
Introduction:
The drivetrain of a vehicle is one of its most important components, as it determines how the engine’s power is transmitted to the wheels. There are several types of drivetrains available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of drivetrains are front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), four-wheel drive (4WD or 4×4), and all-wheel drive (AWD).
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a drivetrain in which the power from the engine is transmitted to the front wheels of the vehicle. FWD is known for its superior handling in snowy or wet conditions and for being more fuel-efficient than RWD systems. However, FWD can produce torque steer under heavy acceleration, and it may not provide the same level of performance as RWD in high-speed driving conditions.
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) is a drivetrain in which the power from the engine is transmitted to the rear wheels of the vehicle. RWD is commonly used in high-performance and luxury vehicles because it provides better handling and performance than FWD systems. RWD also allows for more balanced weight distribution between the front and rear of the vehicle, which can enhance handling and cornering ability.
Four-wheel drive (4WD or 4×4) is a drivetrain that provides power to all four wheels of a vehicle. 4WD is commonly used in off-road and heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and SUVs, because it provides superior traction and handling in challenging terrain and weather conditions. By providing power to all four wheels, 4WD can improve traction and stability on muddy, snowy, or rocky roads.
All-wheel drive (AWD) is a drivetrain that provides power to all four wheels of a vehicle, but it differs from 4WD in that it is designed for everyday driving situations. AWD systems are typically found in passenger cars and crossover SUVs and provide better handling and stability in all weather conditions. AWD can improve traction and handling on wet or slippery roads and can automatically adjust power to each wheel as needed to provide optimal performance.
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
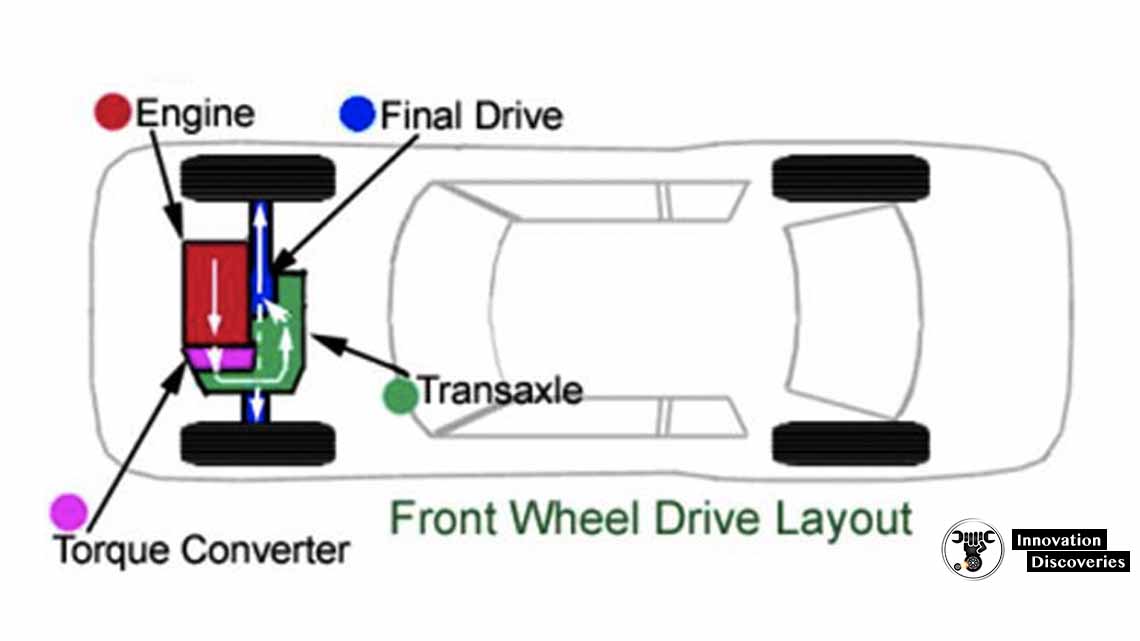
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a type of drivetrain in which the power from the engine is transmitted to the front wheels of the vehicle. In a FWD system, the engine, transmission, and differential are located in the front of the vehicle, and the front wheels are responsible for both steering and power delivery.
FWD is a popular choice for passenger cars and smaller vehicles because it provides better traction and handling in snowy or wet conditions compared to rear-wheel drive (RWD) systems. Since the weight of the engine is located over the front wheels, FWD cars can maintain better grip and stability on slippery roads.
Another advantage of FWD is that it tends to be more fuel-efficient than RWD systems. Since the power is delivered directly to the front wheels, there are fewer components involved in the drivetrain, which reduces friction and mechanical losses.
One disadvantage of FWD is that it can produce torque steer, which is a tendency for the vehicle to pull to one side under heavy acceleration. Additionally, FWD vehicles may not provide the same level of performance and handling as RWD vehicles, particularly in high-speed driving conditions or on winding roads.
Overall, FWD is a reliable and efficient drivetrain option for most passenger vehicles, but it may not be the best choice for high-performance or heavy-duty applications.
Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)
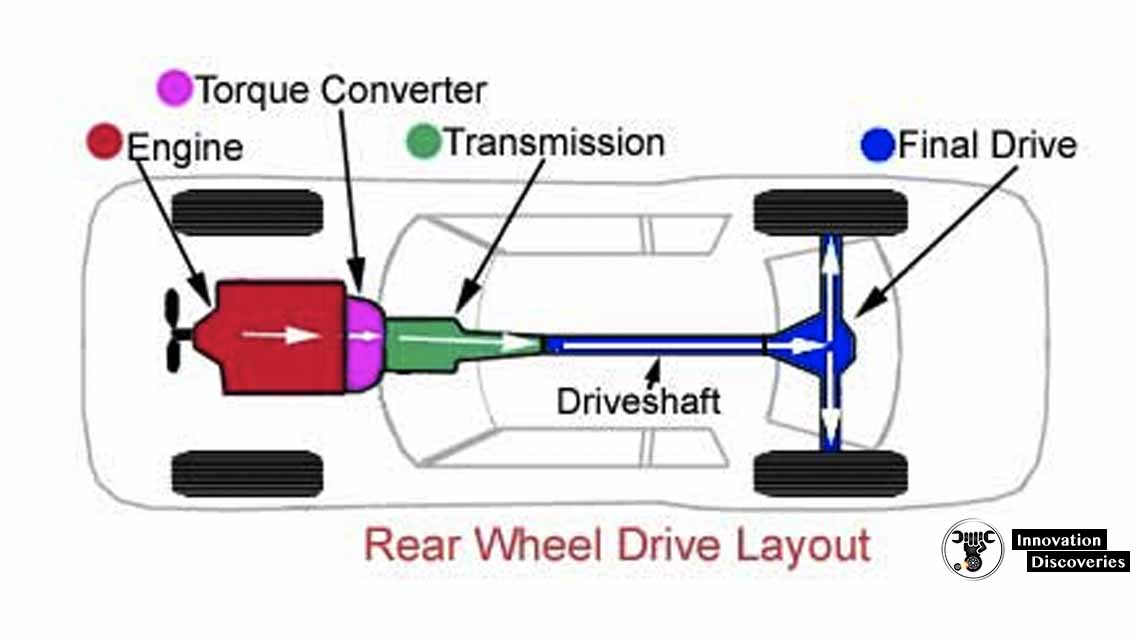
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) is a type of drivetrain in which the engine’s power is transmitted to the rear wheels of the vehicle. In a RWD system, the engine and transmission are located in the front of the vehicle, and a driveshaft sends power to the rear differential, which then powers the rear wheels.
RWD is commonly used in high-performance and luxury vehicles because it provides better handling and performance than front-wheel drive (FWD) systems. RWD allows for more balanced weight distribution between the front and rear of the vehicle, which can enhance handling and cornering ability.
Another advantage of RWD is that it is less susceptible to torque steer, which is a tendency for the vehicle to pull to one side under heavy acceleration, compared to FWD systems. RWD vehicles may also be better suited for towing heavy loads or hauling cargo because the weight is distributed more evenly across the vehicle’s frame.
One disadvantage of RWD is that it may not provide as much traction and stability in wet or slippery conditions as FWD systems. Additionally, RWD vehicles tend to be less fuel-efficient than FWD systems because they require more mechanical components to transfer power to the rear wheels.
Overall, RWD is a reliable and efficient drivetrain option for high-performance and luxury vehicles, but it may not be the best choice for all applications. It is important to consider factors such as driving conditions, vehicle type, and personal preferences when selecting a drivetrain for a particular vehicle.
Four-Wheel Drive (4WD or 4×4)
Four-wheel drive (4WD or 4×4) is a type of drivetrain that provides power to all four wheels of a vehicle. In a 4WD system, the engine’s power is transmitted to all four wheels through a transfer case, which allows the vehicle to operate in both two-wheel drive and four-wheel drive modes.
4WD is commonly used in off-road and heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and SUVs, because it provides superior traction and handling in challenging terrain and weather conditions. By providing power to all four wheels, 4WD can improve traction and stability on muddy, snowy, or rocky roads.
One advantage of 4WD is that it allows for greater towing and hauling capacity than two-wheel drive vehicles. 4WD can also improve vehicle stability and control when driving on steep hills or uneven terrain.
One disadvantage of 4WD is that it can be less fuel-efficient than two-wheel drive vehicles because the extra mechanical components add weight and increase drag. Additionally, 4WD systems can be more expensive to maintain and repair.
Overall, 4WD is a reliable and effective drivetrain option for off-road and heavy-duty vehicles, but it may not be necessary or practical for everyday driving situations. It is important to consider factors such as driving conditions, vehicle type, and personal preferences when selecting a drivetrain for a particular vehicle.
Here’s a video explaining 4WD.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)
All-wheel drive (AWD) is a type of drivetrain that provides power to all four wheels of a vehicle at all times. Unlike four-wheel drive (4WD), which can be manually engaged or disengaged, AWD systems are always active and distribute power automatically to the wheels with the most traction.
AWD systems use a variety of sensors and computer-controlled mechanisms to monitor driving conditions and adjust power distribution accordingly. Some AWD systems are biased towards the front or rear wheels, while others are designed to provide equal power to all four wheels.
AWD is commonly used in high-performance and luxury vehicles, as well as some SUVs and crossovers. AWD provides better handling and traction in a variety of driving conditions, including wet or slippery roads, and can improve performance and stability in corners.
One disadvantage of AWD is that it can be more expensive to purchase and maintain than two-wheel drive vehicles. AWD systems also add weight and complexity to the vehicle, which can reduce fuel efficiency.
Overall, AWD is a reliable and effective drivetrain option for a wide range of vehicles, particularly those that require superior handling and traction in a variety of driving conditions. However, it is important to consider factors such as driving conditions, vehicle type, and personal preferences when selecting a drivetrain for a particular vehicle.


3 Comments