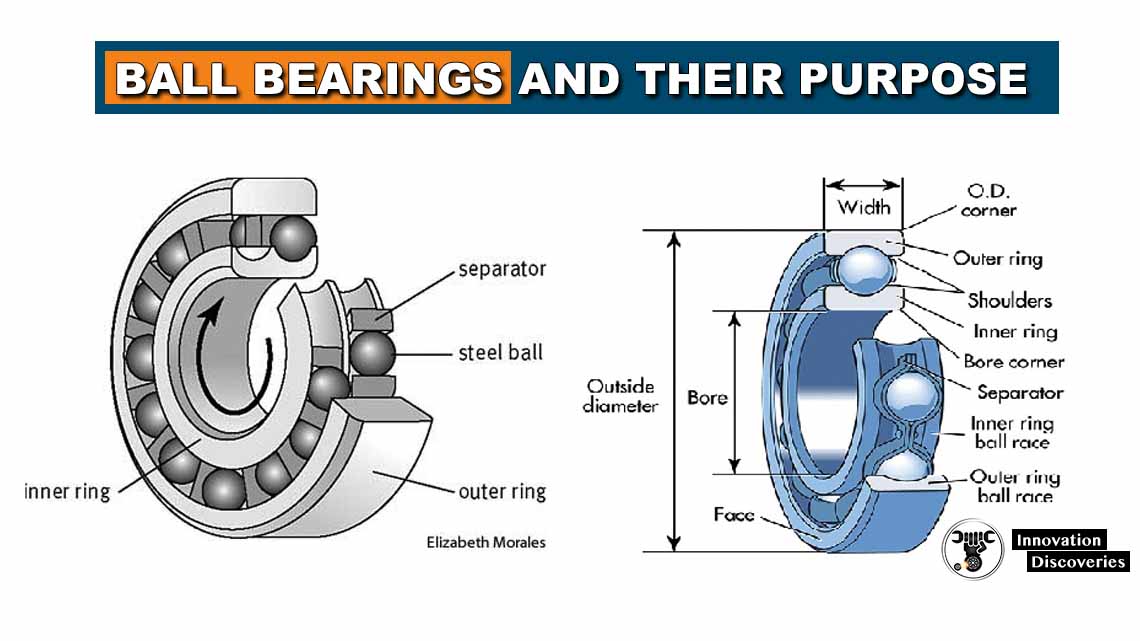
Ball bearings are mechanical devices that play a crucial role in various industries and applications. They are designed to reduce friction and facilitate smooth rotational or linear movement between two or more parts.
This article provides an overview of ball bearings, their construction, working principles, and their significance across different sectors.
Understanding Ball Bearings:
Ball bearings are precision-engineered components composed of an inner and outer ring, a set of balls, a cage to separate the balls, and, in some cases, additional features such as seals or shields.
These bearings are typically made from high-quality steel, although alternative materials like ceramic or stainless steel may be used for specific applications.
The Purpose of Ball Bearings:
The primary purpose of ball bearings is to enable smooth and efficient rotation between two or more parts. They achieve this by minimizing friction and distributing the load evenly, thus reducing wear and tear on the components involved.
The benefits of using ball bearings include:
1. Reducing Friction:
Ball bearings operate on the principle of rolling motion rather than sliding, resulting in significantly lower friction. This allows for smooth rotation and minimizes energy loss due to heat generation.
2. Load Distribution:
Ball bearings are capable of handling both radial loads (forces perpendicular to the shaft) and axial loads (forces parallel to the shaft). The design and arrangement of the balls in the bearing ensure that the load is distributed evenly, enhancing the overall efficiency and longevity of the system.
3. Accuracy and Precision:
Ball bearings offer high rotational accuracy, making them ideal for applications that require precise movement, such as machine tools, robotics, and automotive components. Their low friction and precise operation contribute to the overall performance of these systems.
