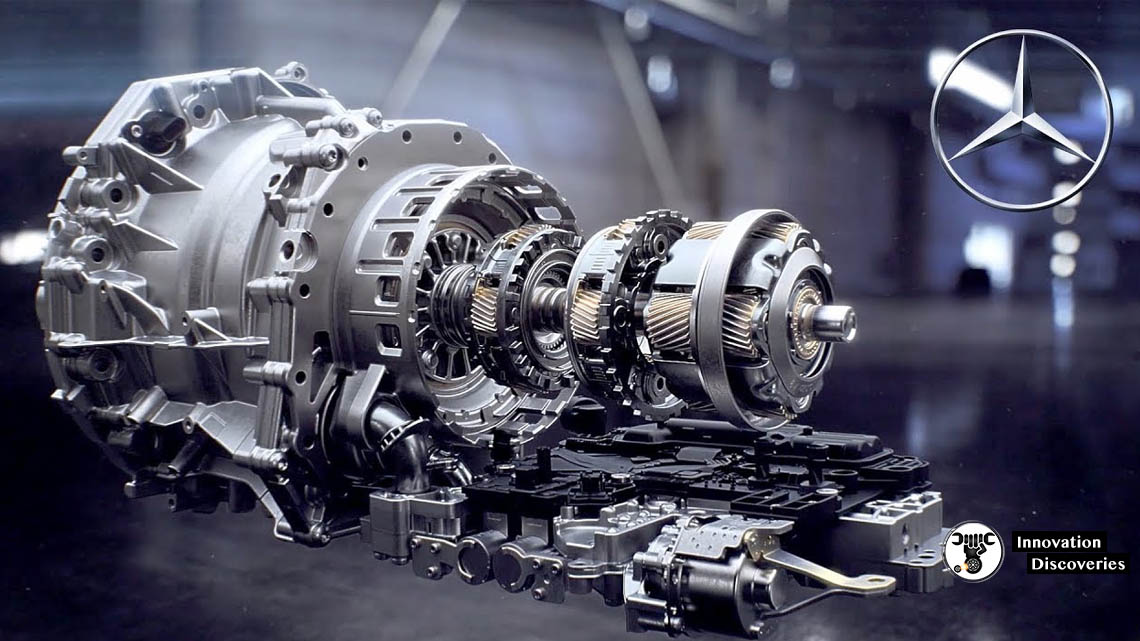
Introduction to Torque Converters
Torque converters are essential components in modern automatic transmissions, bridging the gap between the engine and the transmission. They play a crucial role in ensuring smooth power transfer, enhancing vehicle performance and efficiency.
How Torque Converters Work
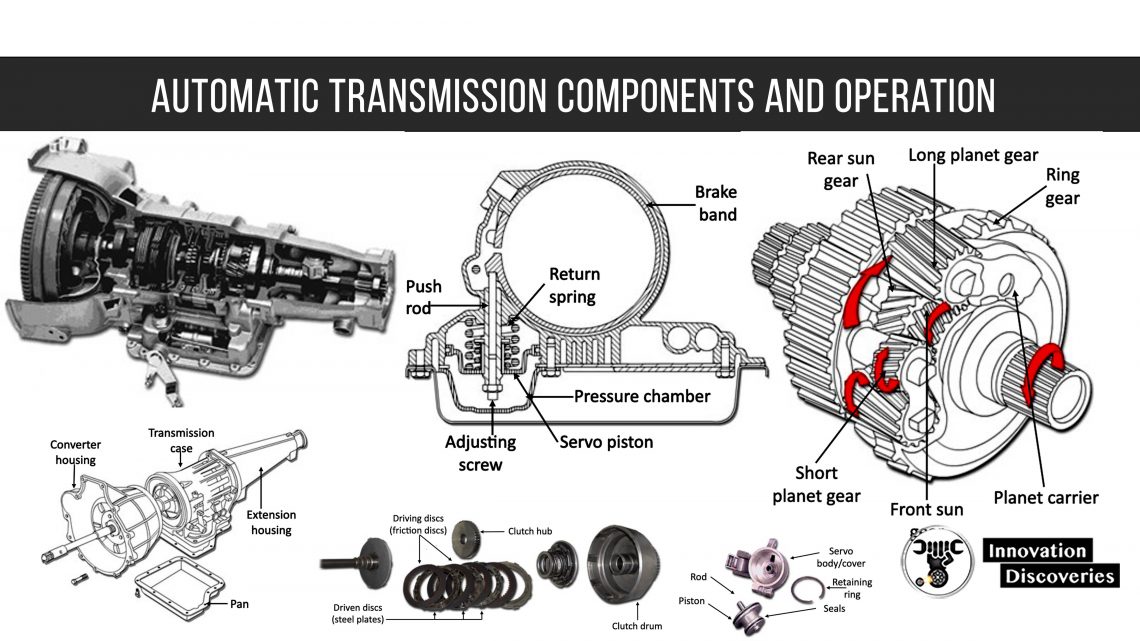
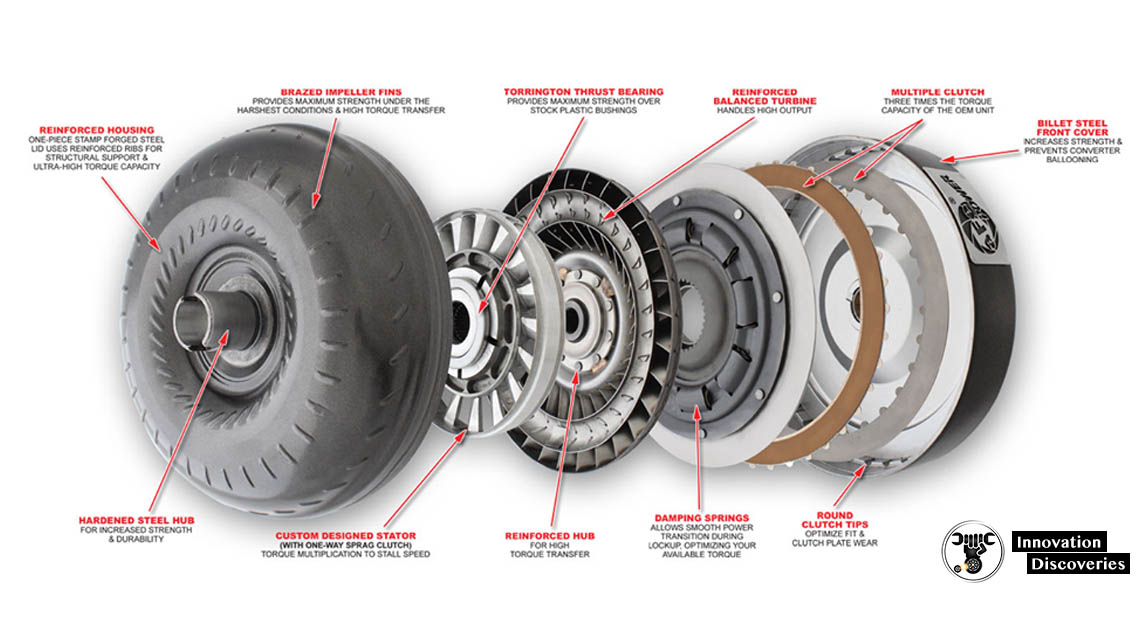
At its core, a torque converter functions on the principles of fluid dynamics to transfer rotational power from the engine to the transmission. It consists of three main components: the impeller (or pump), the turbine, and the stator.
- Impeller: Connected to the engine, it spins with engine rotation, pushing transmission fluid outward.
- Turbine: Connected to the transmission, it receives fluid from the impeller, causing it to spin and transfer power to the transmission.
- Stator: Positioned between the impeller and turbine, it redirects fluid returning from the turbine to the impeller, increasing efficiency and torque multiplication.
When the engine is idling, the torque converter allows the vehicle to stay stationary. As the engine speed increases, the impeller spins faster, and the fluid force grows, causing the turbine to rotate and transmit power to the transmission, propelling the vehicle forward.
Types of Torque Converters
There are several types of torque converters, each suited to different applications:
- Single-Stage Torque Converters: Commonly used in passenger vehicles, they provide a balance of efficiency and performance.
