YouTube has become a force to reckon with ever since it was created back in 2005. That is why it comes as quite a shock when you find out that researchers have come up with a theoretical possibility that they could store 10 petabytes of data in a single gram of DNA. This means that all of YouTube could be fitted on a teaspoon!

The study comes from a team of researchers at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology located in Haifa and the Interdisciplinary Center Herzliya that is also in Israel. It is aimed at a way of examining the possibility of making use of DNA as data storage. This makes it a perfect choice for data storage. However, actually pulling it off is not an easy feat. When it comes to the encoding of information in a DNA, you will need a chain that is comprised of links known as nucleotides. These nucleotides are known as the four building blocks of life and are marked with letters A, C, G, and T. Binary sequences comprised of 0s and 1s are then translated into these four letters.

DNA molecules are produced with the same sequences in a process known as synthesis. increasing the number of letters used to encode the information ; significantly reducing the number of synthesis rounds required to store information on DNA; improving the error correction mechanism used.
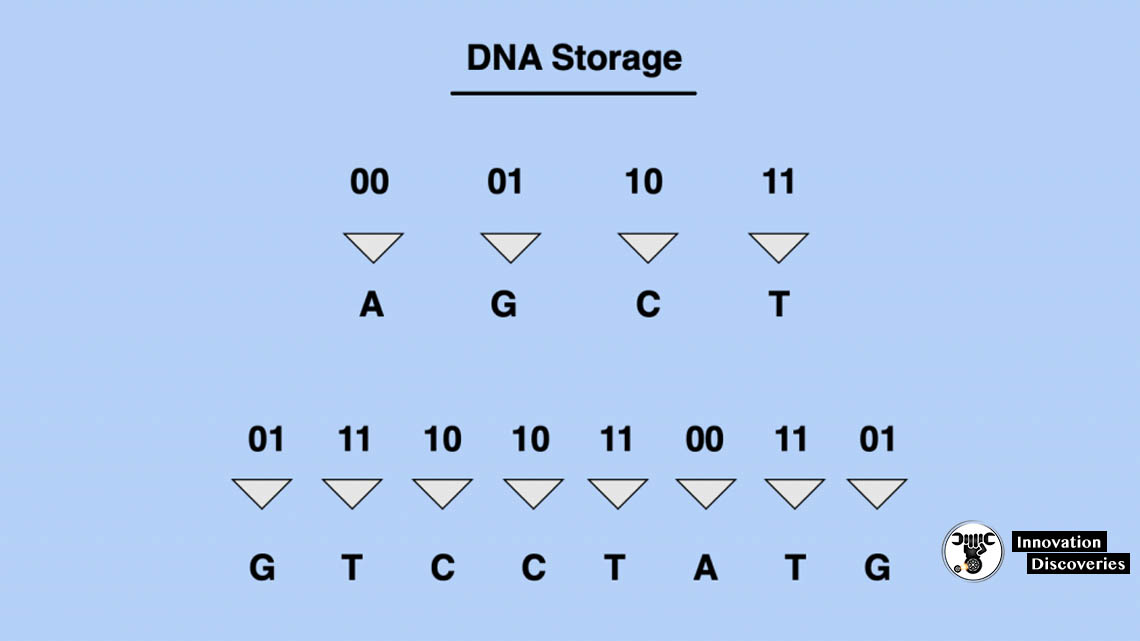
The current synthesis and sequencing processes are inherently redundant because each molecule is produced in large numbers1 and is read in multiple copies during sequencing, says Professor Zohar Yakhini of the Technion in the press statement. “The method we developed leverages this redundancy to increase the effective number of letters well over the original four letters, making it possible for us to encode and write each unit of information in fewer cycles of synthesis.
The research team was able to bring down the number of synthesis rounds that are required per unit of information by 20%. When you consider the complexity of this kind of work, any improvement is much appreciated. The work carried out by these scientists can actually lead to a 75% reduction in the future.





