Turbo hoses can be manufactured with a variety of materials. Various factors dictate the choice of material used.
Some of them are as follows:
• NBR/Nitrile
Very popular in automotive applications due to its high resistance to petroleum products and ability to operate in medium to high temperatures.

Read More:
- What Causes On The Turbocharger Overheat?
- The Differences Between Petrol And Diesel Turbos
- 5 Reasons You Shouldn’t Buy A Turbocharged Car
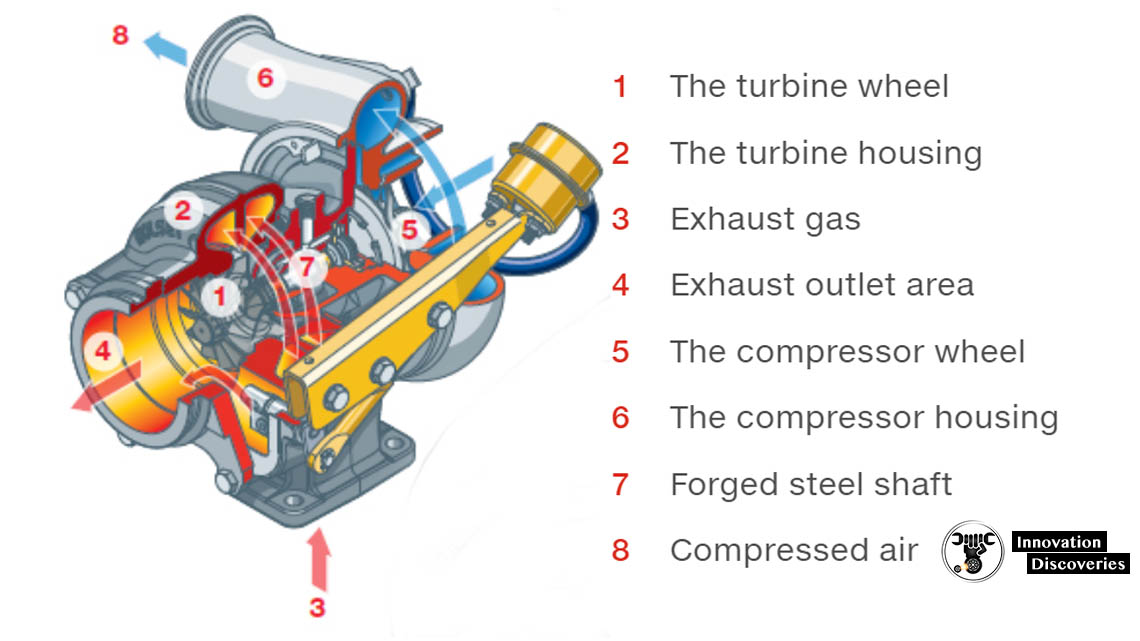
- TURBOCHARGER: COMPONENTS, WORKING PRINCIPLES, AND TYPES
• AEM/Ethylene Acrylic
Excellent heat-aging resistance and can also operate in medium to high-temperature conditions

• EPDM/Ethylene-Propylene
Provides increased strength and excellent extreme temperature resistance.

• VMQ/Silicone (Fluorosilicone)
Delivers unparalleled temperature and compression set resistance and is therefore used in high pressure/temperature applications.

i.e. for vehicles with very high induction charge (boost) pressures.
Turbo hoses generally operate at increased air pressures.
So reinforcement Fibers, such as polyester, Kevlar, and aramid are added to the walls of the hose during their construction
FAILURE AND REPLACEMENT
As with any rubber product, the material naturally degrades over time.
Also, turbo hoses are subject to high levels of stress, which along with contamination from oil and other common automotive chemicals means they will eventually fail and need replacing.
It is important to ascertain if there are any additional factors that may have contributed to the failure.
While installing a new turbo, it’s very important to make sure the old hoses are checked and replaced as necessary.
This will reduce the risk of contamination and help avoid premature failure.
DON’T FORGET THE HOSE CLIPS
Finally, when replacing any hose, the connector( hose clip) is important.

READ MORE:
TURBOCHARGER: COMPONENTS, WORKING PRINCIPLES, AND TYPES
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website








