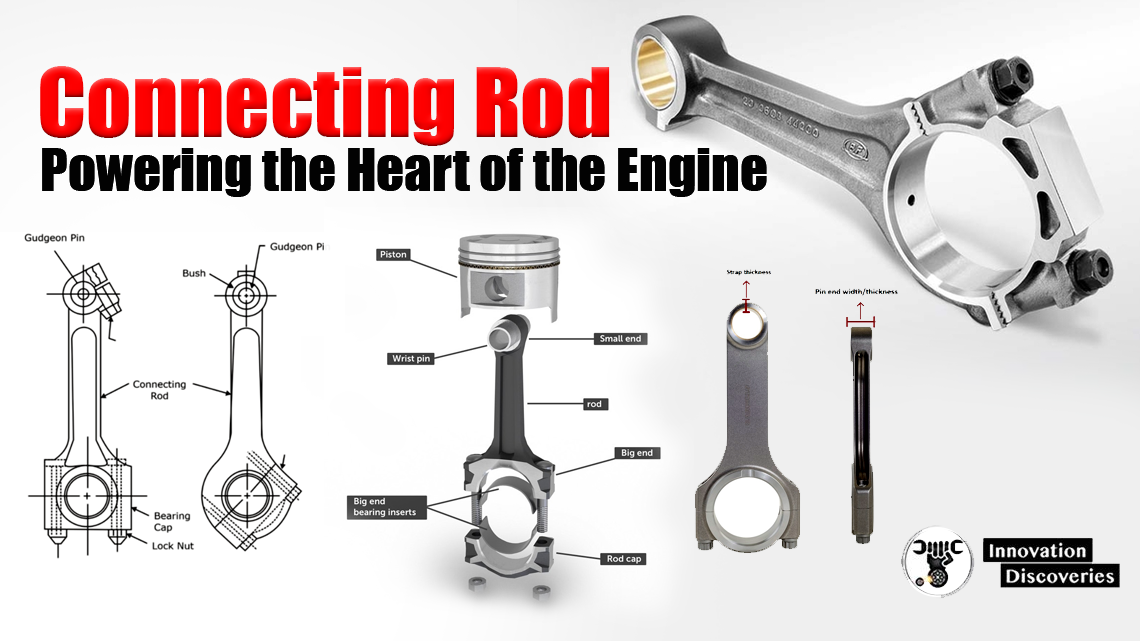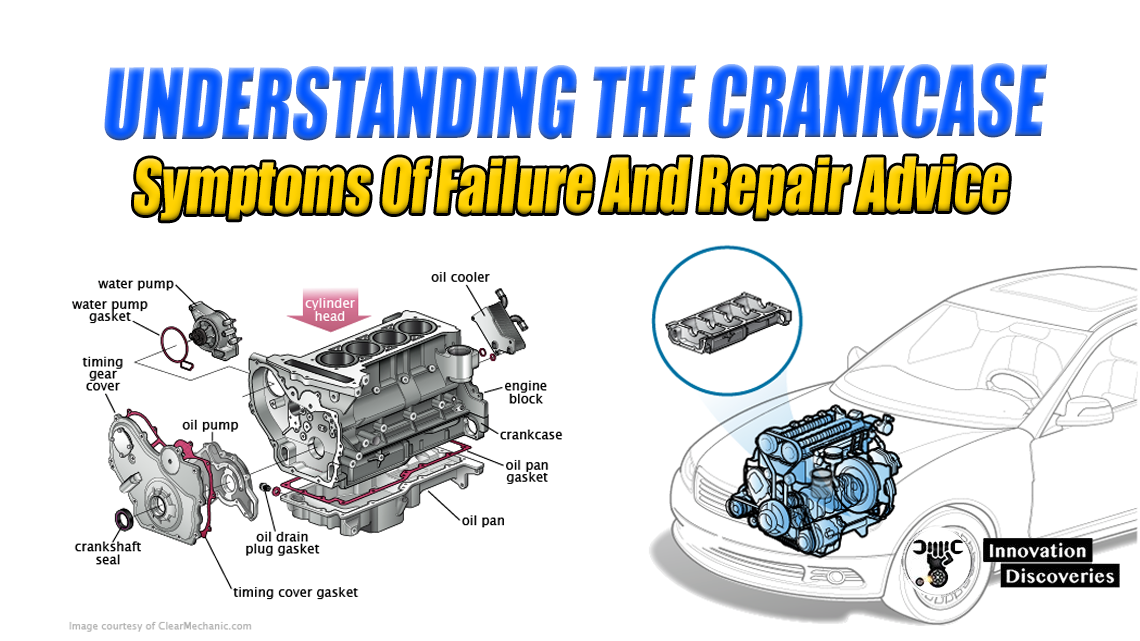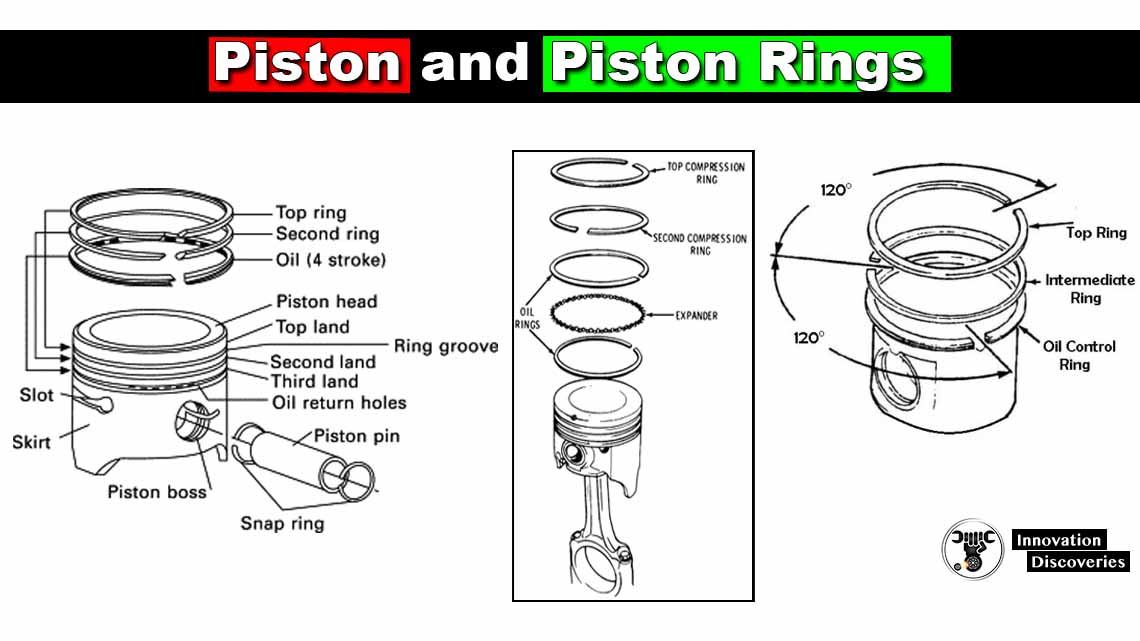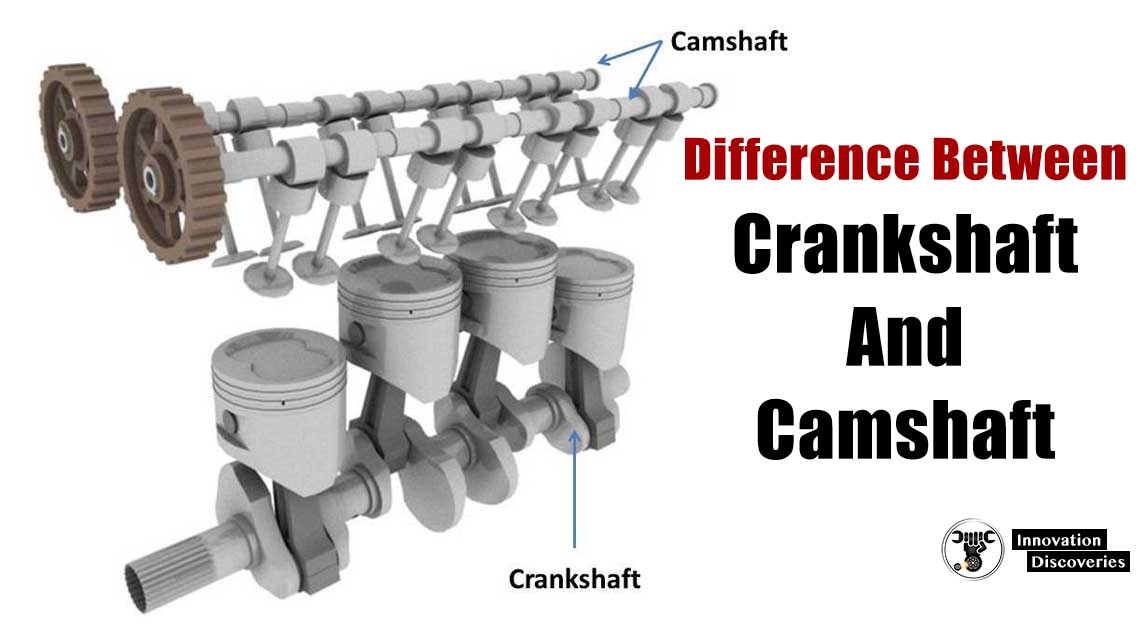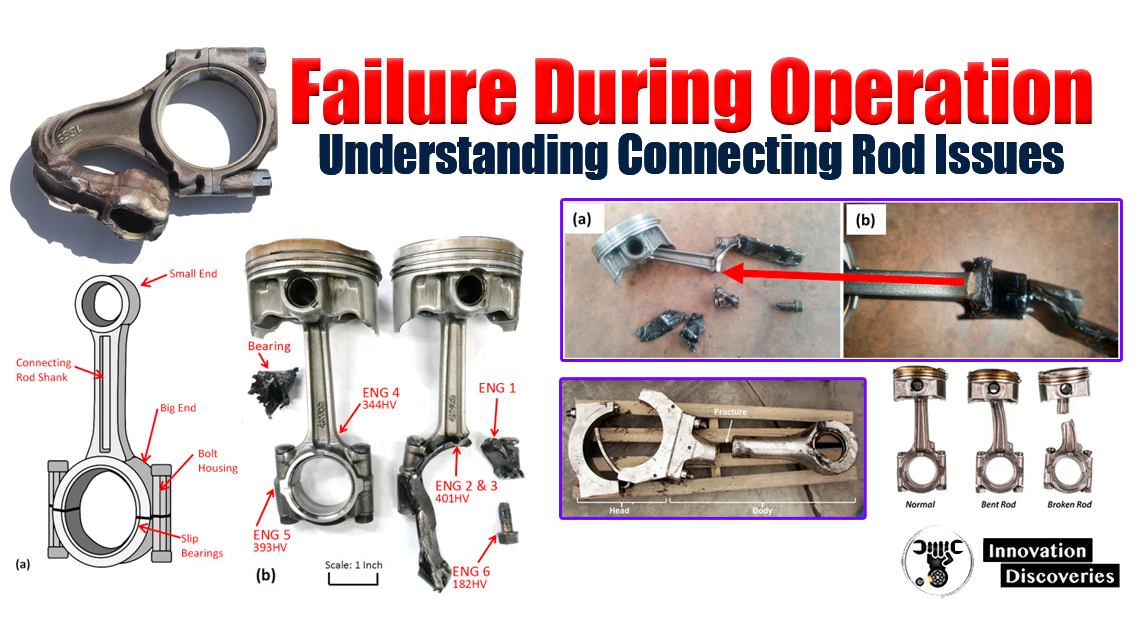
Introduction:
While connecting rods are designed to endure extreme conditions and handle substantial loads, they are not immune to failure. Understanding the potential causes of connecting rod failures is essential for engine owners, mechanics, and enthusiasts alike.
In this article, we will explore common failure modes, their underlying reasons, and preventive measures to mitigate the risk of connecting rod failures during engine operation.

