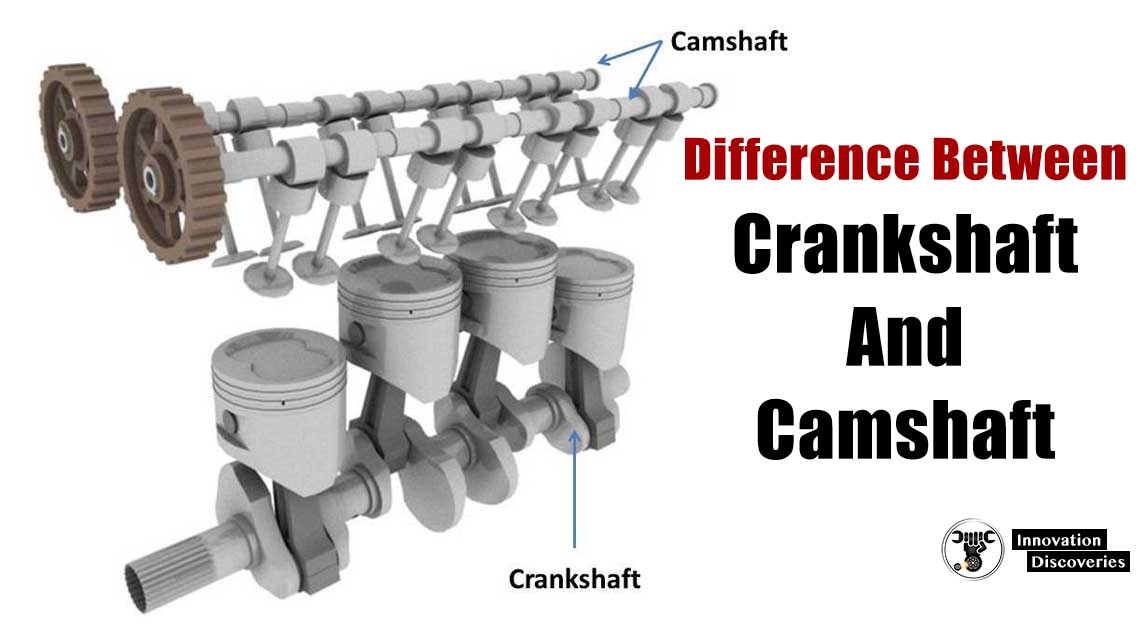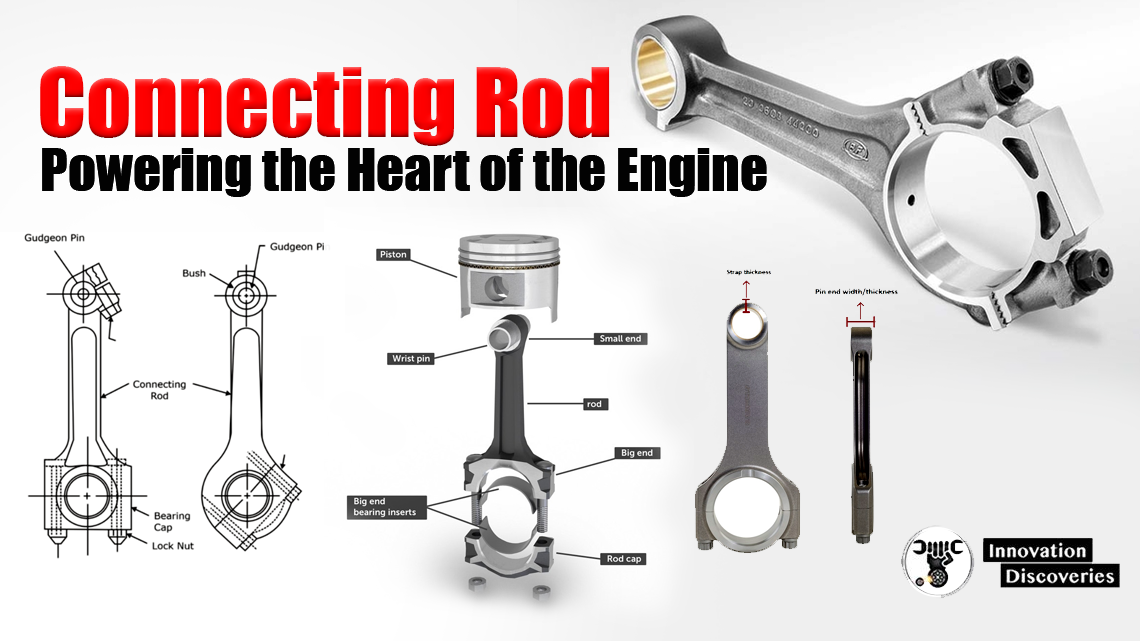
Introduction:
In the realm of internal combustion engines, a small but mighty component holds the key to transforming reciprocating motion into powerful rotational force—the connecting rod.
