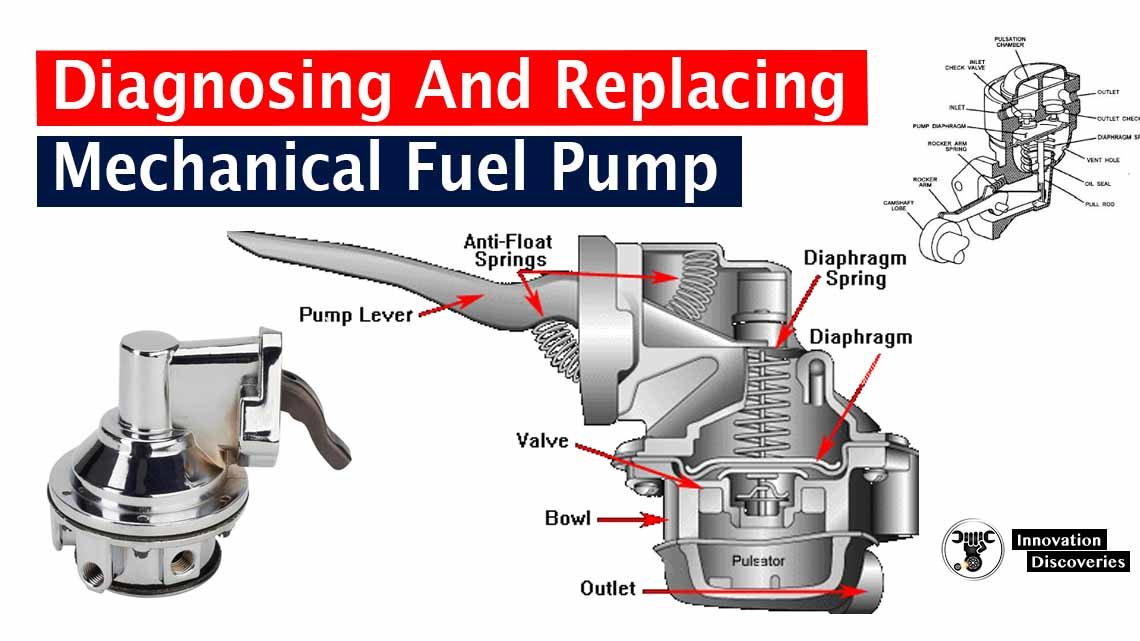
Diagnosing and replacing a mechanical fuel pump can be a crucial task for maintaining the proper functioning of a vehicle’s fuel system.
In this guide, we will discuss the problems associated with mechanical fuel pumps, how to check them, and the steps involved in replacing a faulty pump.
Introduction
A mechanical fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the gas tank to the engine. It is commonly found in older vehicles and operates by using the engine’s motion to create suction and draw fuel into the engine.
Over time, mechanical fuel pumps can develop issues that require diagnosis and replacement.
The Problems of Mechanical Fuel Pumps
There are several common problems associated with mechanical fuel pumps:
1. Vapor Lock
Vapor lock occurs when the fuel in the pump or fuel lines evaporates, causing a blockage in the fuel system. This can happen due to excessive heat or insufficient fuel flow.
Vapor lock results in a loss of fuel delivery, leading to engine stalling or failure to start.
2. Fuel Foaming
Fuel foaming occurs when air bubbles form in the fuel system, usually due to turbulence or excessive agitation. This can disrupt the fuel flow and cause engine misfires, rough idling, or hesitation during acceleration.
3. A Leak in the Pump
Mechanical fuel pumps can develop leaks over time, leading to fuel seepage or spraying. A leaky fuel pump can result in reduced fuel pressure, poor engine performance, and even the risk of fire.
How to Check a Mechanical Fuel Pump
To diagnose a mechanical fuel pump, you can follow these steps:
1. Prepare the vehicle:
Park the vehicle on a level surface, engage the parking brake, and ensure the engine is cool.
2. Locate the fuel pump:
Mechanical fuel pumps are typically located near the engine, either attached to the engine block or mounted on the side.
3. Visual inspection:
Check for any signs of leaks, such as wetness or fuel stains around the pump. Inspect the fuel lines for damage or cracks.