1. Fatigue Failure:
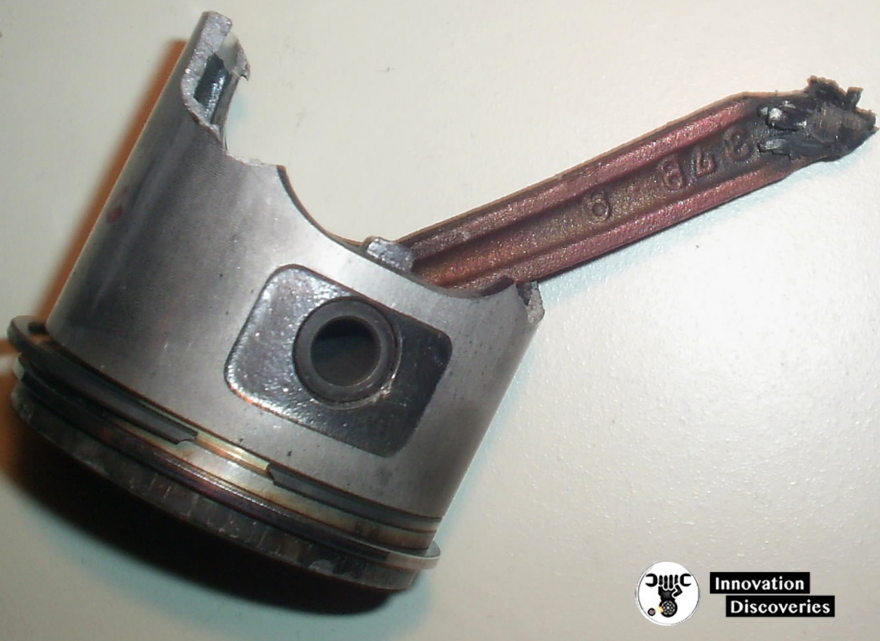
Fatigue failure is a prevalent mode of connecting rod failure, characterized by the gradual weakening and eventual fracture of the rod. Factors contributing to fatigue failure include cyclic loading, excessive engine RPM, inadequate lubrication, and high-stress concentrations.
Over time, these factors can lead to cracks, which propagate until catastrophic failure occurs.
Prevention and Maintenance:
To prevent fatigue failure, regular inspection and maintenance are crucial. Monitoring engine RPM and adhering to manufacturer’s recommendations are essential.
Ensuring proper lubrication, maintaining oil quality, and promptly addressing any abnormalities can help prevent premature fatigue failure.
2. Bearing Failure:
The bearings on both ends of the connecting rod are subjected to significant loads and must withstand repeated motion.
Bearing failures often result from insufficient lubrication, oil contamination, improper bearing clearance, or excessive bearing wear. When the bearings fail, they can cause catastrophic damage to the connecting rod and other engine components.
Prevention and Maintenance:
Regular oil changes using high-quality lubricants and filters are essential to prevent bearing failures. Maintaining proper oil pressure, monitoring oil levels, and addressing any signs of oil contamination or excessive wear are crucial preventive measures.
Additionally, ensuring correct bearing clearances during engine assembly and following manufacturer guidelines is essential for longevity.
3. Rod Bolt Failure:
Rod bolt failures can occur due to inadequate torque, improper installation, or material defects. When rod bolts fail, they can lead to catastrophic engine damage, including piston-to-valve interference, cylinder wall damage, and even complete engine seizure.
Prevention and Maintenance:
Following manufacturer specifications for rod bolt torque during assembly is vital to prevent rod bolt failures. Using high-quality bolts and ensuring proper installation, including thread lubrication, are essential.
Regular inspection of rod bolts during engine maintenance can help detect any signs of wear, stretching, or other abnormalities.
