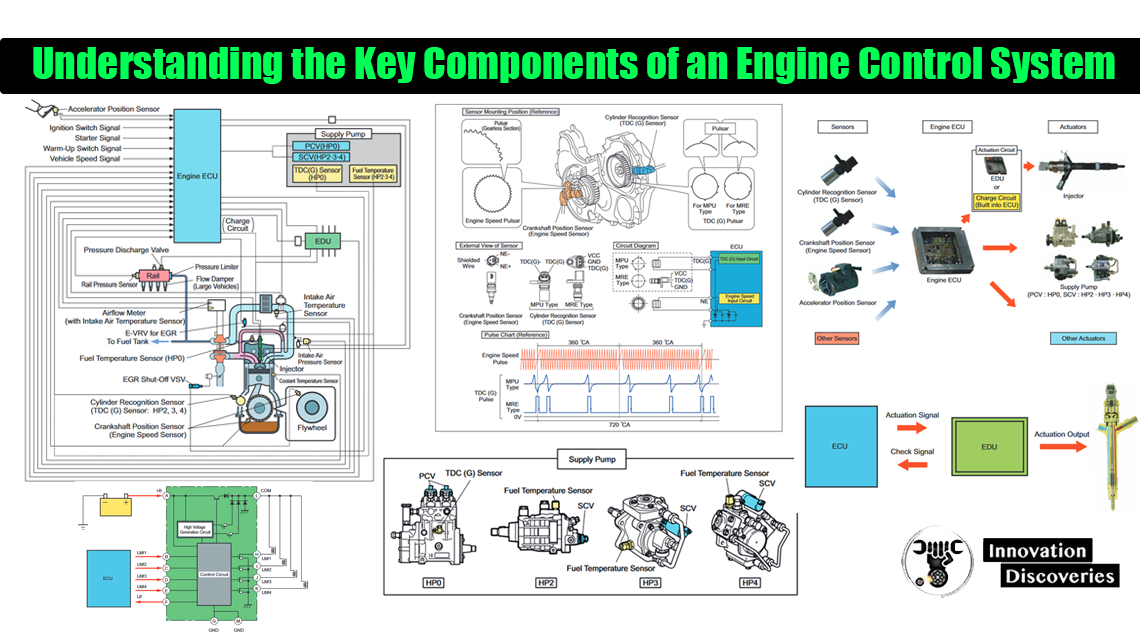
In the world of modern vehicles, the engine control system is a complex network that ensures your car runs smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal emissions. But what exactly makes up this system, and how do its components work together?
In this article, we’ll break down the essential parts of an engine control system and explore their roles in keeping your car running at its best.
The Brain of the System: Engine ECU (Electronic Control Unit)
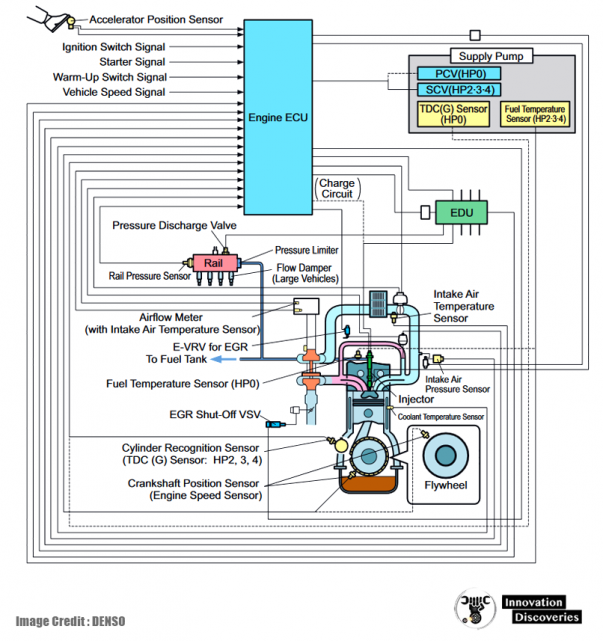
At the heart of every engine control system is the Engine ECU, also known as the Engine Control Module (ECM). This critical component is the brain that orchestrates all engine functions, from fuel injection to ignition timing.
The ECU receives data from various sensors around the engine, processes this information, and then sends commands to different parts of the engine to optimize its performance.
What Does the ECU Do?
The ECU is responsible for a wide range of tasks, including:
- Managing fuel injection and ignition timing.
- Regulating idle speed.
- Controlling emissions to meet environmental standards.
- Diagnosing engine faults and triggering warning lights on the dashboard.
Essentially, the ECU’s job is to ensure that the engine operates efficiently and reliably, no matter the driving conditions.
