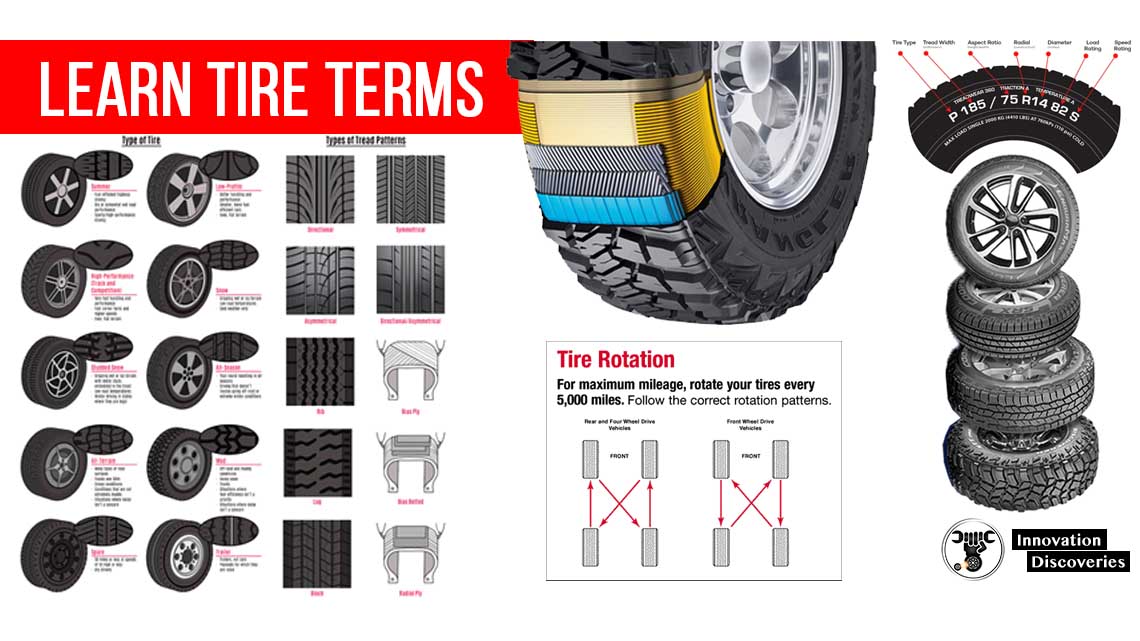
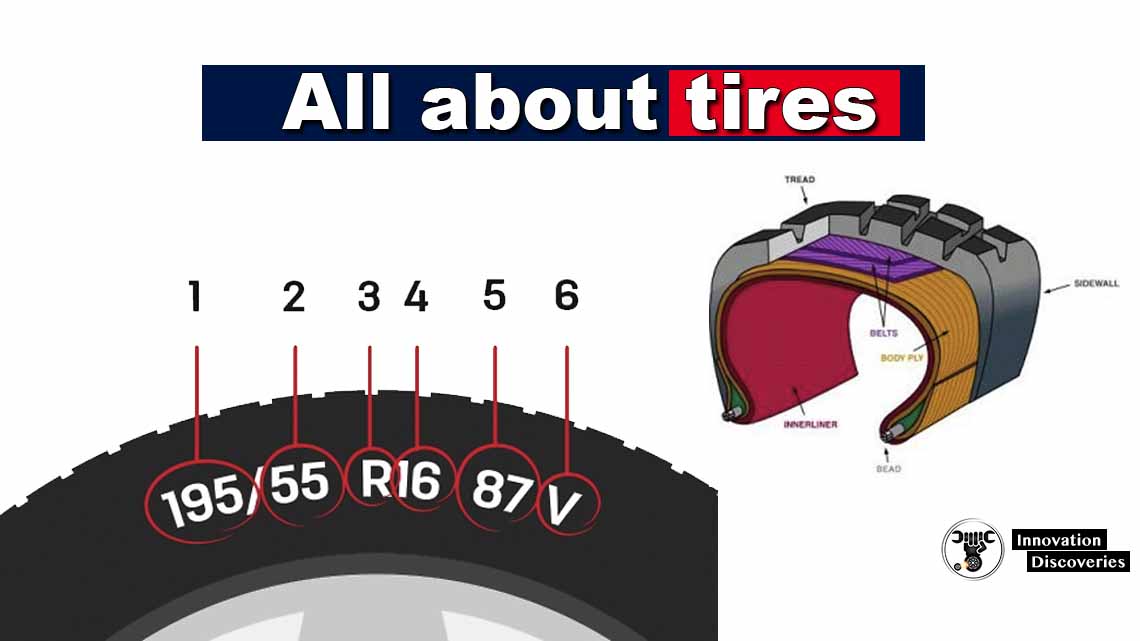
Aspect Ratio
Section height/section width x 100 – ratio between tire height and width
Asymmetric
When opposite sides of a tire’s tread pattern are not identical.
