Introduction
Your car’s ability to start reliably and get you on the road hinges on a crucial component known as the starter. It’s a small yet powerful device that plays a significant role in initiating the complex process of internal combustion.
In this article, we’ll delve into the mechanics of how a starter works and explore its vital role in your car’s ignition system.
Anatomy of the Starting Process:
1. The Ignition Signal:
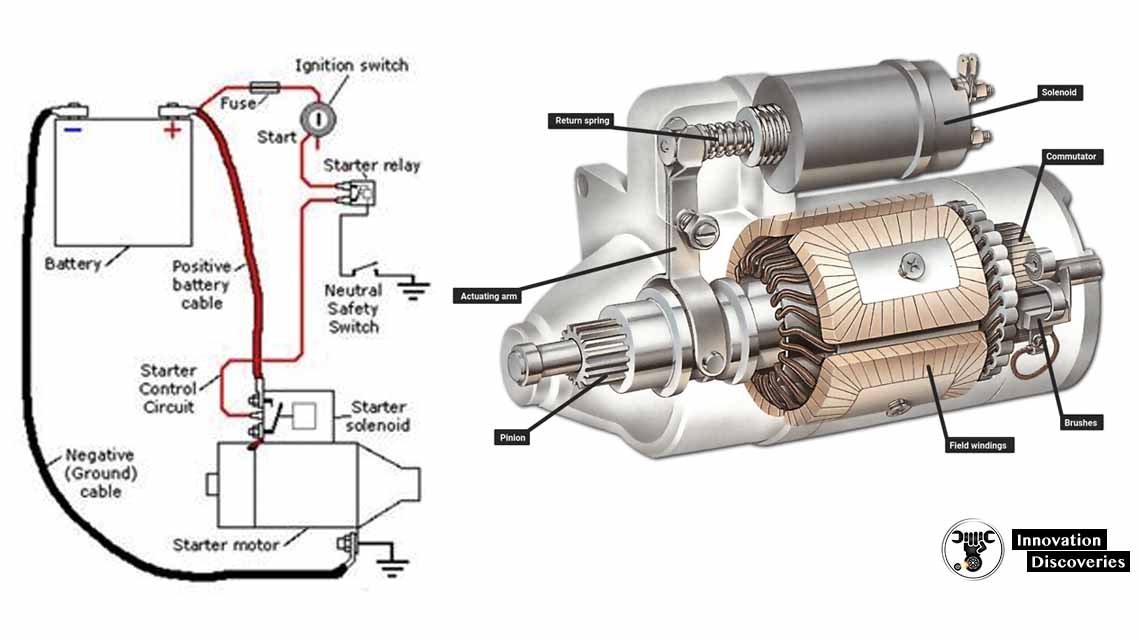
- When you turn your car key or press the start button, an electrical signal is sent to the starter motor.
- This signal is the catalyst for a series of events that will set your engine in motion.
2. Engaging with the Flywheel:
- The starter motor is connected to the flywheel (or flexplate in an automatic transmission), which is directly linked to the engine’s crankshaft.
- A small gear, known as the starter drive, engages with the teeth on the flywheel or flexplate.
3. Cranking the Engine:
- As the starter motor begins to turn, it rotates the flywheel or flexplate.
- This rotation sets the engine’s crankshaft into motion, initiating the up-and-down movement of the pistons.
