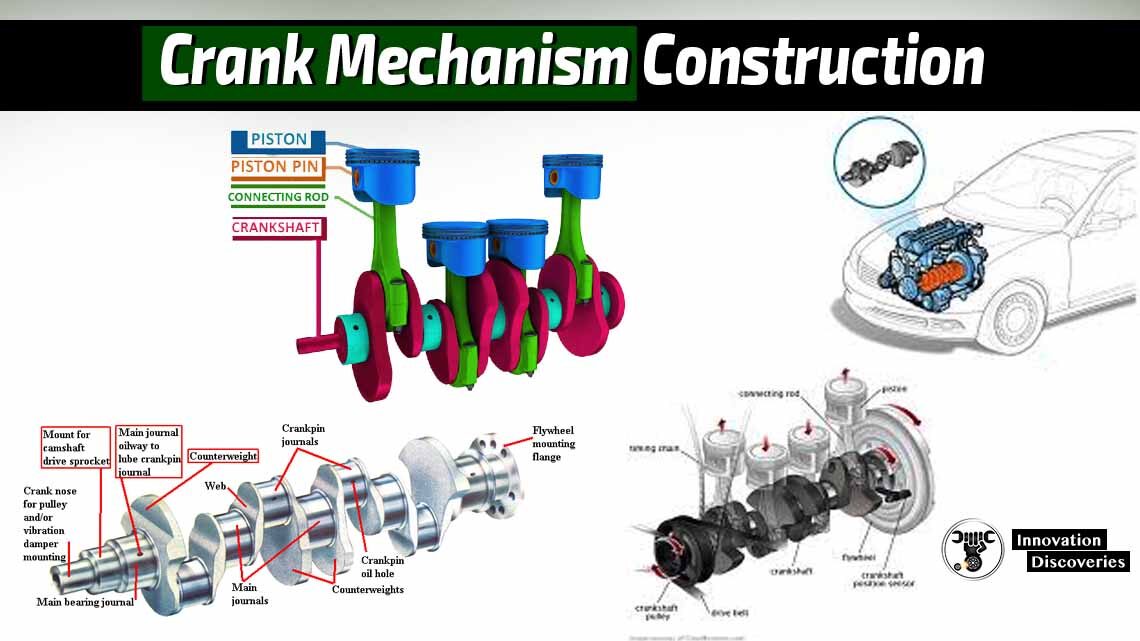
The purpose of a crank mechanism – transforming back-and-forth motion of the pistons to the crankshaft rotation.
Components of the crank mechanism can be a divide into two groups: stationary and moving.
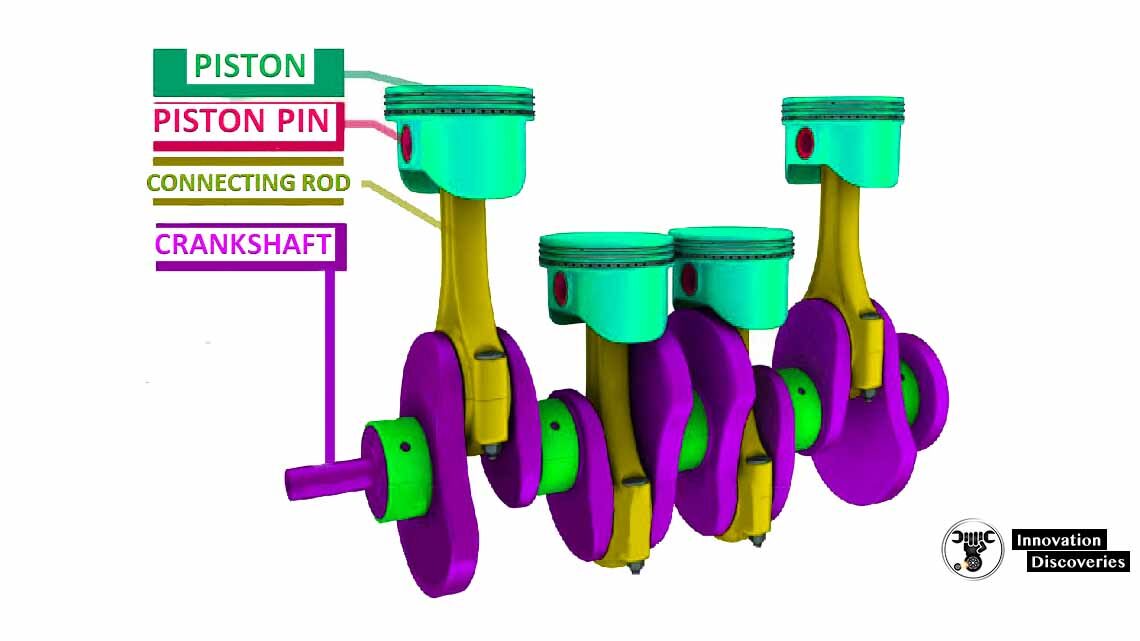
