Introduction
The world of internal combustion engines is divided into two main categories: Spark Ignition (SI) engines and Compression Ignition (CI) engines. These two powerhouses have distinct characteristics that define their operation, performance, and applications.
In this article, we delve into the core differences between SI and CI engines, shedding light on their mechanisms, fuel types, emissions control, and their roles in shaping modern transportation.
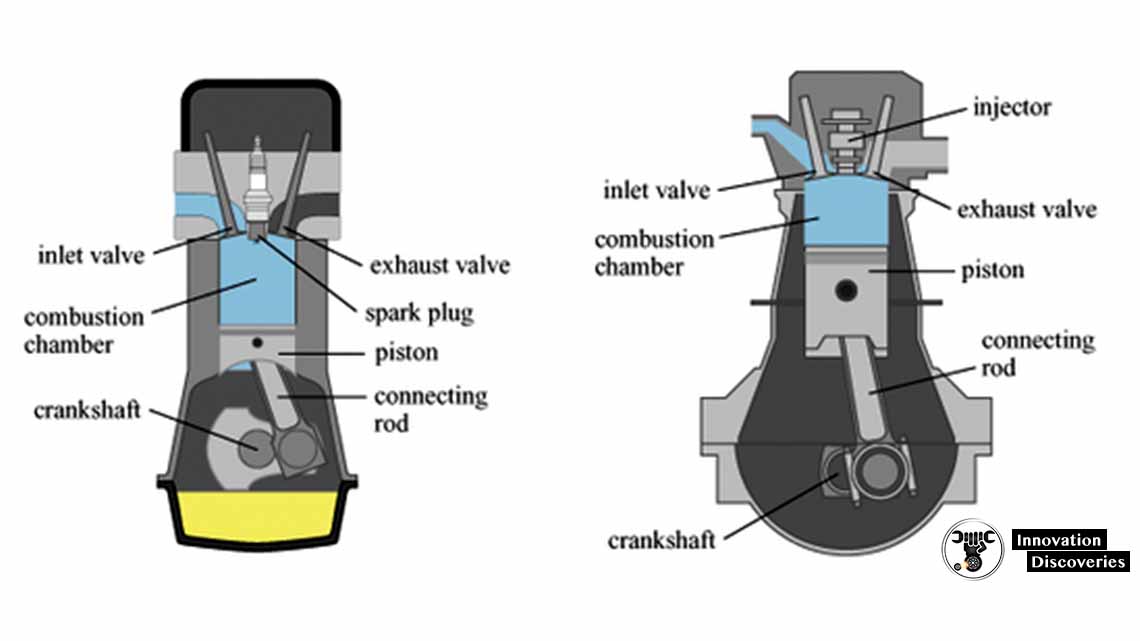
The Ignition Conundrum: SI vs. CI
At the heart of the distinction between SI and CI engines lies the method of ignition. SI engines employ spark plugs to ignite an air-fuel mixture, while CI engines rely on the high temperature and pressure of compressed air to ignite fuel without the need for a spark.
Igniting the Flame: Combustion Process
SI engines orchestrate combustion through carefully timed sparks. The spark plug generates an electric discharge, igniting the premixed air and fuel within the combustion chamber. On the other hand, CI engines embrace the concept of auto-ignition, where fuel is injected directly into highly compressed air. The heat of compression causes spontaneous ignition, propelling the engine into motion.
Fueling the Engines: Gasoline vs. Diesel
The fuel types used in SI and CI engines further distinguish the two categories. SI engines predominantly run on gasoline due to its lower ignition temperature and volatility. In contrast, CI engines opt for diesel fuel, which ignites at higher temperatures and is less volatile. These fuel choices influence engine design, performance, and efficiency.
Balancing the Compression Ratio
Compression ratios—ratios of the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke to the volume when it’s at the top—vary significantly between SI and CI engines. SI engines generally operate with lower compression ratios to avoid knocking, a condition where the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely. CI engines, in contrast, thrive on higher compression ratios that create the extreme temperatures necessary for spontaneous ignition of diesel fuel.
Performance Profiles: Power and Efficiency
SI engines are known for their high power output at high speeds and loads, making them suitable for applications that require rapid acceleration and high RPMs. CI engines excel at delivering high torque at lower speeds and heavier loads, contributing to their popularity in trucks and industrial machinery. Additionally, CI engines tend to exhibit higher thermal efficiency due to their operating principles.
Emissions Control: A Vital Aspect
Emissions control is a critical consideration for both SI and CI engines. SI engines often employ catalytic converters and precise fuel injection systems to manage emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). In CI engines, technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel particulate filters (DPF) address NOx and particulate matter emissions.
The Evolving Landscape: From Combustion to Electrification
While SI and CI engines have been the workhorses of transportation for decades, the landscape is changing. The push for environmental sustainability and advancements in technology have given rise to hybrid powertrains, electric vehicles, and alternative fuels. As the industry moves towards cleaner and more efficient options, SI and CI engines continue to adapt, proving their resilience and adaptability.
Conclusion
The dichotomy between SI engines and CI engines has been a driving force in the automotive and industrial sectors for generations. The method of ignition, fuel types, efficiency profiles, and emissions control strategies all contribute to the unique characteristics of each engine type.
While the path towards a greener future involves diversifying propulsion technologies, SI and CI engines remain steadfast contributors to the legacy of internal combustion, shaping the way we move and inspiring innovations in the world of transportation.
Also, Read:
- IC ENGINE: COMPONENTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS, TYPES, AND TERMINOLOGY
- Why Are Diesel Engines Used In Heavy Vehicles? Epic Reasons
Read More:
- How the ignition system works
- Magneto Ignition System – Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, and Disadvantages with Application
- Battery Ignition System: Parts, Function, Working, Advantages, and Disadvantages
- Carburetor Vs Fuel Injection: Which One Is The Better Option?
- Adjusting a SU carburetor
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website



3 Comments