- Multi-Stage Torque Converters: Found in heavy-duty applications like trucks and industrial machinery, offering higher torque multiplication.
- Lock-Up Torque Converters: Equipped with a clutch mechanism that locks the impeller and turbine together at higher speeds, eliminating slip and improving fuel efficiency.
History and Evolution
The concept of the torque converter dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements in the 1930s and 1940s. Early designs were rudimentary, but continuous innovation led to the highly efficient and reliable torque converters used today.
Torque Converters in Different Vehicles
- Cars: In most passenger vehicles, torque converters enable smooth and efficient automatic transmission operation, contributing to a comfortable driving experience.
- Trucks and Heavy Machinery: In these applications, torque converters handle high torque loads, essential for towing and heavy lifting.
- Marine and Industrial Applications: Torque converters are crucial in marine propulsion and various industrial machines, ensuring efficient power transfer under demanding conditions.
Comparisons and Alternatives
- Torque Converters vs. Manual Clutches: While manual clutches offer direct engagement, torque converters provide seamless power transfer and better handling of variable loads.
- Torque Converters vs. Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCTs): DCTs offer faster shifting and efficiency but are more complex and costly. Torque converters provide a smoother driving experience, especially at low speeds.
Common Problems and Solutions
Torque converters, like any mechanical component, can experience issues:
- Shuddering or Vibration: Often caused by contaminated fluid or worn components. Regular maintenance can prevent this.
- Overheating: May occur due to low fluid levels or blocked cooling lines. Ensuring proper fluid levels and clean lines is crucial.
- Slipping: Indicated by a loss of power transfer, usually due to worn-out internal parts or low fluid pressure. Prompt repair or replacement is necessary.
Maintenance Tips
Maintaining a torque converter involves regular checks and fluid changes:
- Fluid Quality: Use manufacturer-recommended fluid and change it at specified intervals.
- Leaks: Regularly inspect for leaks and address them promptly.
- Performance Checks: Monitor for signs of slipping, shuddering, or overheating and take corrective action if needed.
Performance Upgrades
For performance enthusiasts, upgrading a torque converter can enhance vehicle acceleration and responsiveness:
- Stall Speed Adjustment: Higher stall speed converters improve launch performance.
- Aftermarket Converters: Designed for specific performance needs, they can provide significant gains in acceleration and power delivery.
Future Trends
With the rise of electric and hybrid vehicles, torque converter design is evolving. While electric vehicles don’t require traditional torque converters, hybrid systems often incorporate them for improved efficiency and power management.
Technical Deep Dives
Understanding the intricate mechanics of torque converters involves exploring the role of each component:
- Stator: Enhances torque multiplication by redirecting fluid flow.
- Clutch Mechanisms: In lock-up converters, clutches reduce slip and improve efficiency.
Torque Converter Fluid
Using the correct fluid is vital for optimal performance:
- Fluid Type: Always use the fluid type recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Change Frequency: Regularly changing the fluid ensures the longevity and efficiency of the torque converter.
Torque Converters in Racing
In racing, torque converters are tailored for high-performance applications:
- High Stall Speed: Improves launch and acceleration.
- Reinforced Components: Ensure durability under extreme conditions.
Economics and Cost
Torque converters are a significant part of vehicle manufacturing costs:
- Production Cost: High precision and quality materials increase production costs.
- Repair and Replacement: Regular maintenance can reduce long-term costs, but repairs and replacements can be expensive.
Environmental Impact
Manufacturing and disposing of torque converters have environmental implications:
- Recyclability: Many components can be recycled, reducing environmental impact.
- Manufacturing Practices: Adopting greener practices in production can mitigate environmental harm.
Conclusion
Torque converters are indispensable in modern vehicles, providing smooth and efficient power transfer. Understanding their operation, maintenance, and potential upgrades can enhance vehicle performance and longevity.
As automotive technology evolves, so will torque converter designs, ensuring they remain a crucial component in the automotive industry.
Discover More:
TORQUE CONVERTER: FUNCTIONS, PARTS, WORKING PRINCIPLES, AND TYPES
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website