Moving components of crank mechanism: pistons, piston rings, piston pins, connecting rods, flywheel, crankshaft.
Also, read – PISTON AND PISTON RINGS
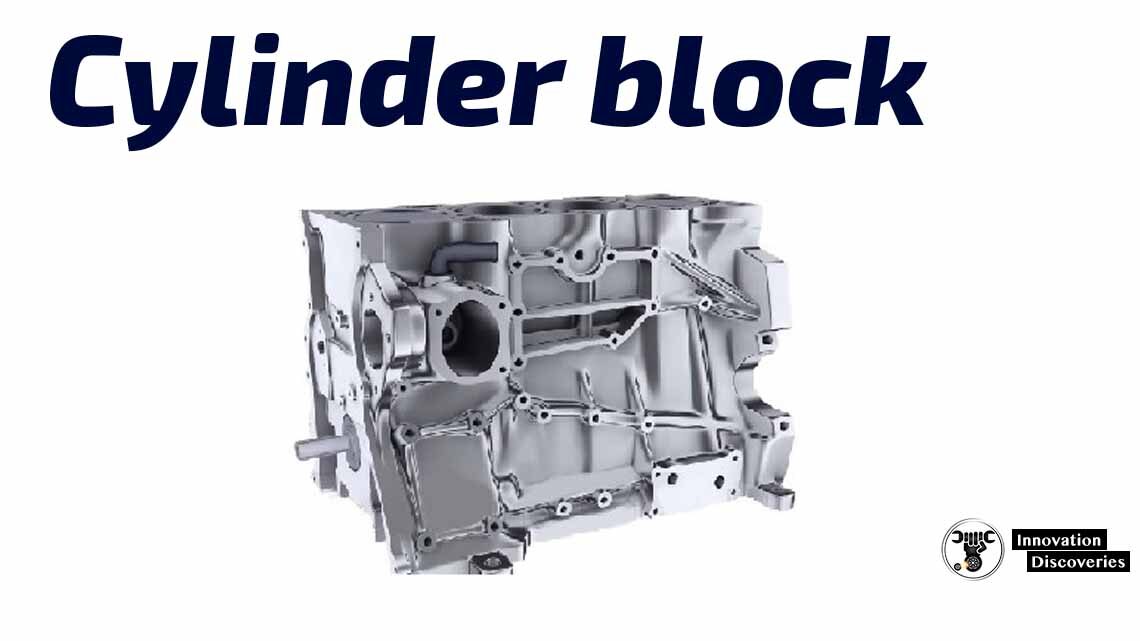
Stationary components of crank mechanism: engine cylinder block, engine head block, cylinders, sump.
Also, read – WHAT IS AN ENGINE BLOCK?
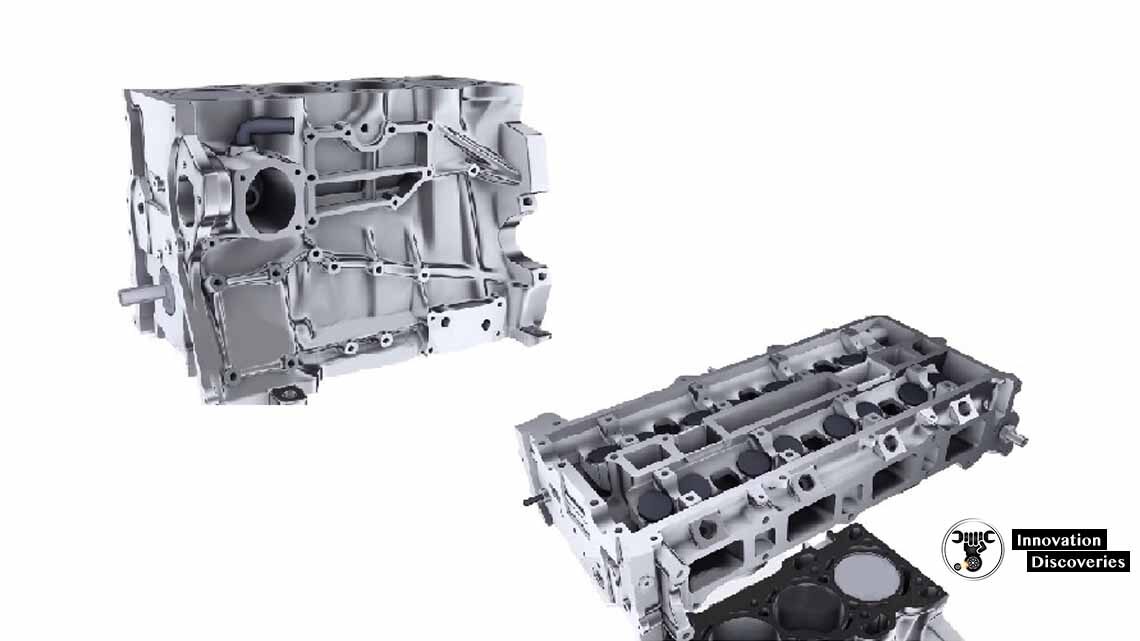