4. Noise and Vibration Reduction:
By minimizing friction and maintaining smooth movement, ball bearings help reduce noise and vibration, enhancing user comfort and preventing potential damage to the surrounding machinery.
Types of Bearings:
- Ball Bearing
- Roller Bearing
- Ball Thrust Bearing
- Roller Thrust Bearing
- Tapered Roller Bearing
- Specialized Bearing

Also, read:
Bearing | Types, Applications, Failures, Selection, Advantages [Full Guide]
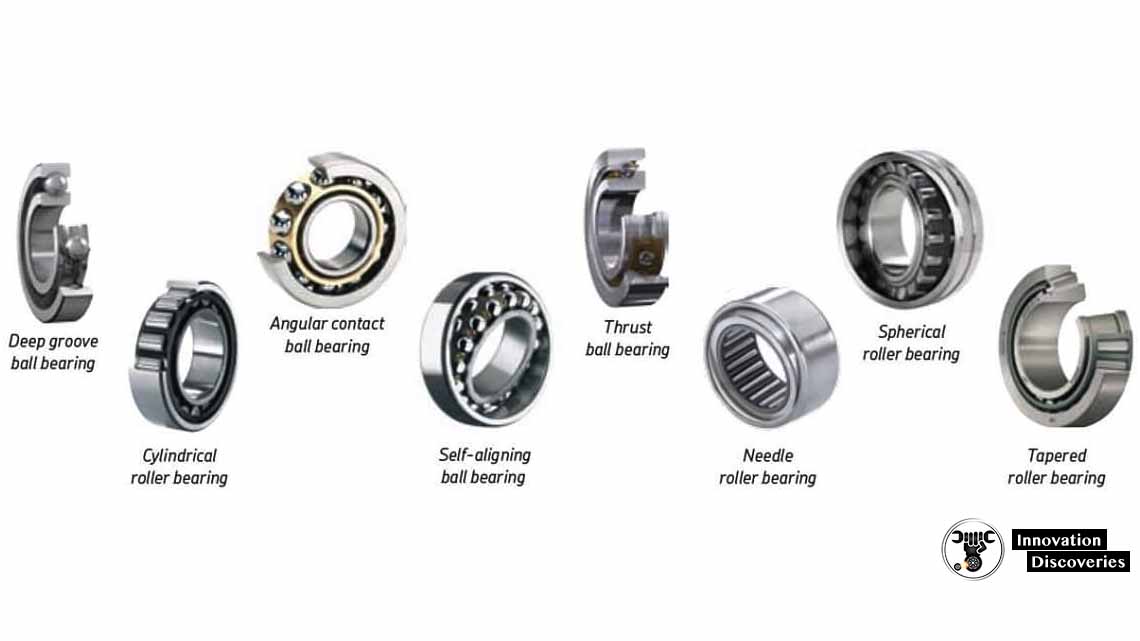
Types of Ball Bearings
There are various types of ball bearings, each designed for specific applications. Some common types include:
1. Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
These bearings have a deep groove design, enabling them to handle both radial and axial loads. They are widely used in applications such as electric motors, appliances, and automotive components.
2. Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Angular contact bearings are designed to withstand both radial and axial loads simultaneously. They are commonly found in machinery that requires high-speed rotation and axial load support, such as machine tool spindles.
3. Thrust Ball Bearings:
Thrust ball bearings are designed to handle axial loads only. They consist of two washers and a set of balls held in a cage. These bearings are used in applications where axial load support is critical, such as automotive transmissions.
Watch video below
Purpose of ball bearing
Conclusion
Ball bearings are essential components in numerous industries, providing smooth rotational or linear motion while minimizing friction, wear, and energy loss.
Their ability to handle different types of loads, precise operation, and noise reduction make them indispensable in applications ranging from automotive and aerospace to industrial machinery and household appliances.
By understanding the types and purpose of ball bearings, engineers and users can select the most appropriate bearing for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of their systems.





One Comment