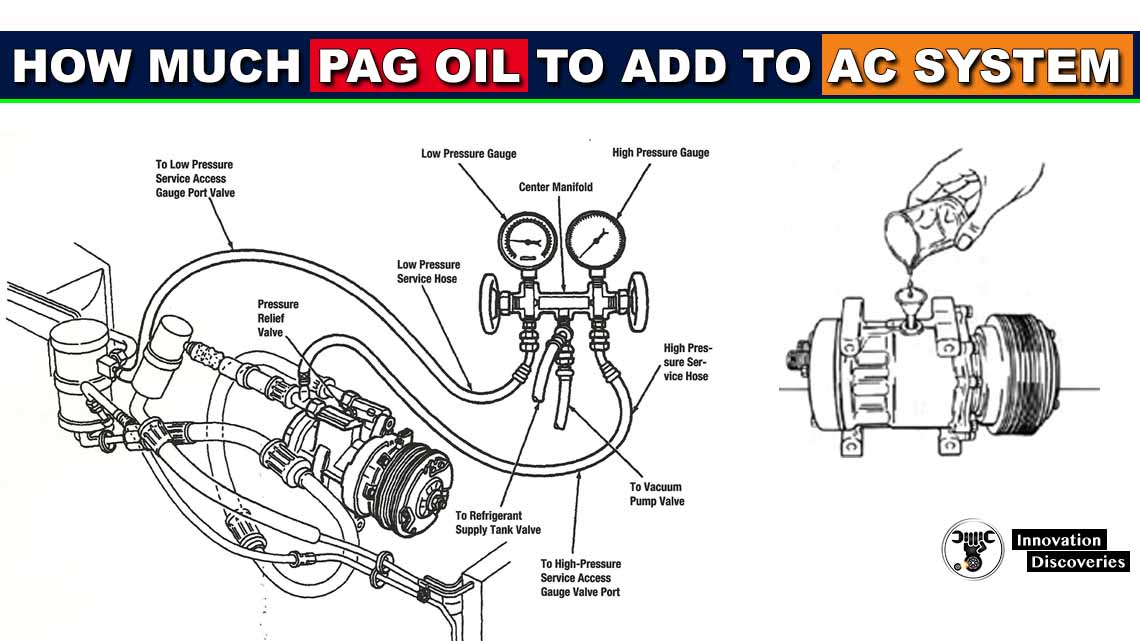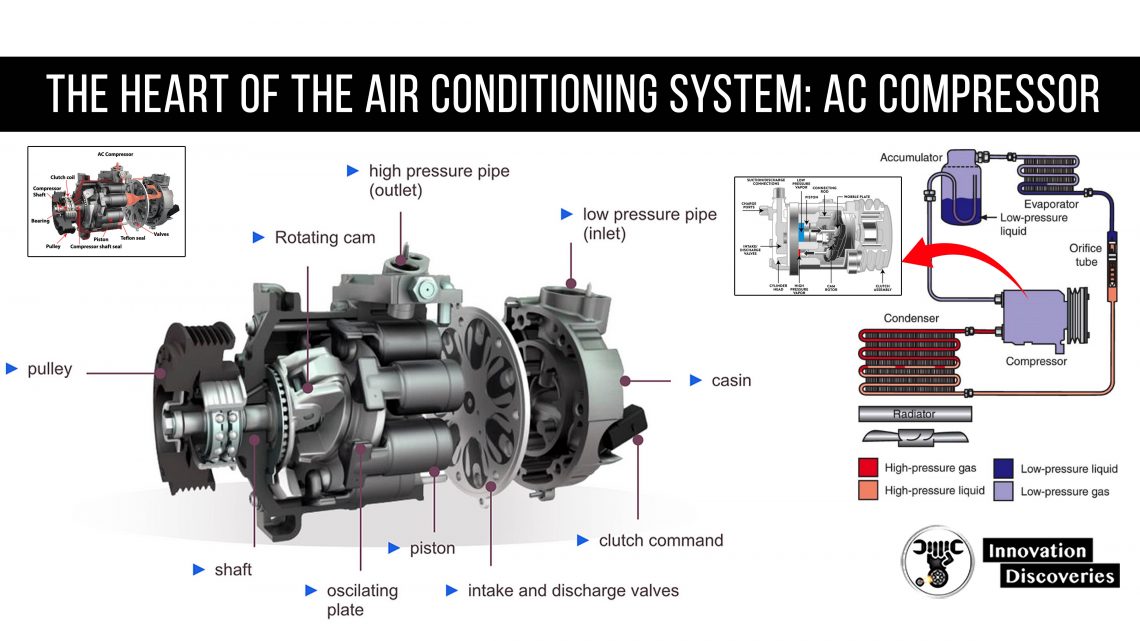
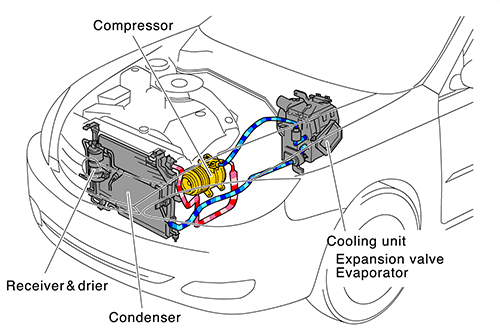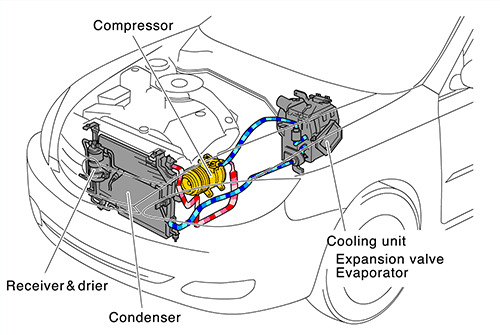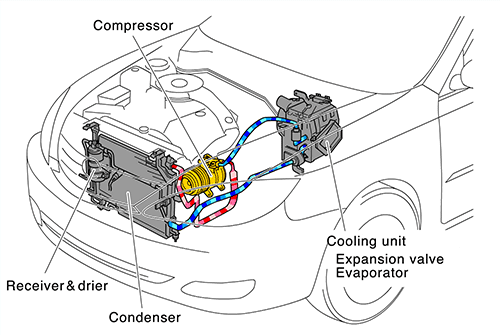
The compressor plays the most important role in the car cooling system. Owing to this element, the refrigerant and oil are distributed throughout the whole system.