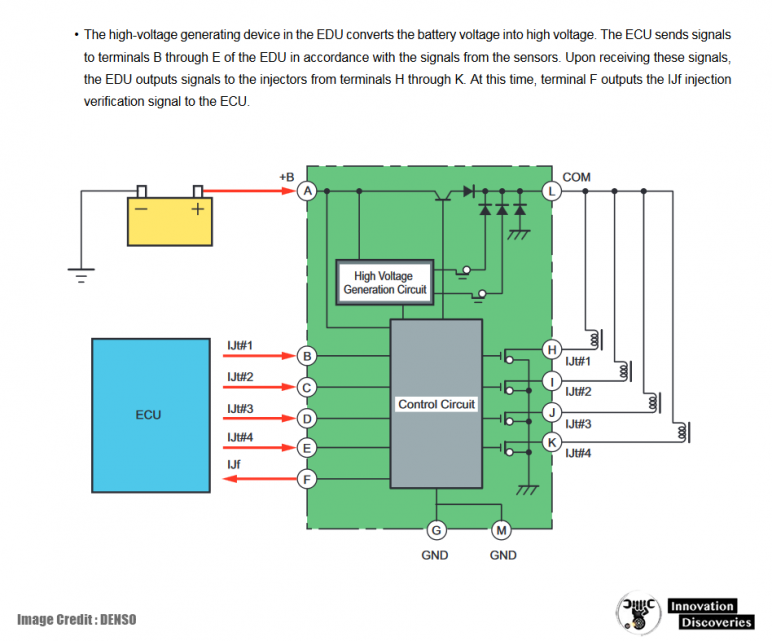
Fuel Injection Control: The Role of the EDU (Electronic Driving Unit)
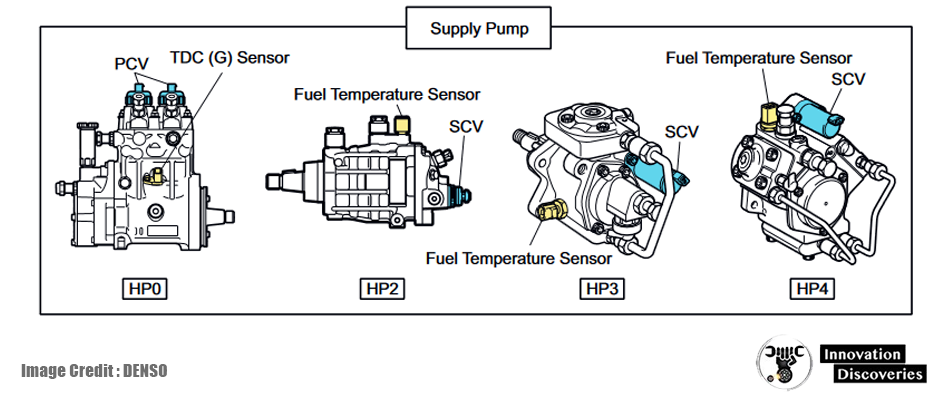
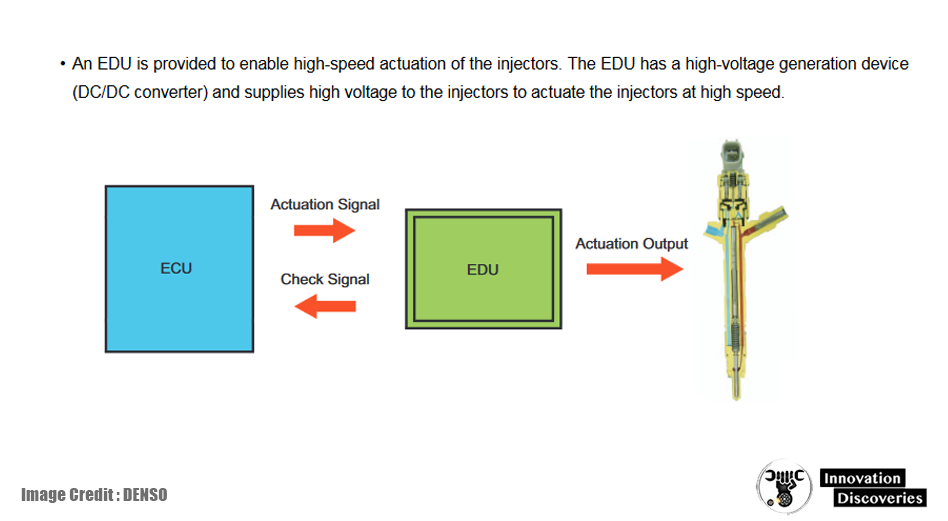
The EDU, or Electronic Driving Unit, is a specialized component that works in conjunction with the ECU to control fuel injection. While the ECU makes the high-level decisions, the EDU translates these commands into precise electrical signals that control fuel injectors and other critical components.
What Does the EDU Control?
The EDU is responsible for:
- Determining when and how much fuel to inject into the engine.
- Ensuring proper fuel atomization for optimal combustion.
- Managing the electrical characteristics of fuel injectors to ensure smooth operation.