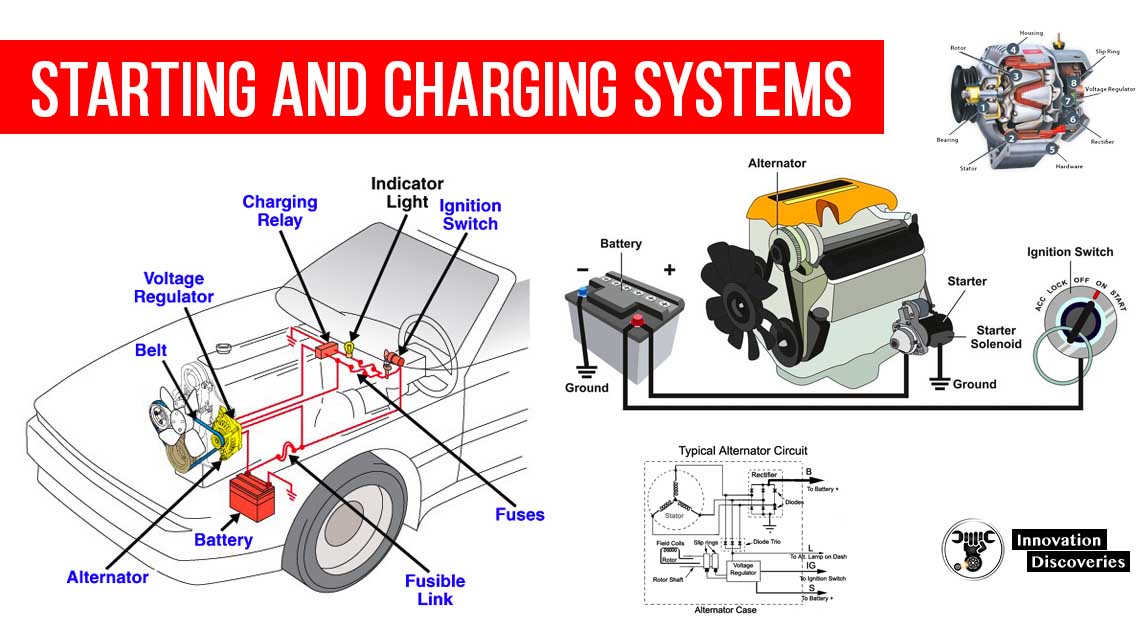
4. Igniting the Combustion Cycle:
- The cranking of the engine, coupled with the fuel injection and ignition systems, triggers the combustion cycle.
- This process ultimately leads to the engine coming to life and the vehicle being ready to move.
CLICK TO READ:
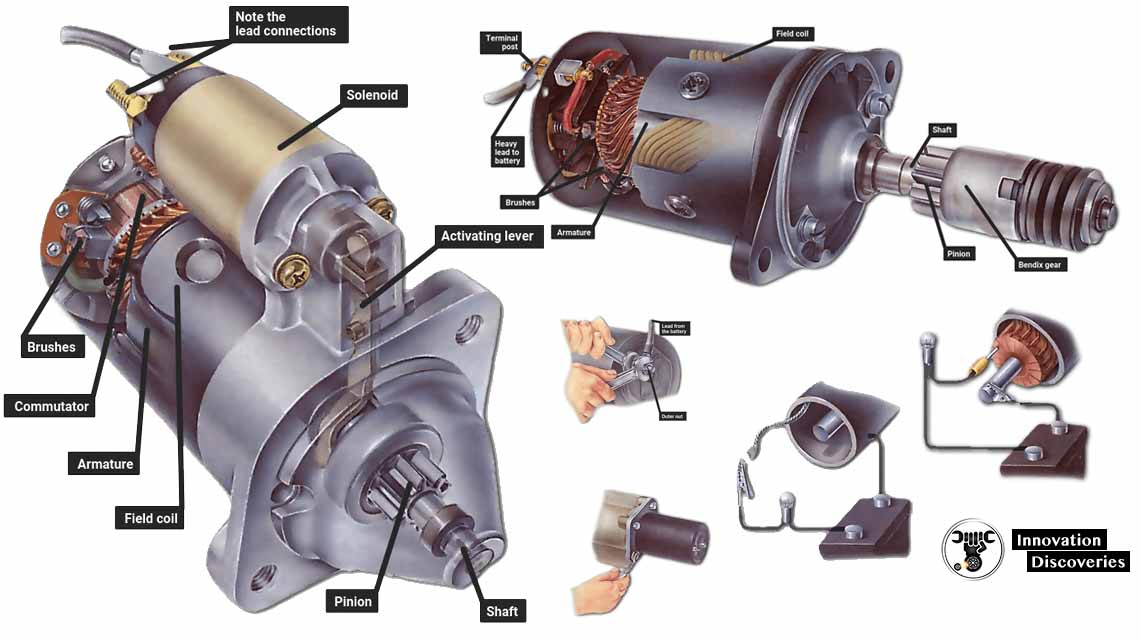
The Importance of Starter Disengagement:
- To prevent damage, a well-designed starter includes a mechanism for automatic disengagement.