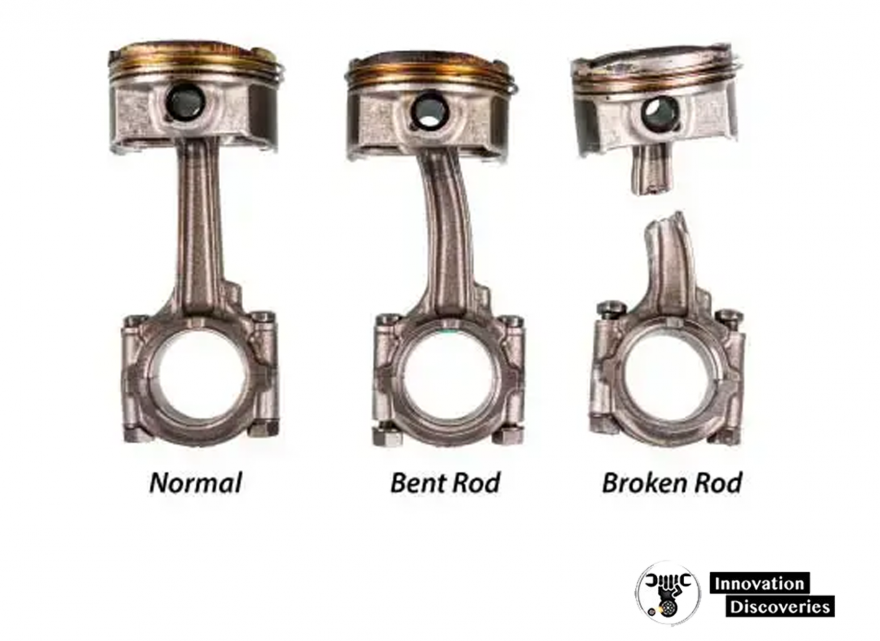
4. Over-Revving:
Excessive engine RPM, often caused by aggressive driving, mechanical malfunctions, or driver error, can lead to connecting rod failure. Over-revving places excessive stress on the connecting rod, leading to bending, distortion, or even complete failure.
Prevention and Maintenance:
Driver awareness and responsible driving habits are crucial in preventing over-revving. Monitoring engine RPM and avoiding excessive acceleration or shifting at high RPMs can significantly reduce the risk.
Regular maintenance, including valve train inspection and adjustment, can also help identify and address potential over-revving issues.

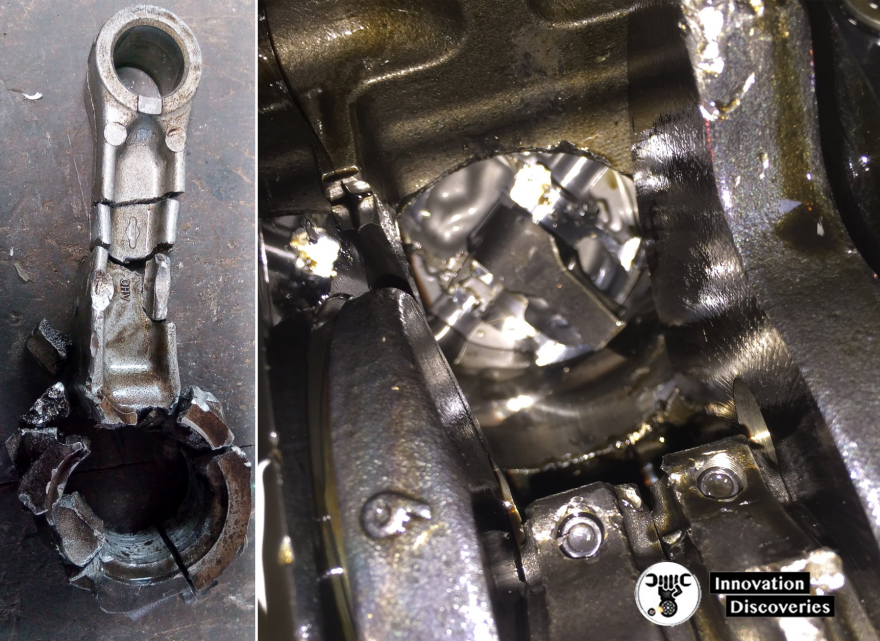
Conclusion:
Connecting rod failures can be disruptive and costly, often resulting in severe engine damage. Understanding the various failure modes, their causes, and implementing preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of such failures.
Regular maintenance, adherence to manufacturer guidelines, and responsible driving habits are key to ensuring the longevity and reliable performance of the connecting rods, contributing to a healthier and more efficient engine overall.
Discover More:
Discover More:

Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website