Introduction:
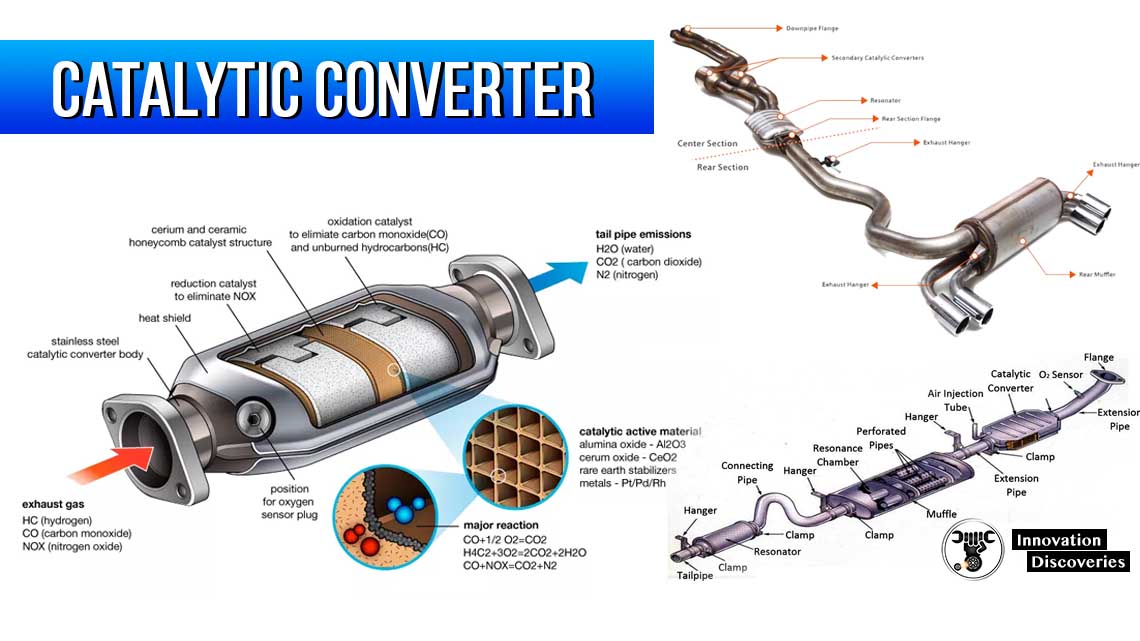
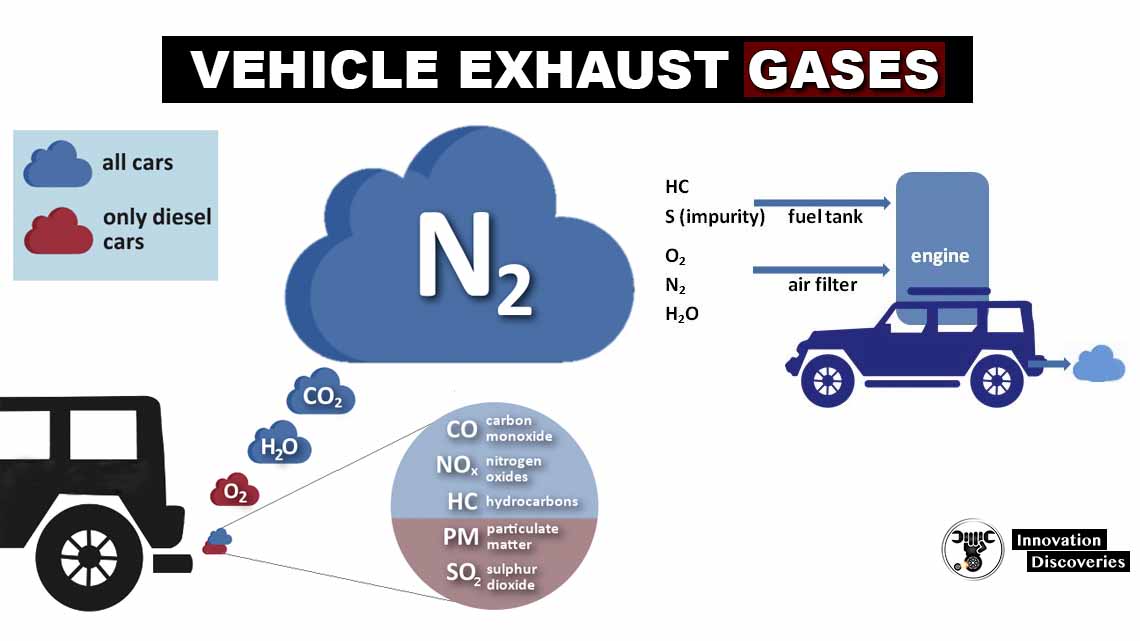
The catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. Its primary function is to convert harmful gases produced by the engine into less harmful emissions before they are released into the atmosphere. Over time, a catalytic converter can become clogged or go bad, resulting in various symptoms and potential performance issues.