This article explores the significance, design, and materials used in connecting rods, shedding light on their critical role in the heart of every engine.
The Purpose of the Connecting Rod:
Nestled between the piston and crankshaft, the connecting rod serves as the crucial link that enables the engine’s operation.
As the piston moves up and down within the cylinder, the connecting rod translates this linear motion into rotary motion, generating the torque necessary to drive vehicles or propel machinery.
Design and Construction:
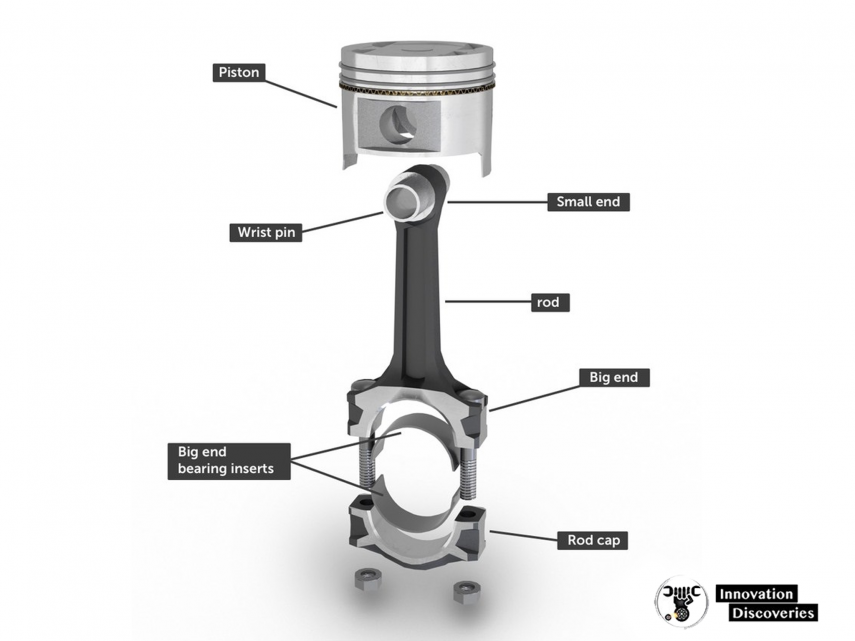
Connecting rods are meticulously engineered to withstand extreme forces and endure the demanding conditions within an engine. Typically consisting of a rod cap, big end bearing, small end bearing, and the rod itself, their design allows for efficient assembly and disassembly during engine maintenance.
The rod cap is a detachable part that facilitates accessibility and ease of maintenance. It enables the connection between the rod and the crankshaft journal.
On the other end, the small end bearing connects the rod to the piston pin, while the big end bearing connects the rod to the crankshaft journal.
Materials and Strength:
The connecting rod must be designed to withstand tremendous loads and stresses. Forged steel, aluminum alloy, and titanium alloy are commonly used materials, chosen based on the specific application.

High-performance engines often employ lightweight yet robust materials like titanium to reduce weight and enhance strength, leading to improved engine performance.
Lubrication and Maintenance:
Proper lubrication is paramount to ensure the smooth operation and longevity of the connecting rod. Bearings, both at the big end and small end, necessitate a constant supply of oil to minimize friction and wear.
Engine oil is circulated through an efficient oiling system that delivers lubrication to the bearings, ensuring optimal performance.
The Future of Connecting Rods:
As engine technologies evolve, connecting rods continue to undergo innovation. Advanced materials, such as carbon fiber composites and advanced alloys, may find their way into connecting rod designs, offering further weight reduction and increased strength.
Additionally, advancements in lubrication systems and manufacturing techniques will likely contribute to enhanced durability and efficiency.