Stationary engine parts
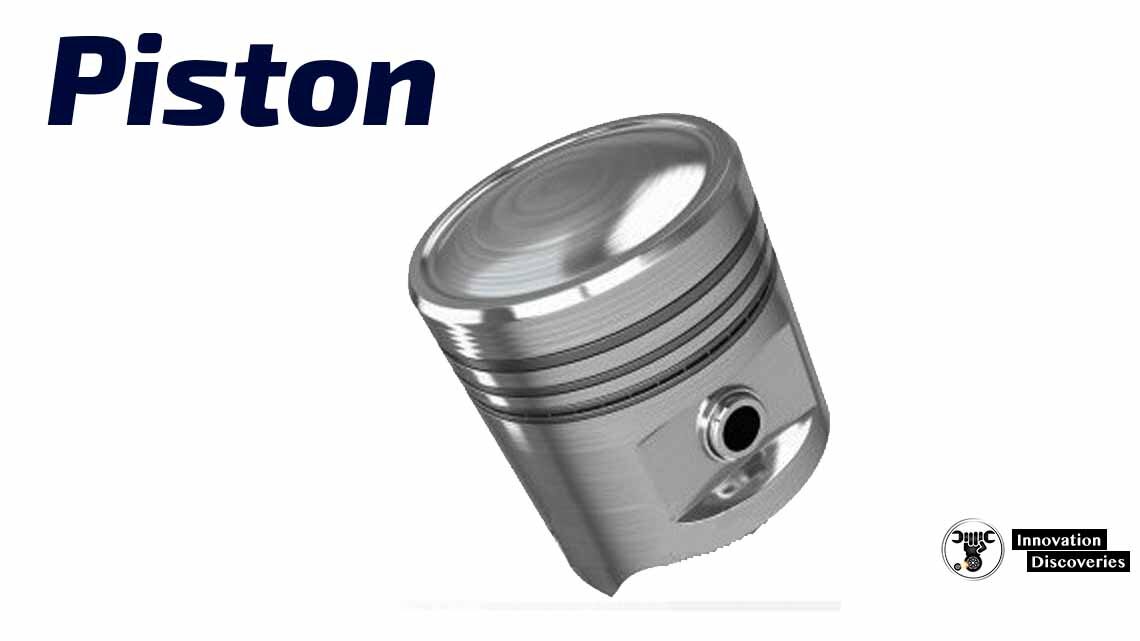
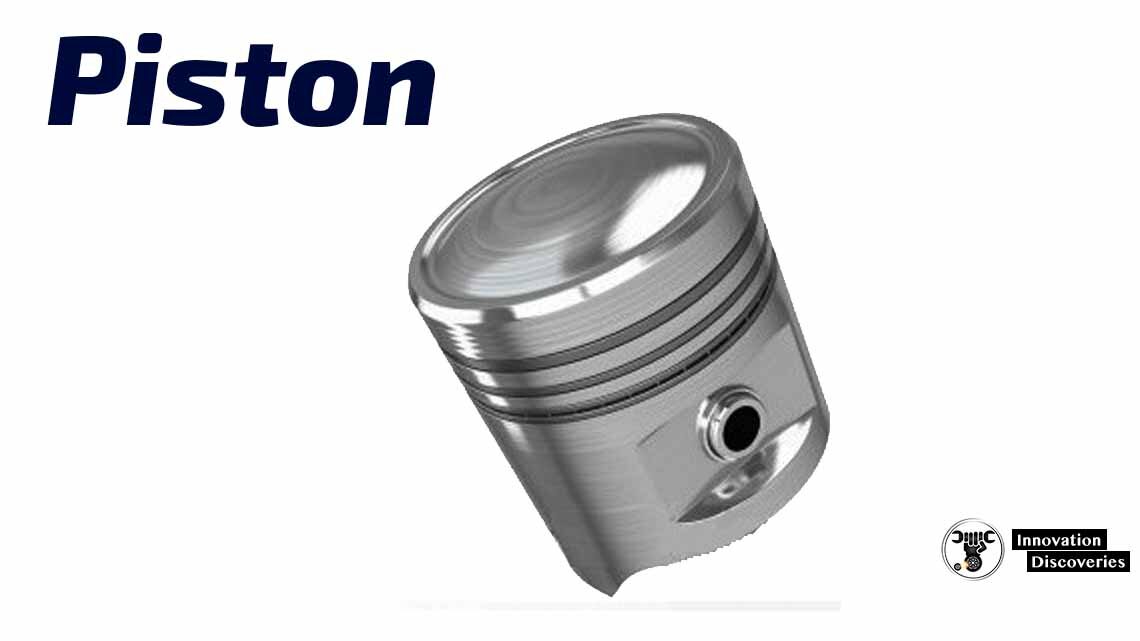
Piston – is a component of an internal combustion engine. Purpose of the piston is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft through a connecting rod.
Also, read – IC ENGINE: COMPONENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS, TYPES, AND TERMINOLOGY