The professionals claim that the compressor stands in for a heart in the bloodstream, and this analogy makes sense.
Compressor functions
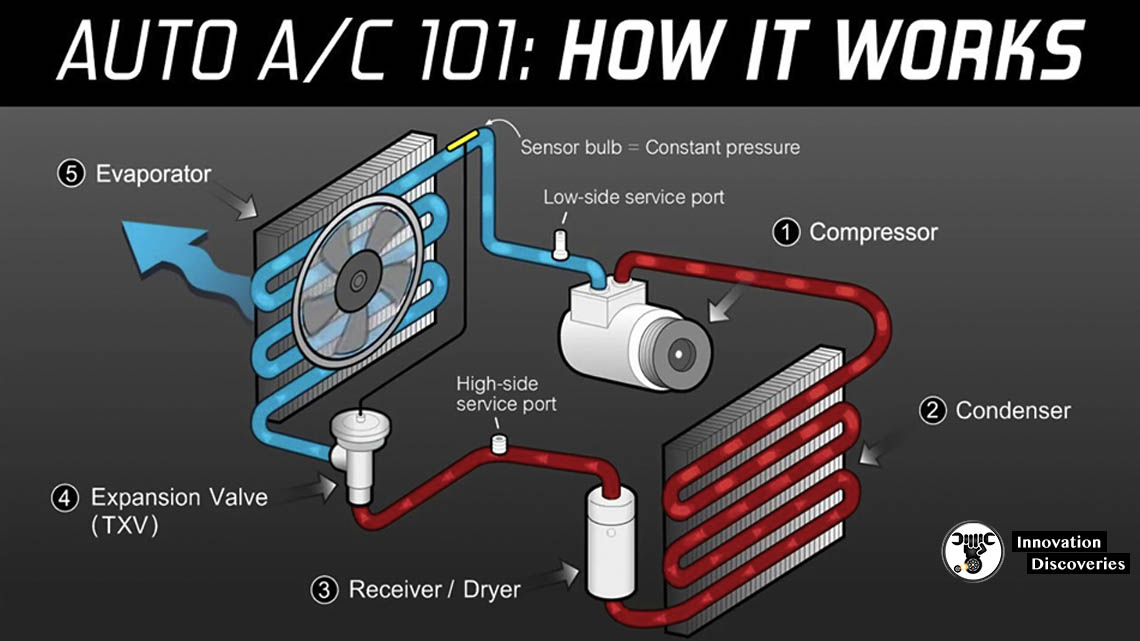
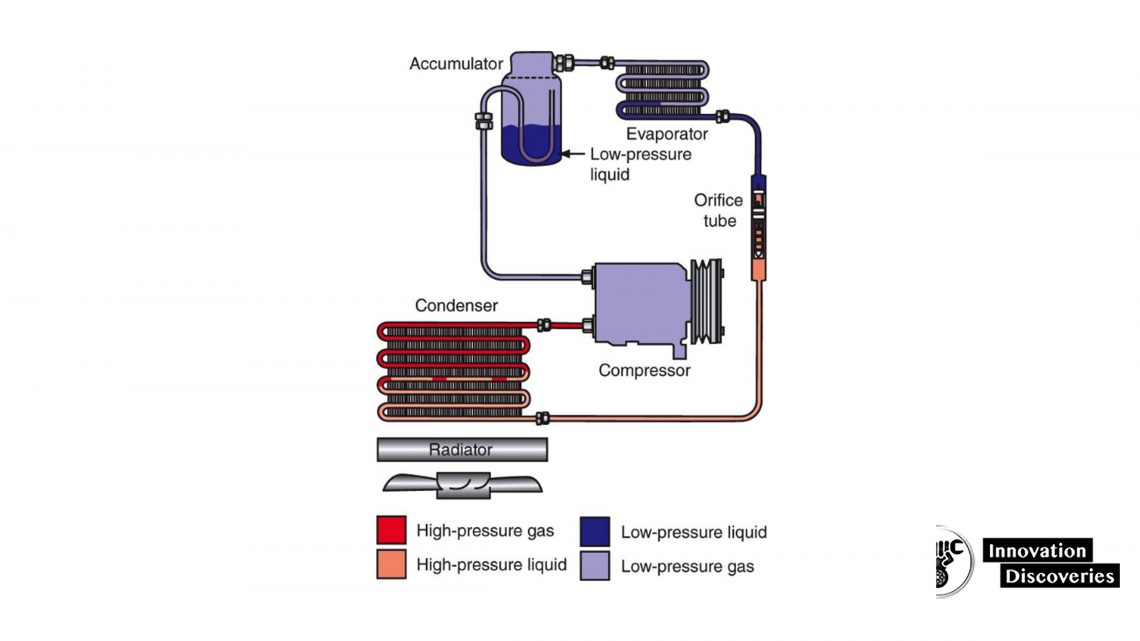
The task of the compressor is the distribution of the refrigerant in the air conditioning system. It is possible due to the pressure differences.
The compressor sucks in the gas refrigerant from the intake of the evaporator and, due to the compression, raises its pressure and transports it to the condenser, where the gas refrigerant turns into a liquid.
The transport of the oil in the refrigerant is also an important role played by the compressor.