By managing the fuel injection process, the EDU plays a vital role in the engine’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
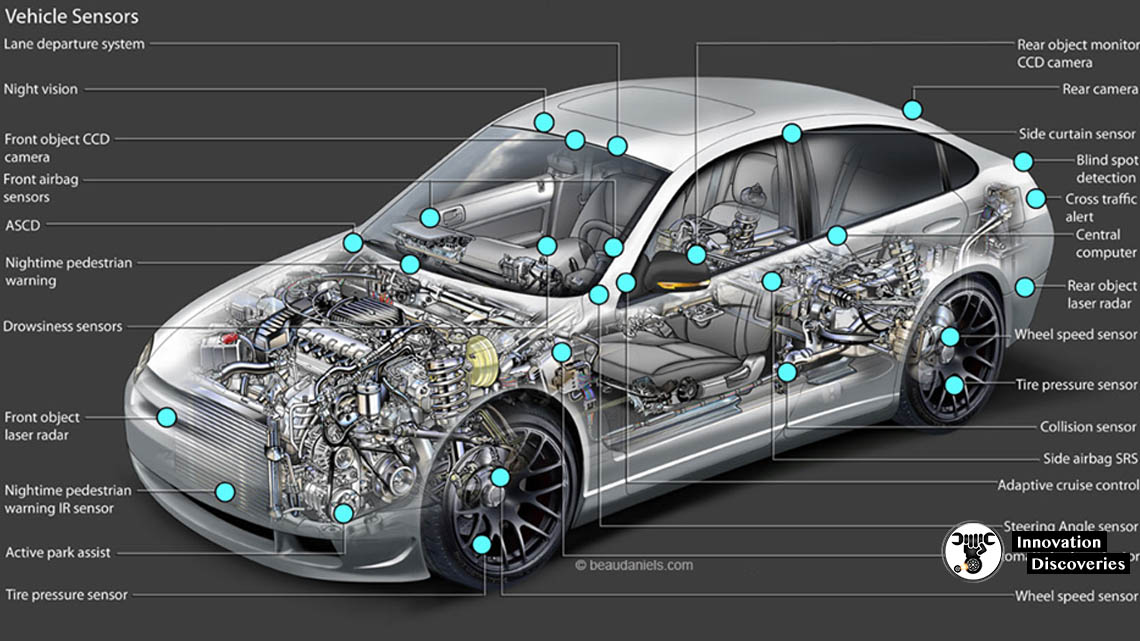
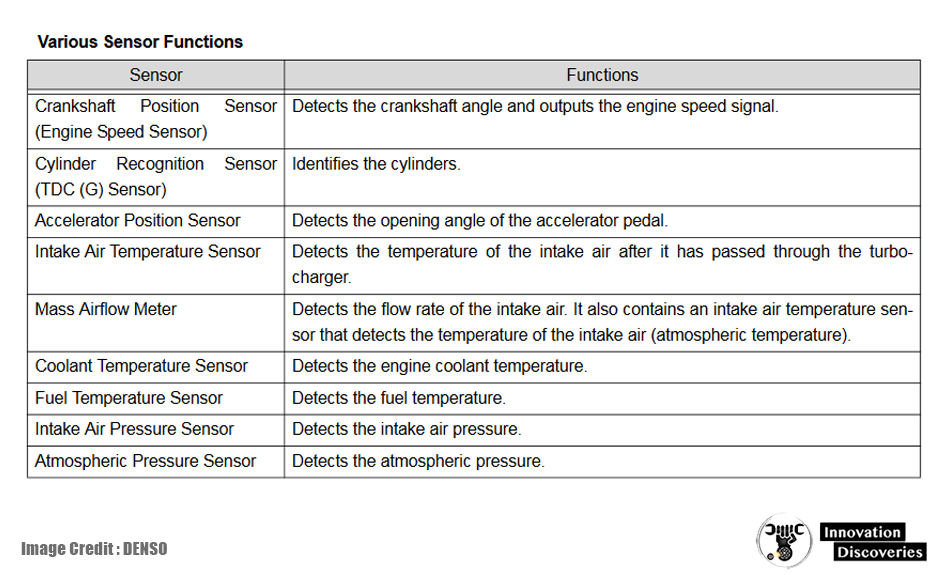
Sensors: The Eyes and Ears of the Engine Control System
To make informed decisions, the ECU relies on a network of sensors that monitor various aspects of the engine and the environment. These sensors provide real-time data, allowing the ECU to adjust engine operations as needed.
