Tired of debating whether diesel or gasoline is better? Let’s settle the score once and for all. In this in-depth article, we explore the strengths and weaknesses of diesel and gasoline engines. From performance and maintenance to long-term reliability and upgrades, this guide helps you make an informed decision about your next vehicle.
Introduction: Diesel vs. Gasoline – The Great Debate
Imagine a tough diesel truck hauling a full load beside a nimble gasoline sedan darting through traffic. Both engines are built for different purposes—but which one is right for you?
As fuel prices, emissions standards, and technologies evolve in 2025, so does the need for clear understanding. Let’s decode the differences and explore the hidden strengths and weaknesses of diesel and gasoline engines.
🔧 Understanding Diesel Engines
What Is a Diesel Engine?
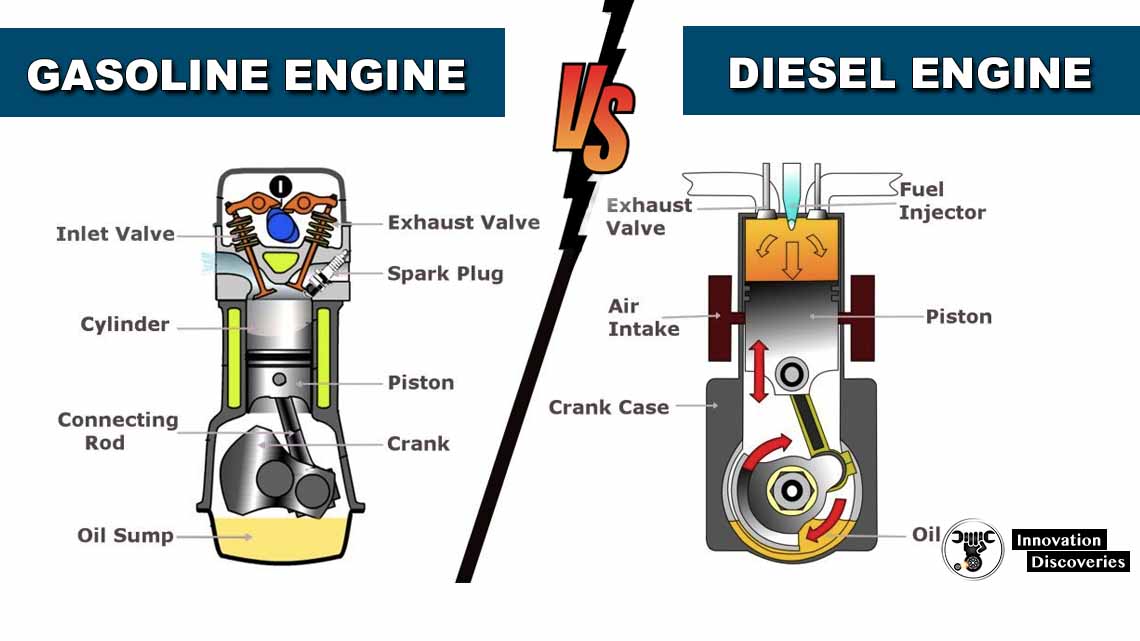
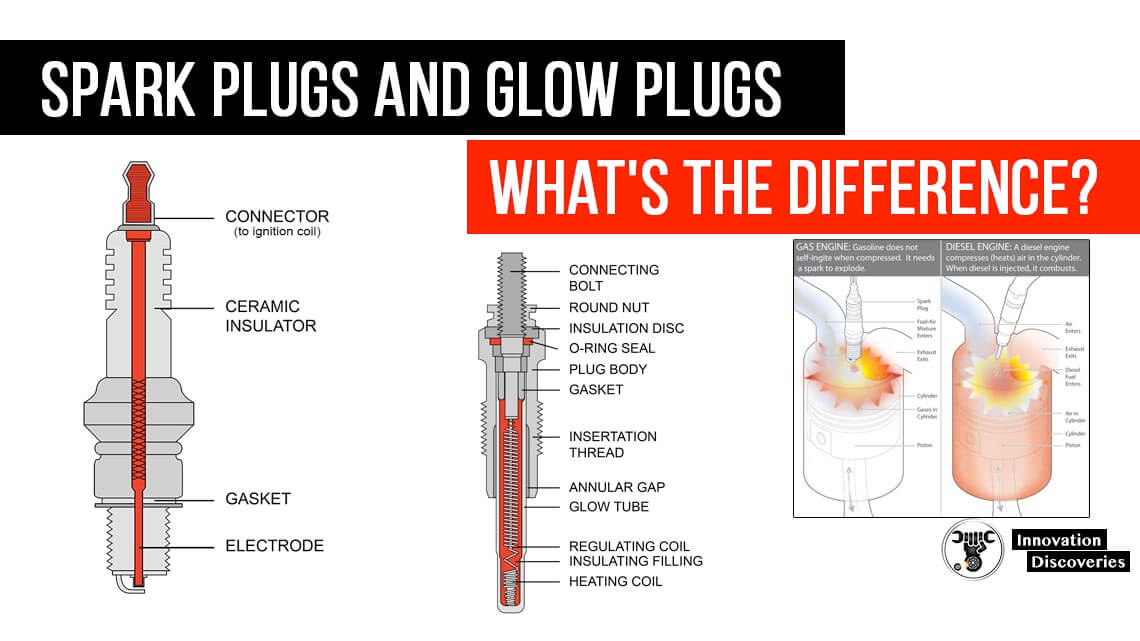
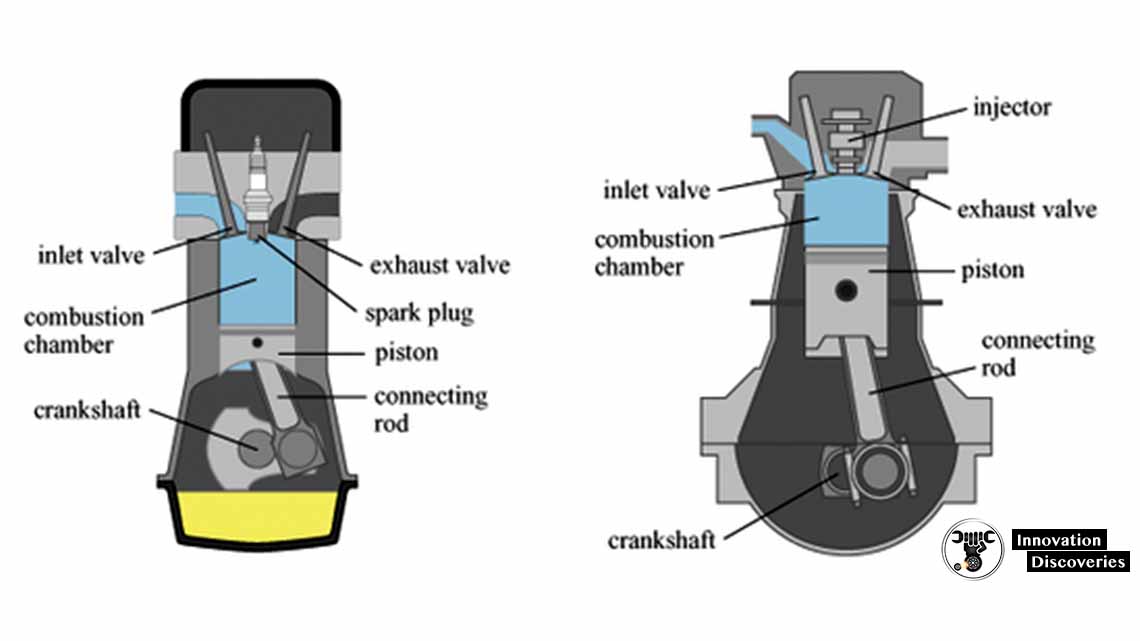
Diesel engines operate using compression ignition, where air is compressed until it’s hot enough to ignite fuel that is sprayed into the combustion chamber—no spark plugs involved.
✅ Diesel Engine Strengths
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel delivers 20–30% better fuel economy than gasoline.
- Torque Output: Diesel engines generate more torque at low RPMs, essential for heavy-duty applications like towing, hauling, and commercial transport.
- Durability: Diesel engines are engineered for longevity, often lasting 500,000+ km with proper care.
- Compression Ratio: Diesel engines typically have a higher compression ratio (14:1 to 25:1), resulting in more efficient energy extraction from fuel.
- Upgrades: Common diesel upgrades include performance chips, turbochargers, intercoolers, and exhaust system mods. These improve torque and fuel economy.
❌ Diesel Engine Weaknesses
- Higher Initial Cost: Due to stronger components and emission systems.
- Emissions: More NOx and particulates, though newer diesels use DPF and DEF to mitigate this.
- Noise & Vibration: Modern diesels are quieter, but still louder than gasoline engines.
- Maintenance: Fuel filters, glow plugs, and DEF systems can increase complexity.
⛽ Gasoline Engines: A Closer Look
How Do Gasoline Engines Work?
Gasoline engines use a spark ignition process, mixing air and fuel before compressing and igniting it with a spark plug.
✅ Gasoline Engine Strengths
- Smoother Operation: Quieter and more refined, ideal for everyday city driving.
- Power Output: Gasoline engines often produce higher horsepower at higher RPMs, making them more responsive.