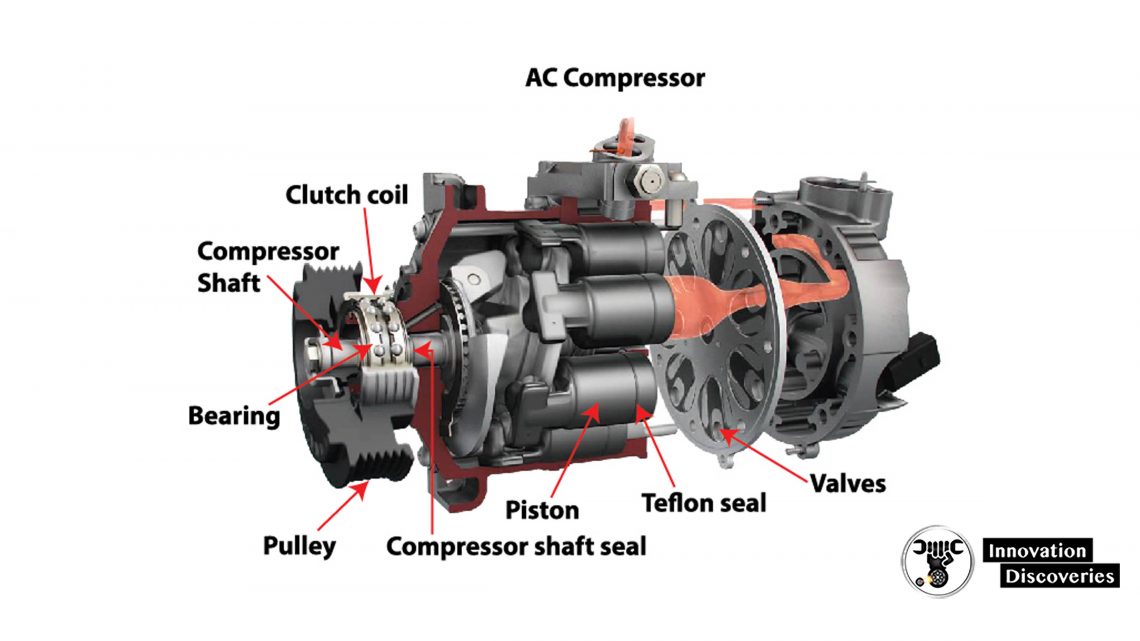
The design of the air conditioning compressor
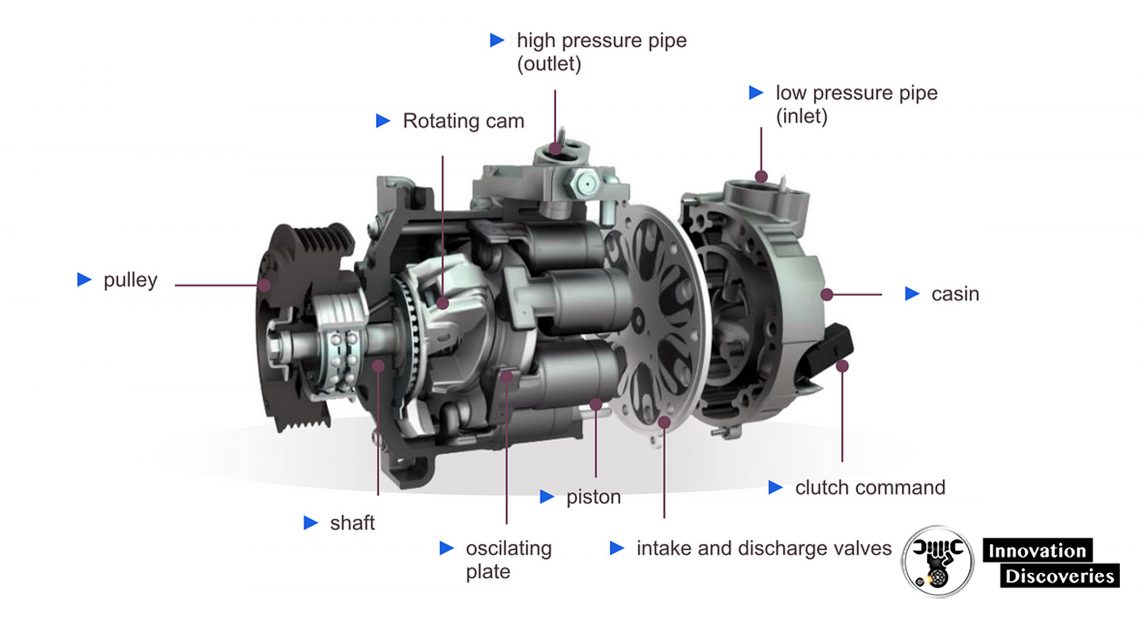
The image above shows the basic construction of the piston-type compressor with a swash plate.