In this article, we will discuss six common symptoms of a clogged or bad catalytic converter, its causes, replacement cost, testing methods, cleaning possibilities, and whether a faulty catalytic converter holds any value.
Where Is It Located?
The catalytic converter is typically located in the exhaust system, between the engine and the muffler. Its exact position may vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
Symptoms of a Clogged or Bad Catalytic Converter
1. Illuminated Check Engine Light:
One of the most common signs of a clogged catalytic converter is an illuminated check engine light on the vehicle’s dashboard. The onboard diagnostic system detects an issue with the emissions system and triggers the light.
However, it’s important to note that other problems can also cause the check engine light to turn on, so further diagnosis is necessary.
2. Starting Difficulties:
A clogged or failing catalytic converter can restrict the flow of exhaust gases, which may lead to difficulties in starting the engine. This symptom is more noticeable after the vehicle has been parked for a while, such as overnight.
3. Reduced Engine Performance:
A clogged catalytic converter can restrict the flow of exhaust gases, affecting the engine’s performance. You may experience a decrease in power, acceleration, and overall responsiveness of the vehicle.
4. Dwindling Fuel Economy:
A clogged catalytic converter can also result in reduced fuel efficiency. Since the exhaust gases are not properly flowing through the converter, the engine may have to work harder, leading to increased fuel consumption.
5. Odd Rattling Noises:
A failing catalytic converter can produce unusual rattling or metallic noises. This sound typically occurs when the ceramic catalyst inside the converter breaks apart or becomes loose due to excessive heat or other factors.
6. Failed Emissions Testing:
During emissions testing, a clogged catalytic converter will not effectively reduce the emissions to meet the required standards. This can result in a failed emissions test, which may prevent the vehicle from being legally driven on the road until the issue is resolved.
What Causes a Catalytic Converter to Clog Up or Go Bad?
Several factors can lead to the clogging or failure of a catalytic converter. Some common causes include:
1. Engine Misfires:
Continuous engine misfires can cause unburned fuel to enter the catalytic converter, leading to its deterioration over time.
2. Oil or Coolant Contamination:
If oil or coolant leaks into the exhaust system, it can contaminate the catalytic converter and cause damage.
3. Fuel Additives:
Certain fuel additives or using the wrong type of fuel can contribute to catalytic converter problems.
4. Physical Damage:
The catalytic converter can be physically damaged by hitting speed bumps or driving over rough terrain, causing blockages or internal damage.
5. Catalytic Converter Replacement Cost:
The cost of replacing a catalytic converter can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of the vehicle, the location of the catalytic converter, and the labor costs at the repair shop. On average, the replacement cost can range from $500 to $2,500 or more.
How to Test for a Clogged Catalytic Converter
There are several methods to test for a clogged catalytic converter:
1. Diagnostic Scan:
A mechanic can use a diagnostic scan tool to check for any error codes related to the catalytic converter or emissions system.
2. Backpressure Test:
By measuring the exhaust system’s backpressure, technicians can determine if there is an obstruction in the catalytic converter.
3. Temperature Test:
Infrared thermometers or thermal imaging cameras can be used to check the temperature of the catalytic converter. A significant temperature difference between the inlet and outlet can indicate a clog.
4. Removal and Inspection:
In some cases, the catalytic converter may need to be physically removed and inspected for blockages or internal damage.
Can a Clogged Catalytic Converter Be Cleaned?
In general, a clogged catalytic converter cannot be effectively cleaned. If it is severely clogged or damaged, replacement is usually the recommended solution.
Can a Bad Catalytic Converter Be Fixed?
When a catalytic converter goes bad, it cannot be easily fixed. It is a complex component that requires replacement if it is clogged, damaged, or not functioning properly.
Is a Bad Catalytic Converter Worth Anything?
Although a faulty catalytic converter may no longer serve its intended purpose, it can still hold value due to the precious metals present inside, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals can be recycled and used for various industrial applications. However, it is illegal and environmentally harmful to tamper with a catalytic converter or remove it without proper authorization.
Conclusion:
A clogged or bad catalytic converter can lead to various symptoms and performance issues in a vehicle. It is important to address these problems promptly to maintain engine efficiency, pass emissions testing, and comply with environmental regulations. If you suspect a clogged catalytic converter, it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic who can diagnose the issue accurately and recommend the appropriate course of action, which may include catalytic converter replacement.
Discover More
Read: DIRECT INJECTION CARBON BUILD UP: SYMPTOMS AND PREVENTIVE MEASURES
Also, read: DIESEL BLACK SMOKE: REASONS AND SOLUTIONS
Diesel Particulate Filter
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website