Key Sensors and Their Functions
Here are some of the most important sensors in an engine control system:
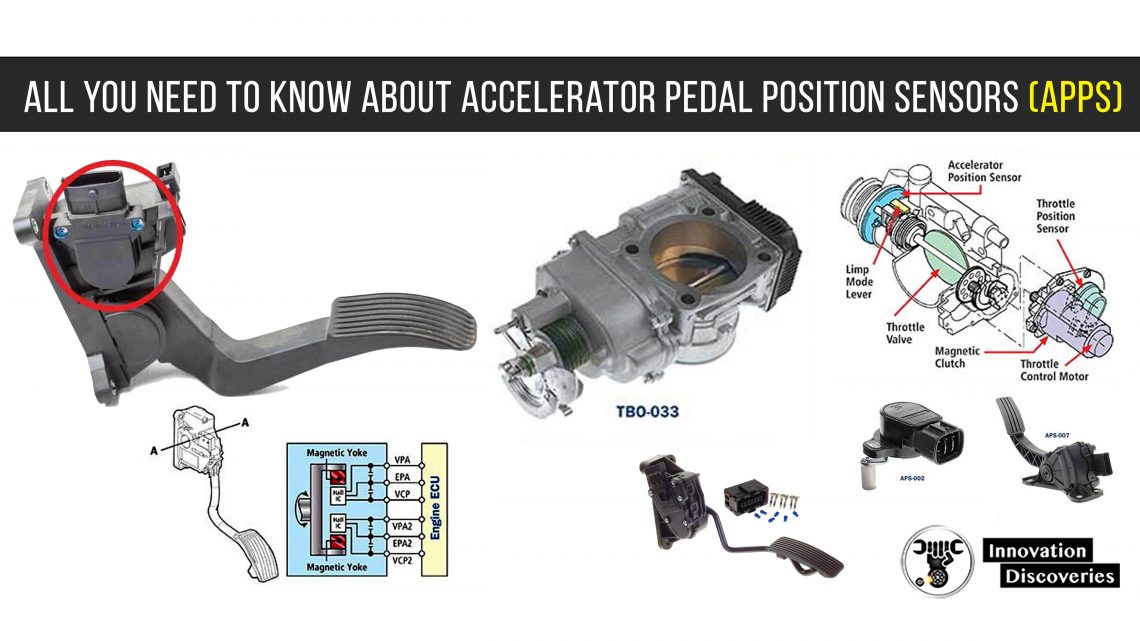
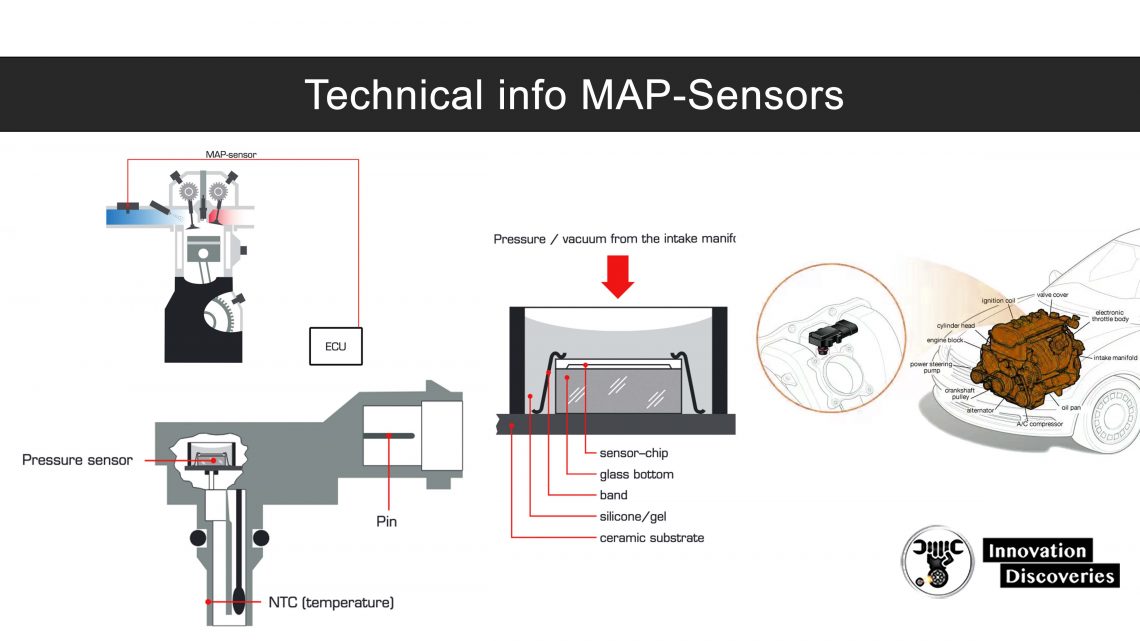
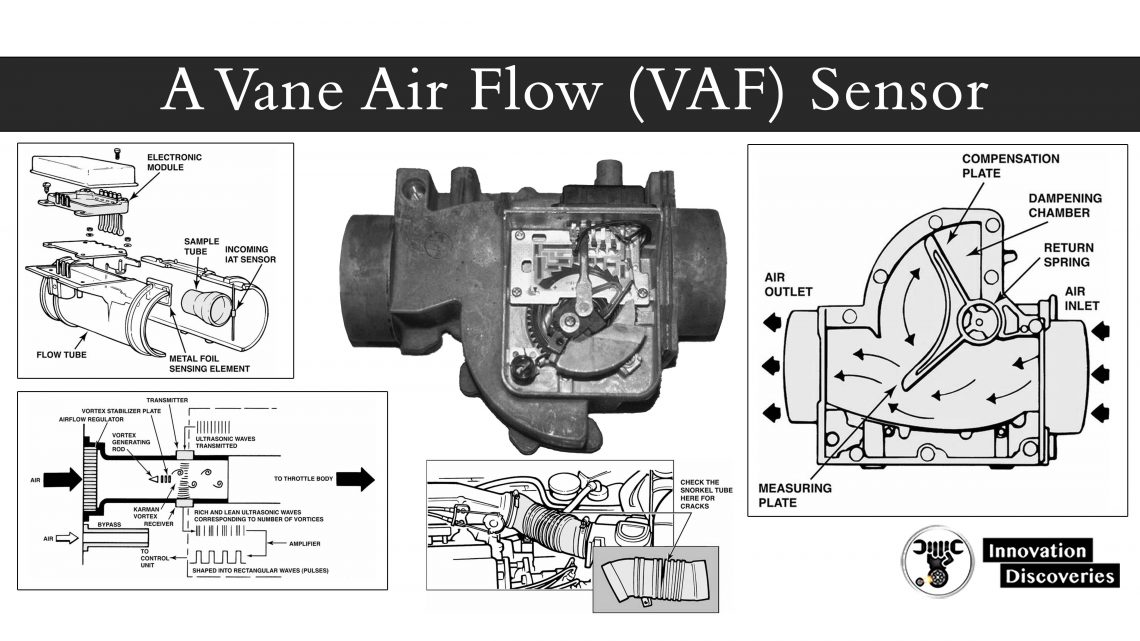
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor: Measures the volume of air entering the engine, which helps determine the appropriate fuel injection rate.