Backside Setting
The distance from the mounting surface of the wheel, which contacts the hub, to the back rim flange. It is sometimes referred to as the backspacing or backside measurement.
Balance
The even distribution of weight on a mounted wheel and tire.
Bias-Belted Tire
A passenger-type tire which has two rubberized plies of cords that are crossed over one another at an angle (on a bias) plus two reinforced belts that encircle the tires under the tread.
Block Tread Design
A tire tread pattern made of raised rubber compound segments.
Bolt Circle
Sometimes referred to as bolt pattern: The number of lug holes on the diameter of the imaginary circle that each lug hole is centered on.
Carcass
The portion of a tire that is the foundation for the tread, belts, bead, and sidewall.
Casing
The structure of tire cords is locked around wire beads.
Compound
The general term referring to the chemical formula for the tread material.
Criss-Cross Torquing
The recommended sequential tightening of the lug nuts in a pattern across from one another helps ensure even tightening.
Grooves
Circumferential channels between and the tread ribs of a tire.

Hub Centric
A situation where the center bore of the wheel is made to match up with the diameter of the automobile hubs; the wheel is then balanced by the center hold rather than the lug holes.
Hydroplaning
Loss of traction at high speeds caused by a wedge of water that lifts a tire off the road surface.
Load Rating
The maximum weight that the tire is designed to carry; dictated by the tire’s construction.
Metric passenger-type tires are offered with a Standard Load Rating (up to 35 psi), or Extra Load Rating (up to 41 psi).
LT Metric (truck type) tires are offered with ply ratings of C (8 ply), D (8 ply), and (10 ply) and at various inflation pressures up to 80 psi.
Read: WHEELS: PARTS, SIZES, BOLT PATTERNS, WHEEL OFFSET, ONE-PIECE VS TW-PIECE WHEEL AND HOW THEY MADE

Low Profile
A term describing a tire with a low relative aspect ratio or series classification (short sidewall, wide tread).
Negative Offset
A condition where the wheel’s mounting surface is closer to the inside of the wheel; when the mounting surface is inboard the wheel’s centerline.
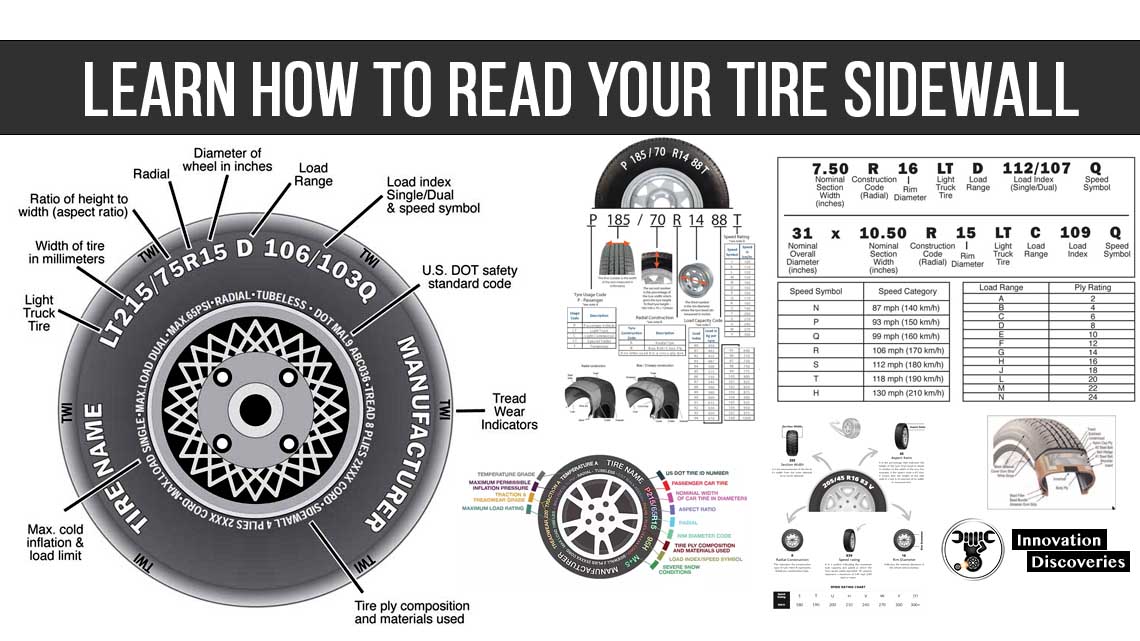
Nominal Rim Diameter
Diameter of rim seat supporting the tire bead. Examples: 13′, 15″ and 16.5″.
