making sure that the source has the correct voltage and type of current called for on the nameplate of the tool.
- Do not allow power cords to come in contact with sharp objects, nor should they kink or come in contact with oil, grease, hot surfaces, or chemicals.
- Never use a damaged cord. Replace it immediately.
- Check electrical cables and cords frequently for overheating. Use only approved extension cords, if needed.
- See that all cables and cords are positioned carefully so they do not become tripping hazards.
- Treat electricity with respect. If water is present in the area of electrical tool operation, be extremely cautious and if necessary, disconnect the power tool.
SAFETY EQUIPMENT
Safety equipment is for you. It will protect you from injury and may possibly save your life.
Some of the more common types of safety equipment for your personal protection follow.
SAFETY SHOES

Safety shoes protect and prevent injury or loss of toes. Some safety shoes are designed to limit damage to your toes from falling objects.
A steel plate is placed in the toe area of such shoes so that your toes are not crushed if an object falls on them.
Other safety shoes are designed SAFETY SHOES for use where danger from sparking could cause an explosion.
Such danger is minimized by the elimination of all metallic nails and eyelets and the use of soles that do not cause static electricity.
EYE PROTECTION
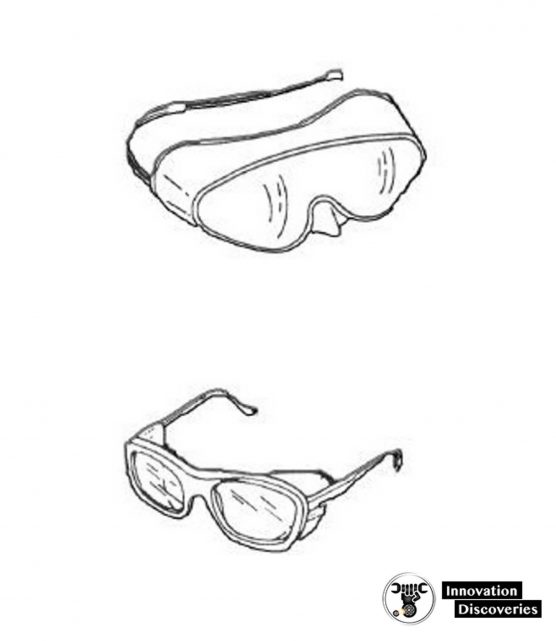
Proper eye protection is of the highest importance for all personnel.
Eye protection is necessary because of hazards caused by infrared and ultraviolet radiation, or by flying objects such as sparks, globules of molten metal, or chipped concrete and wood, etc.
These hazards are always present during welding, cutting, soldering, chipping, grinding, and a variety of other operations.
You must use eye protection devices such as helmets, hand shields, and goggles during eye-hazard operations.
Appropriate use of goggles will limit eye hazards. Some goggles have plastic windows which resist shattering upon impact.
Others are designed to limit harmful infrared and ultraviolet radiation from arcs or flames by the use of appropriate filter lenses.
Remember, eye damage can be extremely painful. Protect your eyes.
GLOVES
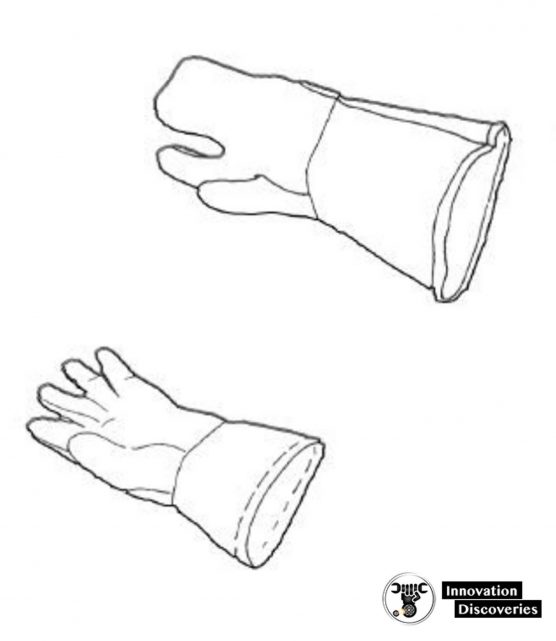
Use gloves whenever you are required to handle rough, scaly, or splintery objects.
Two types are shown above.
Special flameproof gloves are designed for gas and electric welding to limit danger and damage from sparks and other hot, flying objects.
Personnel working with electricity are usually required to wear insulating rubber gloves.
Be sure to follow all regulations prescribed for the use of gloves.
Gloves must not be worn around rotating machinery unless sharp or rough material is being handled.
If such is the case, extreme care should be used to prevent the gloves from being caught in the machinery.
HELMETS