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): Monitors the position of the throttle valve to inform the ECU about driver input.
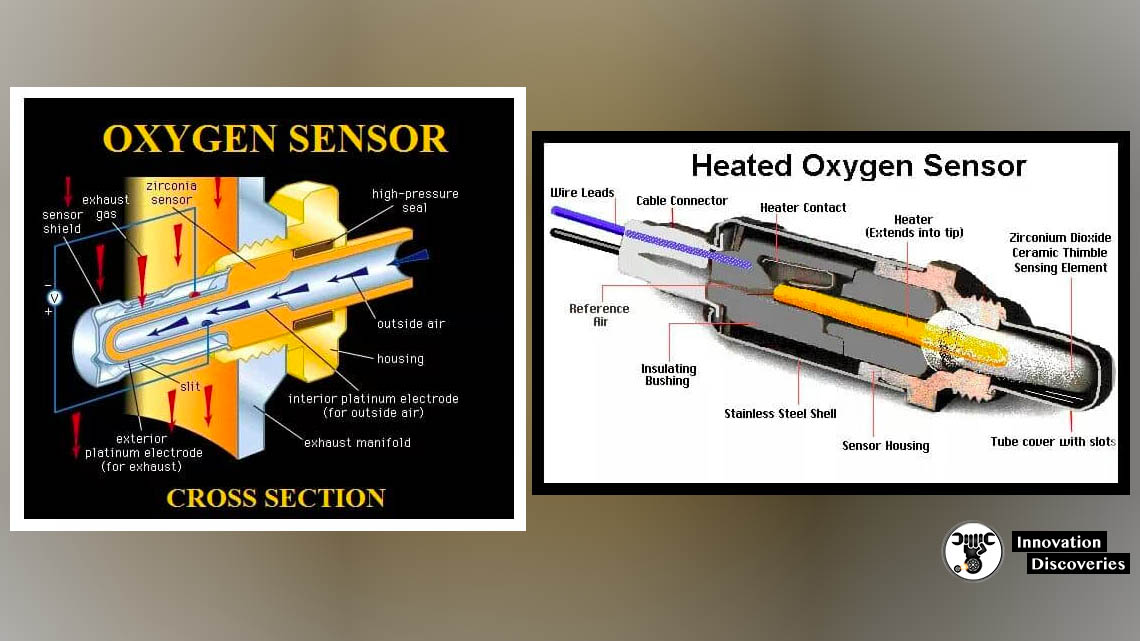
- Oxygen (O2) Sensors: Detects the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, helping to adjust the fuel-air mixture for efficient combustion.