It is the most commonly used solution. The work of the piston-type compressors consists of the transformation of the rotational movement of the shaft into the linear movement of the pistons.
The torque is transmitted from the engine via the pulley in the drive system.
The compressor may be equipped with a traditional clutch or an electronic control valve (see the image)—this solution is most often used nowadays.
Types of compressors
When comparing the latest car models with the older ones, most drivers will probably be able to see the difference in the functioning of the air conditioning systems.
The latter construction entailed a perceptible jerk and lowering of the engine speed when the air conditioning was turned on.
Similarly, when the fan was off, the reduction of the load on the unit could be felt.
Newer constructions do not generate such a problem, because of the evolution of the compressor.
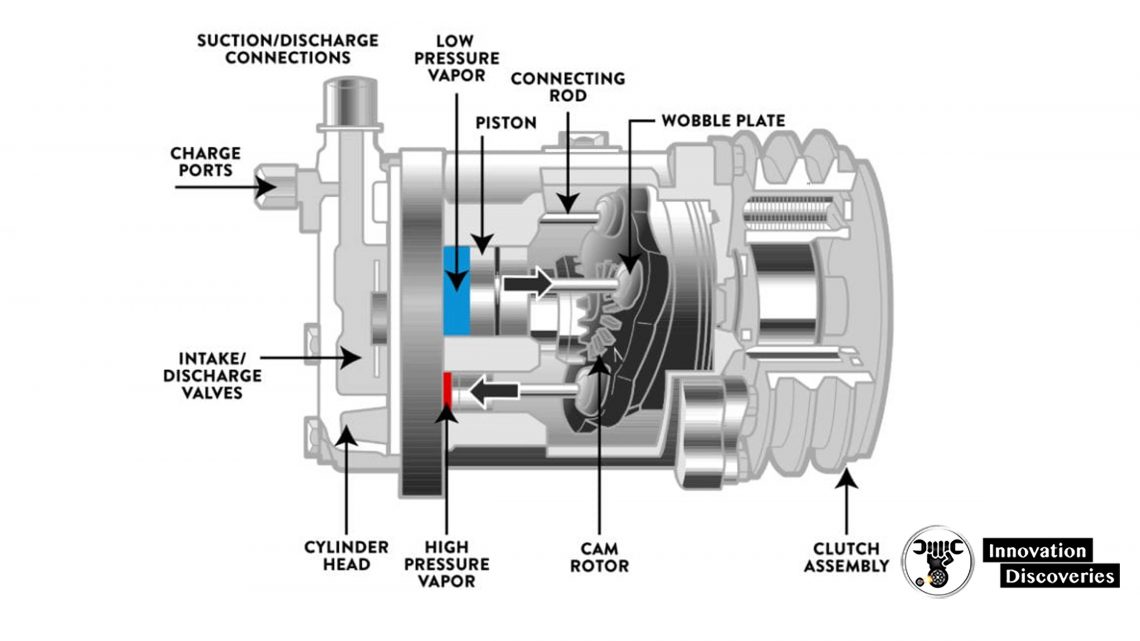
In short, there are two types of compressors with a swash plate technology: constant and variable capacity.
In the case of the constant capacity compressors, the oscillating plate remains at the same angle independent of the usage conditions.
- This variant cannot adjust the cooling power of the system precisely, and only the complete compressor shutdown cycles are possible.
- The pistons work constantly, inducing the flow of the refrigerant. The compressor is enabled via the electromagnetic clutch pulley.
- In this solution, the compressor efficiency depends on the rotary speed transmitted to the pulley.
- This angle is variable and is responsible for the operation of the piston. It depends on the energy requirements and the pressure and temperature at the inlet of the compressor shell.
- The greater the need for cold, the larger the cylindrical capacity – the maximum plate angle equals the maximum piston stroke.
The position of the oscillating plate is controlled by a valve.
This valve may be controlled internally using a pressure-sensitive element, or by an external electro-valve controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU).
Externally controlled compressors have much better control over the piston movement and, consequently, better temperature control.
READ MORE
DOWNLOAD
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website