A piston ring is a split ring that fits into a groove on the outer diameter of the piston in an internal combustion engine.

Connecting rod – is a member, which connects a piston to a crankshaft in a reciprocating engine.

Crankshaft – is a mechanical part that performs a conversion between reciprocating motion piston and connecting rod to rotational motion. When crankshaft defecting is not possible to avoid costly repair, so you can see crankshaft repair cost here.

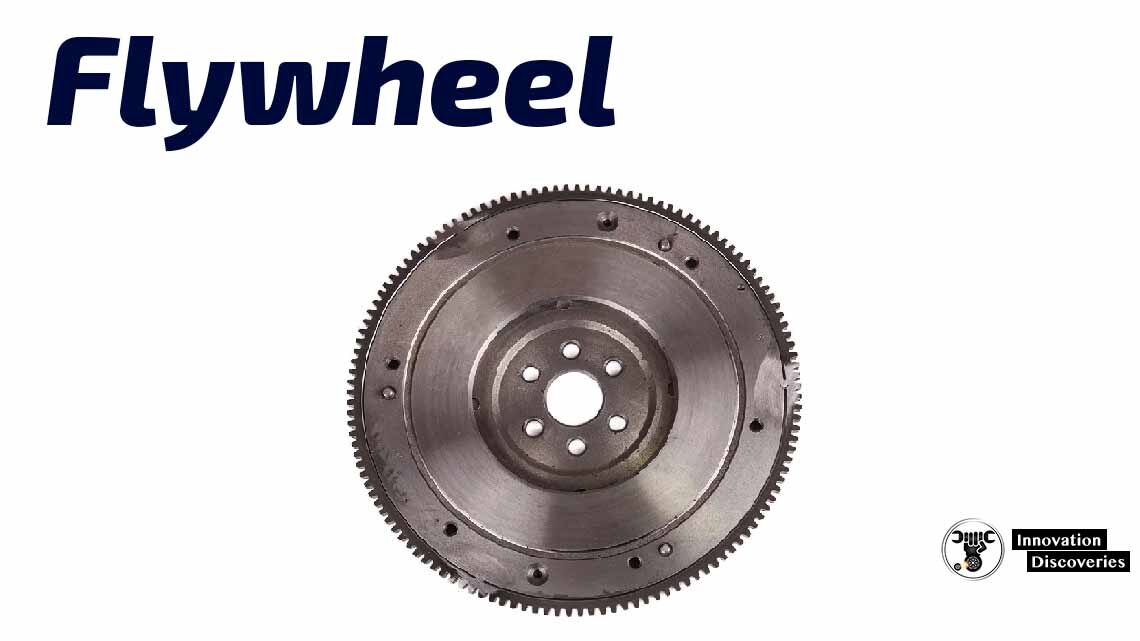
The flywheel is – a mechanical device designed to efficiently store crankshaft rotational energy.

The engine cylinder block is – the structure, which contains the cylinders, and other parts, of an internal combustion engine.
Engine cylinder head – sits above the cylinders on top of the cylinder block in an engine.

The cylinder is – the space in which the piston travels is the central working part of an engine.







One Comment