Offset
The positive or negative distance from the wheel’s centerline to the mounting surface of the wheel.
Overall Diameter
The diameter of the inflated tire without any load.
Overall Width
Maximum width in cross-section of the unloaded tire including protruding sides ribs and decorations.
Ply
A layer of rubber-coated fabric or wire making up the tire casing.
Positive Offset
A condition where the wheel’s mounting surface is closer to the street side of the wheel; when the mounting surface is outboard the wheel’s centerline.
Radial Ply Tire
A type of tire that has one or more rubberized plies of cords running from bead to bead (at right angles to the tread and parallel to each other), plus two or more plies of reinforced belts that encircle the tire under the tread.
Ribs
Part of a tire tread pattern created by grooves that run circumferentially around the tire.
Rim Diameter
The distance between bead seat to bead seat at beat seat radius.
Rim Flange
The edge of the wheel’s rim that the clip-on weights attach to.
Rim Width
The distance between the inside surfaces of the rim flanges.
Section Height
The distance from rim seat to outer tread surface of an unloaded tire.
Related Content:

Section Width
The linear distance between the outside sidewalls of an inflated tire without any load (exclusive of protruding side ribs and decorations).
Series
A numerical representation of a tire’s aspect ratio; for example, 50 series.
Shoulder Blocks
Raised rubber compound segments on the part of the tire tread nearest the sidewall.
Sipes
Slits in the tire tread. Small cuts in the surface of the tread to improve traction.
Steel Belt
A belt material used in radial tires. Its high stiffness provides good handling and low treadwear.
Tire Profile
A term representing the portion of a tire measured as its aspect ratio or series.
Quick Links:
- ALL ABOUT TIRES, WHAT IS THE MEANING OF NUMBERS ON THE TYRE? WHAT IS INSIDE THE TYRE?
- WHEN TO PUT YOUR VEHICLE IN 4-WHEEL DRIVE?
- WHEELS: PARTS, SIZES, BOLT PATTERNS, WHEEL OFFSET, ONE-PIECE VS TWO-PIECE WHEEL AND HOW THEY MADE
- THE DEFINITIVE GUIDE TO RUN FLAT TIRES
- NOISY TIRES?
- KNOWING THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CAR TIRE ROTATION VS ALIGNMENT
- GEAR RATIO AND TIRE SIZE CHART
- HOW TO RESET TIRE PRESSURE SENSOR: A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
Tread Blocks
Raised rubber compound segments on the outside visible part of a tire.
Tread Width
The portion of the tread design that comes in contact with the road.
Unsprung Weight
The total weight of the automobile’s components is not supported by the suspension system; wheels and tires are prime examples.
UTQG
Uniform Tire Quality Grade – A government-mandated tire rating system based on a tire’s performance in treadwear durability, traction, and temperature resistance. UTQG ratings are branded on the tire’s sidewall.
Varied-Pitch Ratio
Variations of angles and sizes of a tire’s tread elements that reduce ride noise levels.
Zero Offset
A condition where the wheel’s mounting surface coincides with the centerline of the wheel.
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website