4. Fuel pressure test:
Attach a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel pump outlet and crank the engine. Observe the pressure reading on the gauge. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the pressure is within the acceptable range.
5. Vacuum test:
Connect a vacuum gauge to the fuel pump inlet and start the engine. Monitor the vacuum gauge reading, ensuring it remains steady and within the manufacturer’s recommended range.
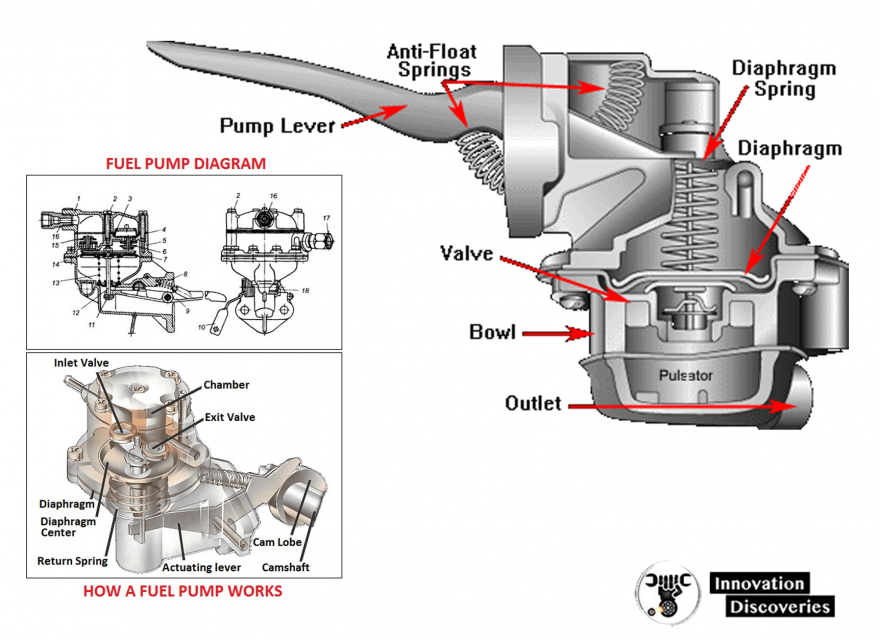
If the fuel pressure or vacuum readings are outside the acceptable range, or if there are signs of leaks, it is likely that the mechanical fuel pump is faulty and needs replacement.
How to Replace a Mechanical Fuel Pump
Replacing a mechanical fuel pump involves the following steps:
1. Gather necessary tools and materials:
This may include a new mechanical fuel pump, a replacement gasket, wrenches, pliers, and a drip pan to catch any spilled fuel.
2. Disconnect the battery:
Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent accidental sparks or electrical hazards.
3. Relieve fuel pressure:
Locate the fuel pressure relief valve, typically found on the fuel rail, and depress it to release any residual pressure in the fuel system.
4. Remove the old pump:
Disconnect the fuel lines from the pump, ensuring you have the drip pan ready to catch any fuel. Loosen and remove the bolts or mounting hardware securing the pump to the engine.
5. Install the new pump:
Position the new pump in place, using a new gasket if necessary. Secure the pump with the appropriate bolts or mounting hardware, ensuring it is tightly fastened.
6. Reconnect the fuel lines:
Attach the fuel lines to the new pump, ensuring they are properly connected and tightened.
7. Reconnect the battery:
Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery, ensuring a secure connection.
8. Test the fuel pump:
Start the engine and monitor its performance. Check for any leaks and ensure proper fuel flow.
Conclusion
Diagnosing and replacing a faulty mechanical fuel pump is essential for maintaining the proper functioning of a vehicle’s fuel system.
By understanding the problems associated with mechanical fuel pumps, performing diagnostic tests, and following the appropriate steps for replacement, you can ensure reliable fuel delivery and optimal engine performance.
However, it is always recommended to consult a professional mechanic or refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions related to your vehicle model.
Read More:
- Checking, adjusting and refitting drive belts
- What is Automobile Injector and its Types
- Common Problems of the Fuel Delivery System
- 3 Symptoms of Bad Valve Seals and Piston Rings and Replacement Cost
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website



One Comment