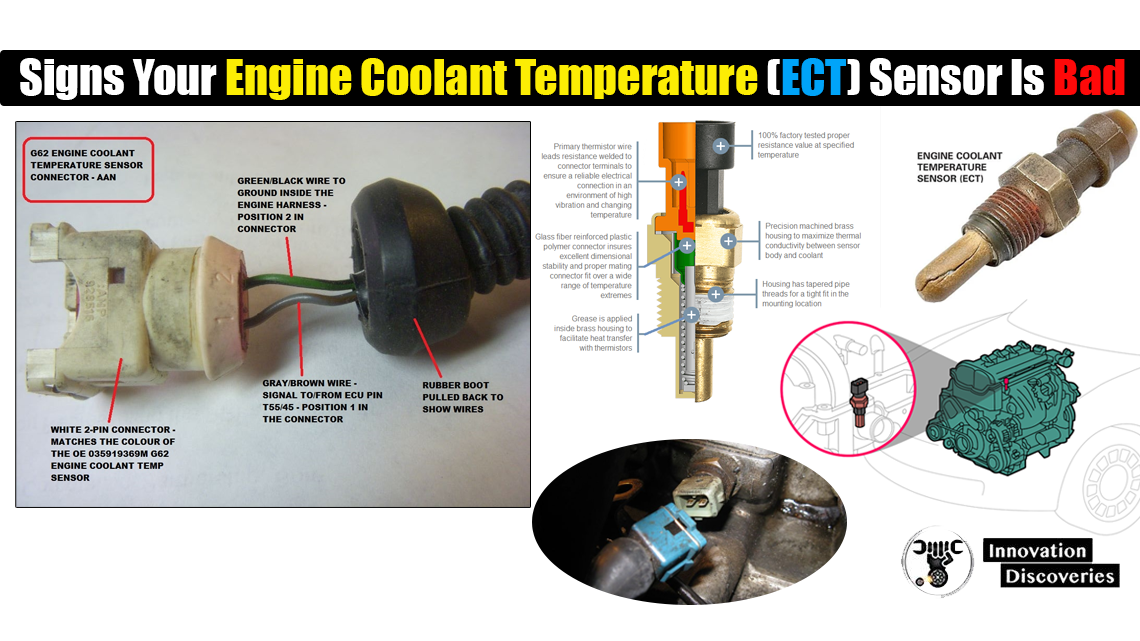
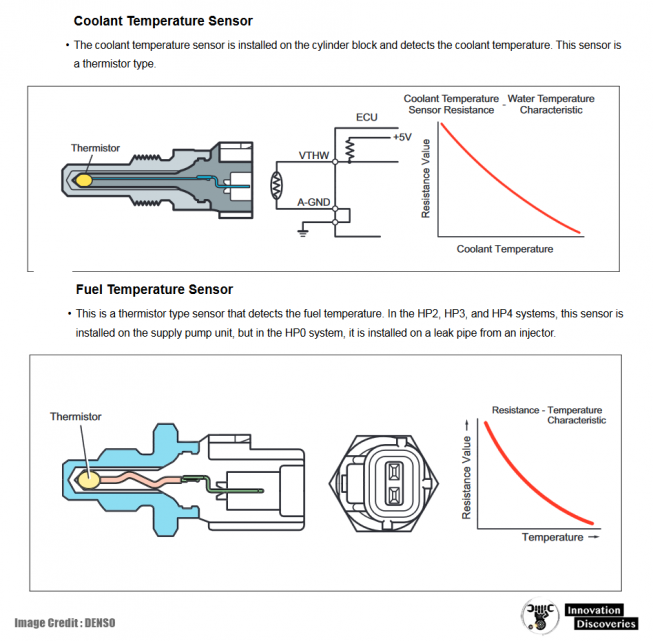
- Coolant Temperature Sensor: Measures engine coolant temperature, providing data for temperature regulation.
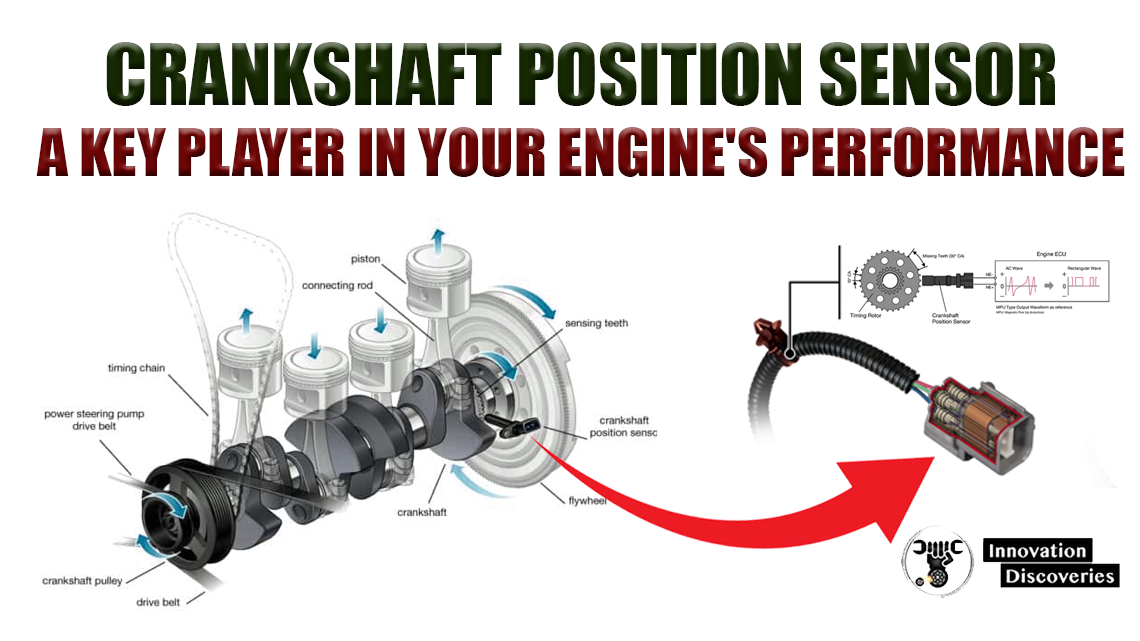
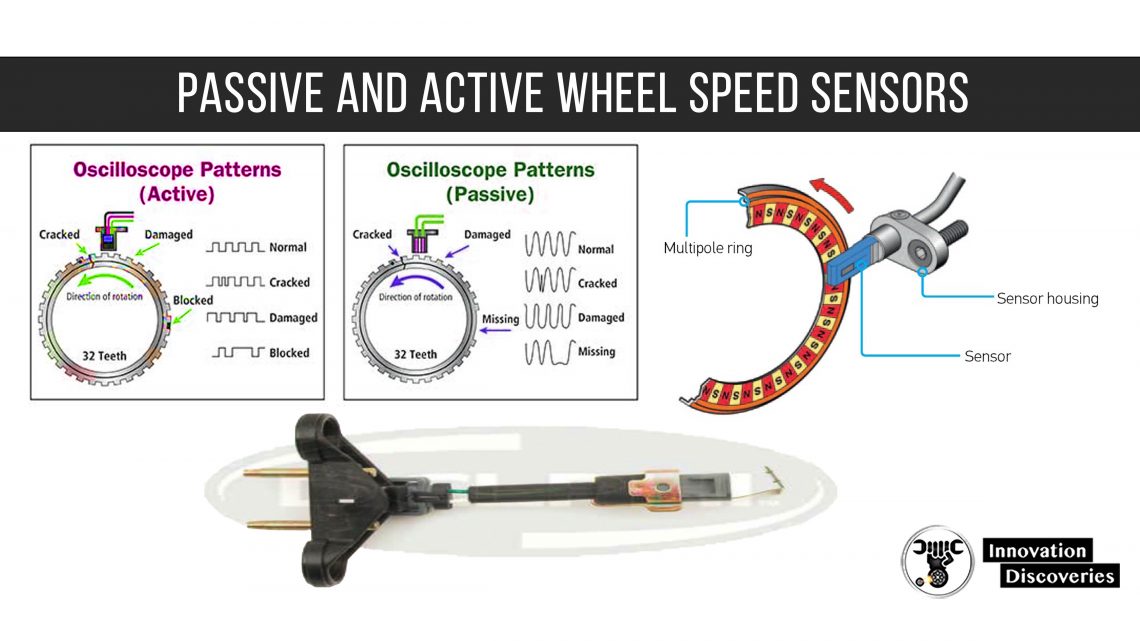
- Crankshaft Position Sensor: Tracks the position and speed of the crankshaft to ensure proper engine timing.
- Camshaft Position Sensor: Assists in synchronizing valve timing for optimal engine performance.
- Knock Sensor: Detects engine knock (abnormal combustion) and prompts the ECU to adjust ignition timing.
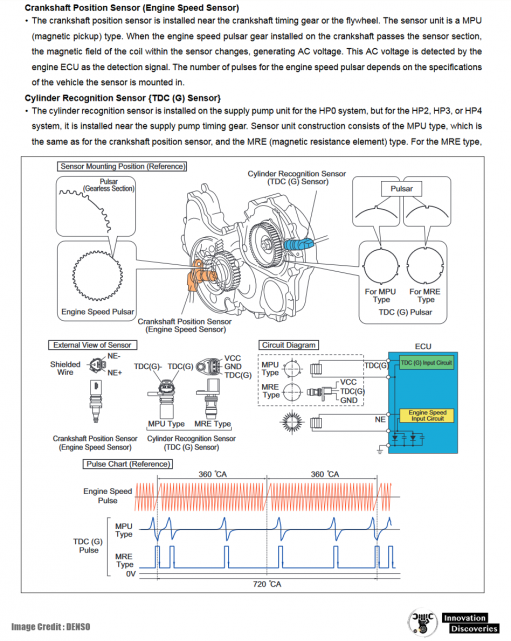
{TDC (G) Sensor}

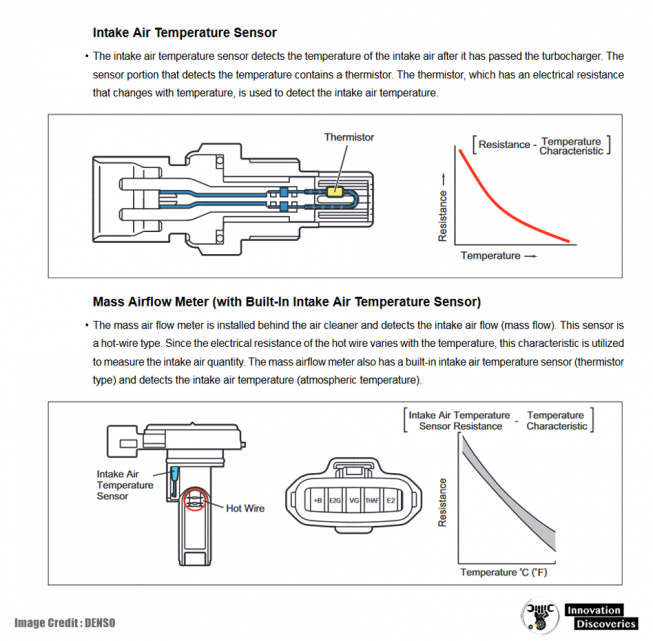
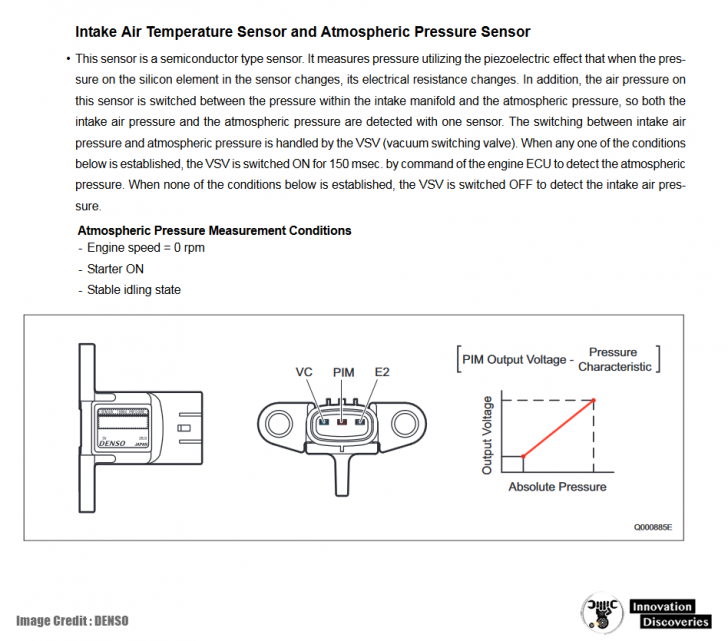
Bringing It All Together: How These Components Interact
