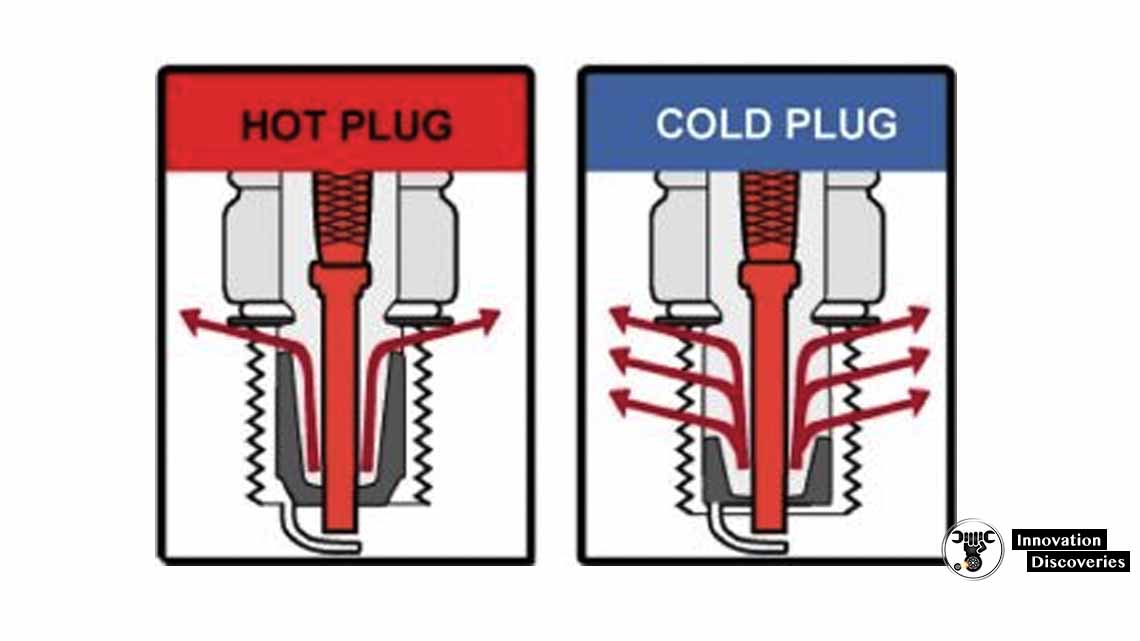
Spark plugs come in various heat ranges, commonly referred to as “hot” or “cold” plugs. The heat range of a spark plug refers to its ability to dissipate heat from the combustion chamber.
Here’s an explanation of the difference between hot and cold spark plugs:
1. Heat Dissipation:
Hot spark plugs have a longer insulator nose and a shorter heat transfer path, which means they retain more heat within the combustion chamber. They are designed for engines that operate at lower temperatures or under lighter loads.
Cold spark plugs have a shorter insulator nose and a longer heat transfer path, allowing them to dissipate heat more efficiently. They are used in engines that operate at higher temperatures or under heavy loads.
2. Engine Performance:
Hot spark plugs are beneficial for engines that frequently run at low speeds or idle for extended periods, as they help prevent fouling by burning off deposits more effectively.
Cold spark plugs are suitable for high-performance engines or those subjected to heavy loads and high speeds, as they help prevent pre-ignition (detonation) by dissipating heat efficiently.
3. Fuel Efficiency:
Hot spark plugs can contribute to better fuel efficiency in engines that operate at low temperatures or under light loads, as they ensure complete combustion of the fuel-air mixture.
Cold spark plugs may lead to slightly lower fuel efficiency in everyday driving conditions due to their tendency to keep the combustion chamber cooler, which may not optimize fuel combustion.
4. Engine Protection:
Hot spark plugs can help prevent spark plug fouling in engines that don’t reach optimal operating temperatures regularly, ensuring consistent ignition performance.
Cold spark plugs offer protection against pre-ignition, which can damage engine components and reduce performance.
Application:
Hot spark plugs are typically used in engines with low compression ratios or in colder climates.
Cold spark plugs are commonly used in high-performance engines, turbocharged or supercharged engines, and racing applications where engine temperatures are higher.
It’s essential to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations or a knowledgeable mechanic when choosing spark plugs for your engine to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Using the wrong heat range of spark plug can lead to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential damage to engine components.
Also, read:
What happens when the plug is too hot?
When a spark plug is too hot:
1. Pre-ignition or Detonation:
Excessive heat in the combustion chamber can cause the air-fuel mixture to ignite prematurely before the spark plug fires.
This premature ignition, known as pre-ignition or detonation, can lead to engine knocking, pinging, and potentially damaging engine components.
2. Insulator Damage:
The insulator of the spark plug may overheat and become damaged or cracked, compromising the integrity of the spark plug and leading to misfires or electrical arcing.
3. Combustion Chamber Deposits:
Excessive heat retention in the combustion chamber can lead to the formation of carbon deposits on the spark plug electrodes and insulator nose.
These deposits can interfere with proper spark plug operation, leading to misfires and reduced engine performance.
4. Engine Overheating:
In some cases, excessively hot spark plugs can contribute to engine overheating, especially in high-performance or heavily loaded engines.
Overheating can cause various engine problems, including decreased performance, increased emissions, and potential damage to engine components.
What happens when a plug is too cold?
When a spark plug is too cold:
1. Fouling:
Cold spark plugs may not reach optimal operating temperatures, leading to incomplete combustion of the air-fuel mixture.
This incomplete combustion can result in the accumulation of carbon deposits (fouling) on the spark plug electrodes, inhibiting proper spark generation and leading to misfires and reduced engine performance.
2. Poor Fuel Economy:
Cold spark plugs may contribute to poor fuel economy, especially in everyday driving conditions where the engine may not reach high operating temperatures.
Inefficient combustion due to cold spark plugs can result in wasted fuel and decreased fuel efficiency.
3. Difficulty Starting:
In colder climates or during cold starts, cold spark plugs may have difficulty igniting the air-fuel mixture, leading to rough idling, hesitation, or difficulty starting the engine.
4. Engine Damage:
Persistent use of spark plugs that are too cold for the engine’s operating conditions can lead to engine damage, including increased wear on piston rings, cylinder walls, and other components due to incomplete combustion and increased friction.
In summary, using spark plugs that are either too hot or too cold for the engine’s operating conditions can result in various problems, including poor performance, decreased fuel efficiency, and potential engine damage.
It’s essential to choose spark plugs with the appropriate heat range recommended by the manufacturer for your specific engine and operating conditions.
Read More:
- How to Replace Worn Spark Plugs in a Car
- Common Spark Plug Misfire Symptoms
- How Variable Valve Timing Works, And How it Makes Your Engine Better
- Professional Tips On How To Start A Flooded Engine
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website








5 Comments