Protective helmets (hard hats) come in a variety of shapes.
They may be made of tough polyethylene or polycarbonate, one of the toughest hat materials yet developed.
When falling objects strike the hats, the shock-absorbing suspension capabilities minimize injuries.
Regular hard hats must be insulated so that personnel may be protected from accidental head contacts with electrical circuits and equipment at comparatively low voltages (less than 2200 volts).
Electrical workers requiring head protection necessary to their duties or the working environment must wear insulating safety helmets or all-purpose protective helmets which must be capable of withstanding 20,000-volt minimum proof-tests
SAFETY BELTS AND SAFETY STRAPS
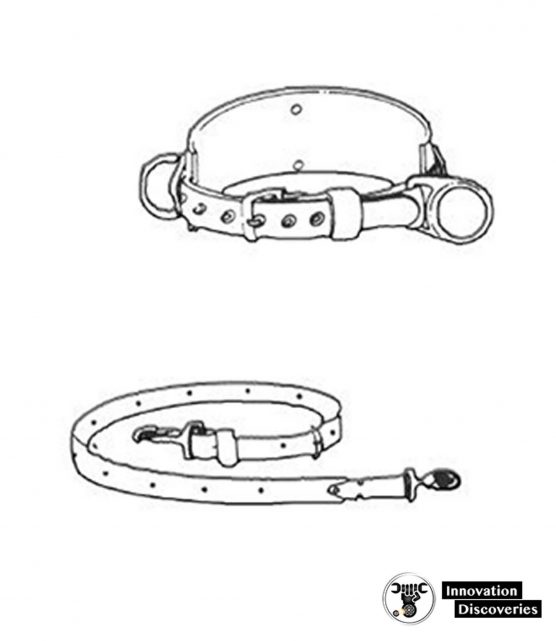
The safety belt and safety strap are a must when working in high places.
The safety belt, strapped around the waist, contains pockets for small tools. It also has two D-rings used to attach the safety strap.
The safety strap is a nylon-reinforced leather belt that is placed around the item to be climbed.
It is then attached to the two D-rings on the safety belt.
EAR PROTECTION
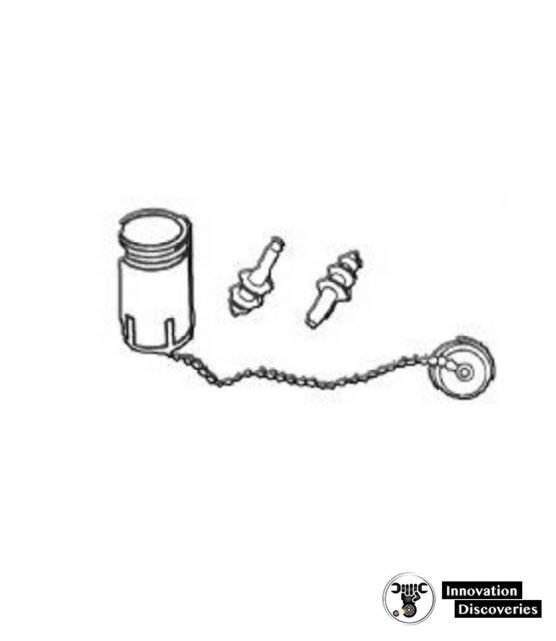
Proper hearing protection is a must when working with or around certain types of power tools.
Some tools are capable of producing dangerously high noise levels which, if ignored, can result in serious hearing loss or injury. Use the hearing protection regularly.
Stay tuned for the rest of this tutorial tomorrow…
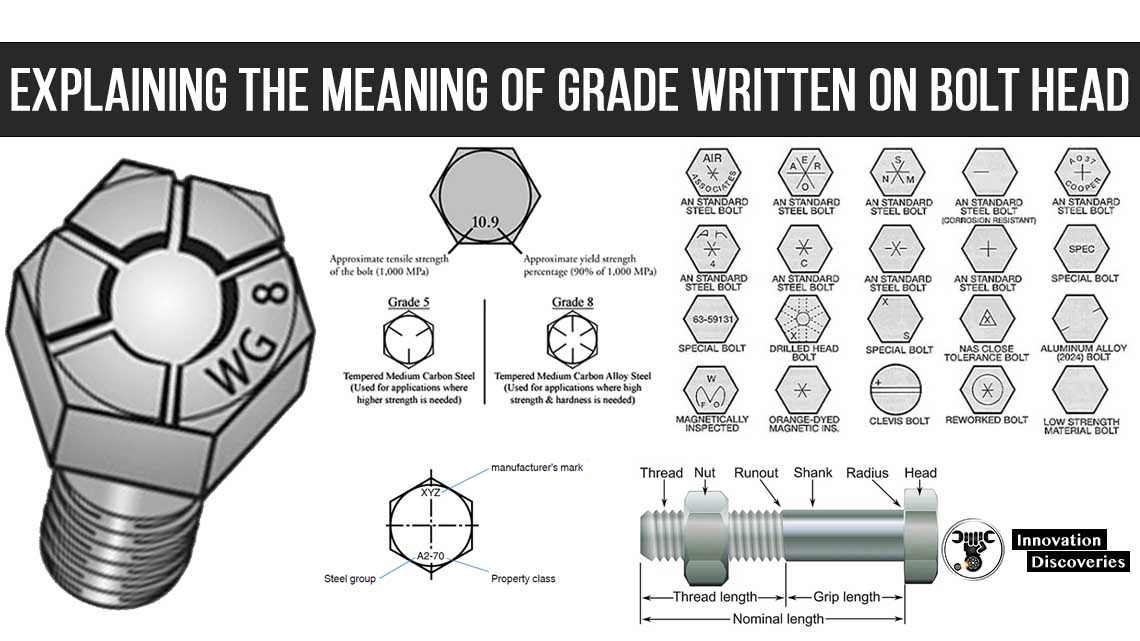
READ: EXPLAINING THE MEANING OF GRADE WRITTEN ON BOLT HEAD





One Comment