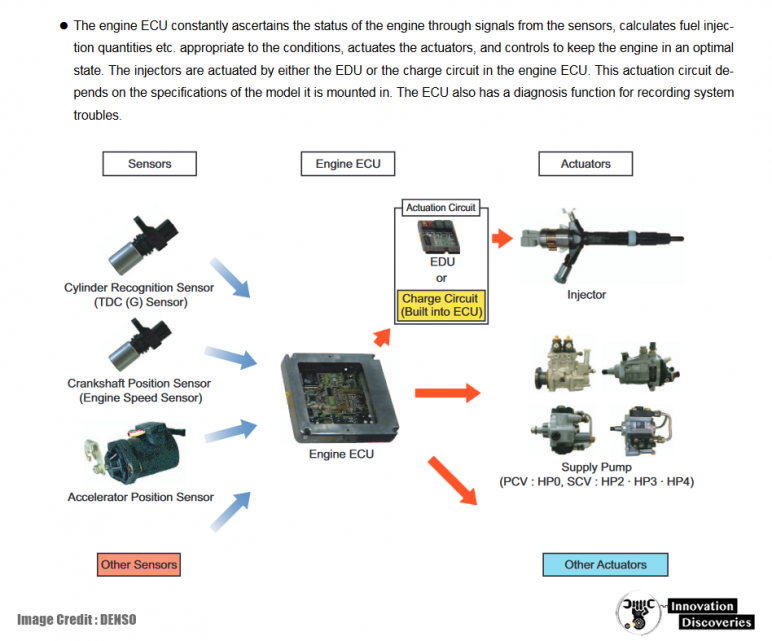
The engine control system is a dynamic loop of data collection, processing, and command execution. Here’s how it works:
- Data Collection: Sensors collect real-time data from the engine and its surroundings, providing a comprehensive view of engine conditions.
- Data Processing: The ECU analyzes the sensor data and determines the best course of action for optimal engine performance.
- Command Execution: The ECU sends instructions to the EDU and other actuators, controlling fuel injection, ignition timing, and more.
- Feedback Loop: The sensors continuously provide feedback to the ECU, allowing it to adjust engine operations based on changing conditions.
This harmonious interaction between components ensures that your vehicle’s engine runs smoothly, with a balance of power, efficiency, and emissions control. If any component malfunctions or provides inaccurate data, it can lead to suboptimal engine performance or even trigger a check engine light.
Understanding these components and their roles can help you appreciate the complexity and sophistication of modern vehicles.
It can also be valuable when dealing with car maintenance or troubleshooting engine issues. By having a basic grasp of how the engine control system works, you can make more informed decisions about your vehicle’s care and upkeep.
Discover More:
ECU CHIP TUNE | IGNITION TIMING | INCREASE HORSEPOWER
VEHICLE SENSORS: FUNCTIONS AND TYPES

Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website