- Lower Upfront Cost: More affordable to buy and maintain initially.
- Readily Available Fuel: Easy access almost everywhere.
- Upgrades: Turbo kits, ECU tuning, air intake systems, and exhaust mods are popular. Gasoline engines often cater better to performance tuning enthusiasts.
❌ Gasoline Engine Weaknesses
- Lower Fuel Efficiency: Burns more fuel per km.
- Lower Torque: Especially noticeable in towing or off-road scenarios.
- Compression Ratio: Typically ranges from 8:1 to 12:1, meaning less energy efficiency.
- Maintenance: More frequent oil changes, spark plug replacements, and higher wear due to operating at higher RPMs.
⚖️ How the Two Engines Differ (Side-by-Side Breakdown)
| Feature | Diesel Engine | Gasoline Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Diesel | Petrol/Gasoline |
| Ignition Type | Compression Ignition | Spark Ignition |
| Torque | High (especially at low RPMs) | Moderate to High (at higher RPMs) |
| Power Output (HP) | Lower but steady | Higher peak HP |
| Compression Ratio | 14:1 to 25:1 | 8:1 to 12:1 |
| Fuel Efficiency | 20–30% more efficient | Less efficient |
| Noise & Vibration | Louder, especially under load | Quieter, smoother ride |
| Reliability | Highly durable, fewer RPMs = less wear | Moderate, subject to wear at higher RPMs |
| Maintenance Costs | Costlier parts, but less frequent servicing | Cheaper parts, but more regular maintenance |
| Upgrade Potential | Torque upgrades (chips, turbo, exhaust) | HP-focused (turbo, ECU tuning, air intake) |
| Vehicle Type Suitability | Trucks, SUVs, Off-roaders, Long-distance | Sedans, hatchbacks, performance cars, hybrids |
The Future of Engines: Beyond Diesel and Gasoline
As sustainability becomes a global priority, many regions are encouraging transitions toward electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid technologies. Governments are tightening emission regulations, and automakers are innovating with clean combustion and fuel-saving technologies.
Yet, diesel and gasoline are far from obsolete—especially in 2025.
- Clean Diesel: Advanced DPF, SCR, and EGR systems are making diesel cleaner than ever.
- Turbocharged Gasoline Engines: Smaller, more powerful, and fuel-efficient.
Expect internal combustion engines to evolve further while EVs take center stage in urban environments.
🚘 Choosing the Right Engine: Based on Your Needs
Ask yourself:
- Do I drive long distances regularly?
- Do I need towing capability or carry heavy loads?
- Do I care more about fuel efficiency or ride comfort?
- What’s my budget for purchase and long-term maintenance?
Our recommendation:
- Choose Diesel if you need high torque, fuel efficiency, and long-term durability—especially for commercial, agricultural, or rural use.
- Choose Gasoline if you drive short distances, want smoother acceleration, or prioritize low initial costs.
💬 Conclusion
There’s no one-size-fits-all winner in the diesel vs. gasoline debate. It all boils down to your driving habits, budget, and future plans. With new technologies constantly reshaping the landscape, now is the perfect time to educate yourself before making a vehicle investment.
Which engine type do you prefer and why? Let us know in the comments!
❓Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What’s the main difference between diesel and gasoline engines?
A: Diesel engines use compression ignition and deliver more torque, while gasoline engines use spark ignition and produce higher RPM and horsepower.
Q2. Which is cheaper to maintain: diesel or gasoline?
A: Gasoline engines are generally cheaper to maintain short term, but diesel engines may have lower lifetime maintenance if serviced properly.
Q3. Do diesel engines last longer than gasoline?
A: Yes, diesel engines are more durable and typically outlast gasoline engines by a large margin, especially in heavy-duty applications.
Q4. Can I upgrade my diesel or gasoline engine for better performance?
A: Yes. Diesel upgrades focus on torque and efficiency (e.g., performance tuners, turbo enhancements), while gasoline upgrades often boost horsepower (e.g., cold air intake, turbo kits, ECU tuning).
Q5. What’s better for city driving—diesel or gasoline?
A: Gasoline engines are better for stop-and-go traffic and short trips due to smoother operation and quicker warm-up.
Q6. Are diesel engines being banned?
A: Some cities and countries are introducing diesel restrictions to curb pollution, but modern diesel vehicles with proper emission controls are still widely used—especially for commercial and long-haul transport.
Discover More:
- How the ignition system works
- Magneto Ignition System – Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, and Disadvantages with Application
- Battery Ignition System: Parts, Function, Working, Advantages, and Disadvantages
- Carburetor Vs Fuel Injection: Which One Is The Better Option?
- Adjusting a SU carburetor
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website