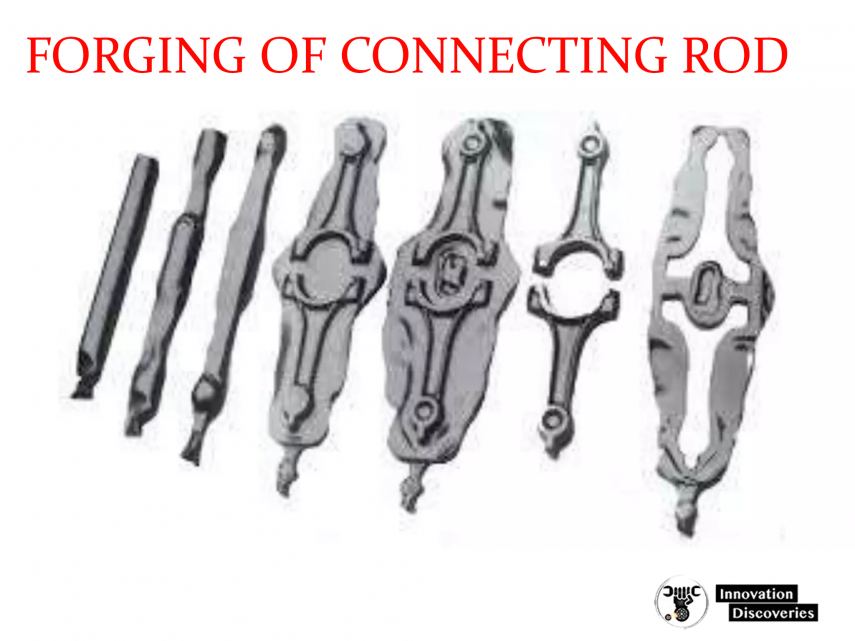
CONNECTING ROD MATERIALS
- Generally there are a few materials that are commonly used in the creation of connection rods. Like steel alloy, aluminum and titanium.
- The connecting rods are usually made of steel alloys like 42CrMo4, 43CrMo4, 44csr4, C-70, EN-8D, SAE1141, etc. Connecting rods are usually drop forged out of a steel alloy.
- Aluminum and titanium are both materials that are also used in the manufacturing of connecting rods for performance vehicles.
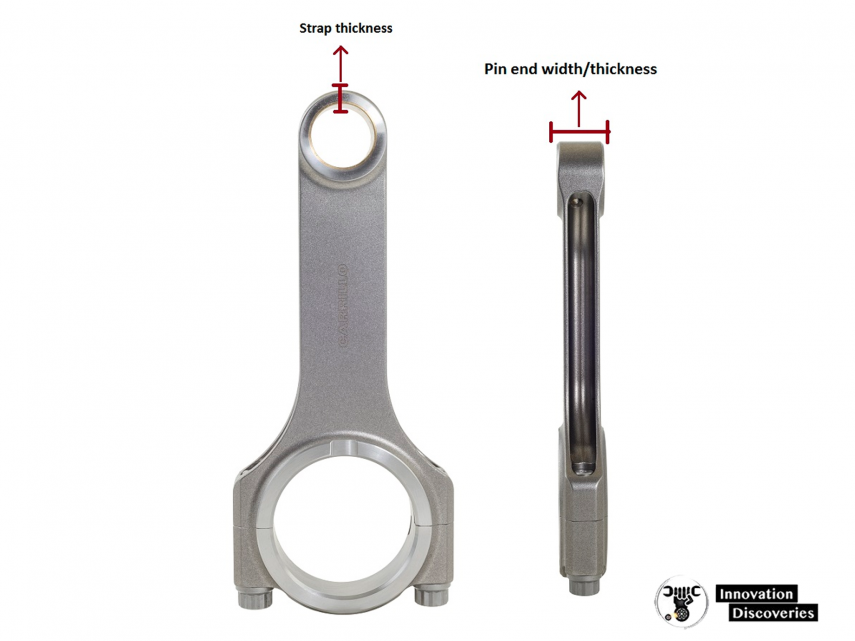
Conclusion:
The connecting rod remains an unsung hero within the internal combustion engine, quietly translating the piston’s reciprocating motion into the robust rotational force that powers our vehicles and machinery.
Engineered with precision, employing high-quality materials, and supported by efficient lubrication systems, connecting rods play a vital role in optimizing engine performance and reliability.
As engines evolve, so too will the connecting rod, ensuring that it continues to be a fundamental component in driving the world forward.
Discover More:
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website