- Once the engine is running, the starter motor is disengaged from the flywheel or flexplate.
- This crucial step ensures that the starter doesn’t continue trying to turn the engine over, which could lead to mechanical issues.
CHECKING AND REPLACING THE STARTER MOTOR
Signs of Starter Issues:
- Slow Cranking Sound: If you notice a sluggish cranking sound when starting your car, it could indicate a problem with the starter motor.
- Clicking Noise: A repetitive clicking noise when attempting to start the engine might point to issues with the starter solenoid or electrical connections.
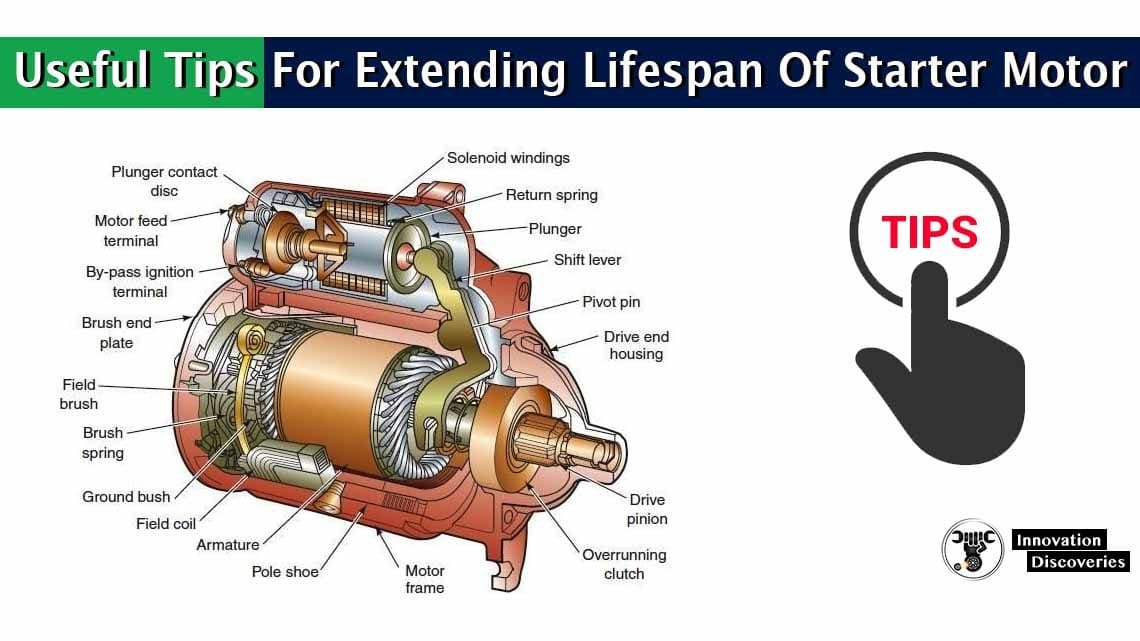
Maintenance and Troubleshooting:
- Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and reliability of your starter.
- If you experience any of the aforementioned signs, it’s advisable to consult with a qualified mechanic promptly.
Conclusion:
Your car’s starter may be a small component, but its role in the ignition process is paramount. Understanding how it works and being aware of potential issues can help you address problems early, ensuring your vehicle starts smoothly every time.
The next time you turn the key and hear the engine roar to life, you can appreciate the intricate dance orchestrated by the unsung hero – the starter.
RELATED CONTENT:
- STARTING SYSTEM: COMPONENTS AND WORKING PRINCIPLES
- HOW TO TEST A NEUTRAL SAFETY SWITCH IN 3 STAGES
- CAPACITOR-DISCHARGE IGNITION(CDI) WORKING PRINCIPLE, ITS ADVANTAGE AND DISADVANTAGE
- CAR ALTERNATOR FUNCTIONS AND SYMPTOMS OF FAILURE
- USING A CAR BATTERY CHARGER
- CAR BATTERY OR ALTERNATOR: WHICH ONE IS THE CULPRIT BEHIND A DEAD CAR?
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website