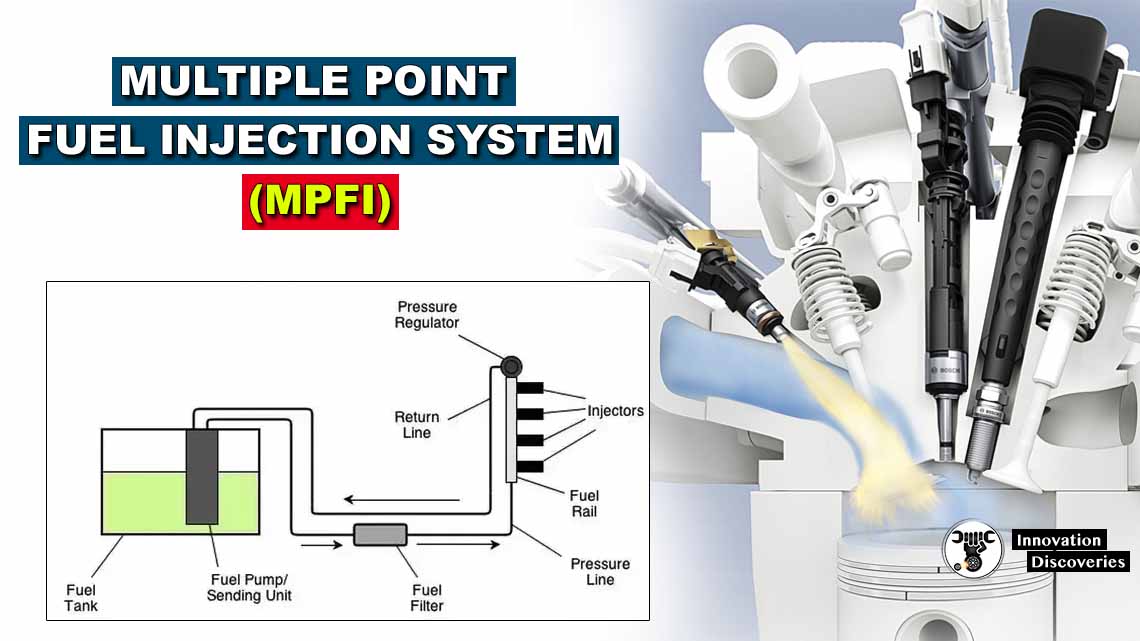
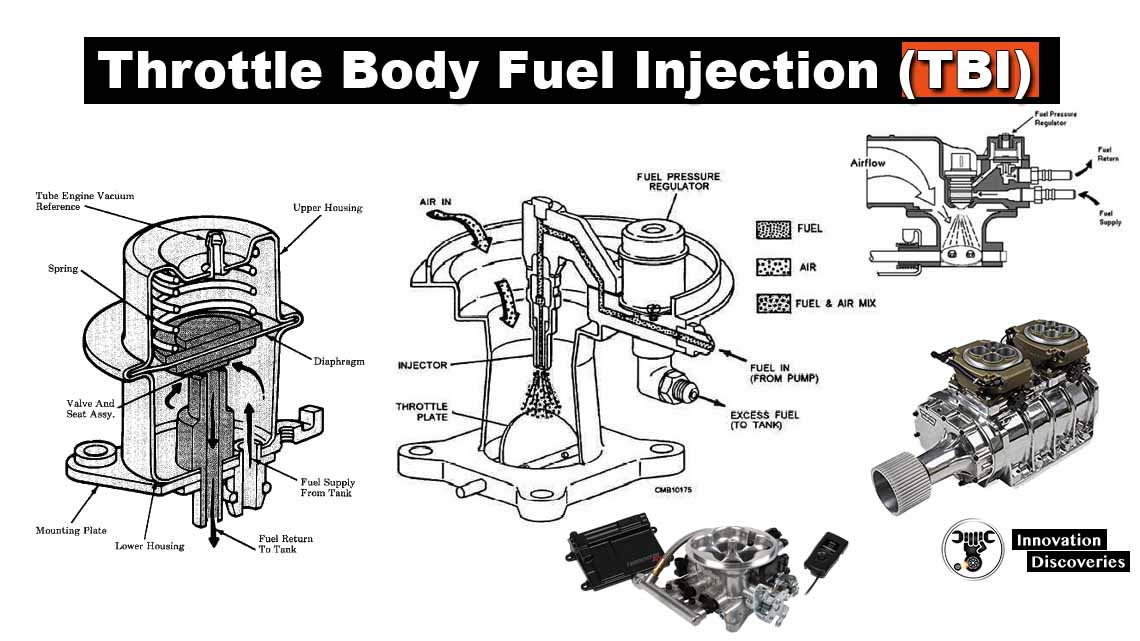
Introduction:
Fuel injectors play a crucial role in the functioning of a vehicle’s engine, as they are responsible for delivering the right amount of fuel into the combustion chamber.
Over time, these injectors can accumulate deposits and contaminants, hindering their performance and negatively impacting your vehicle’s efficiency.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of clean fuel injectors, the symptoms of dirty injectors, and various cleaning options to maintain optimal engine performance.
What Are Fuel Injectors?
Fuel injectors are components in a vehicle’s engine that deliver pressurized fuel directly into the combustion chamber. This process is controlled by the engine control unit (ECU), which calculates the precise amount of fuel needed based on various factors such as engine speed, load, and temperature.
Modern vehicles typically use electronic fuel injection systems, where the fuel injectors play a crucial role in achieving fuel efficiency and optimal engine performance.
Clean Injectors Improve Performance
Clean fuel injectors are essential for maintaining peak engine performance. When fuel injectors are free from deposits and contaminants, they can deliver fuel with precision, ensuring efficient combustion.
Here are some key benefits of clean fuel injectors:
1. Improved Fuel Efficiency:
Clean injectors contribute to better fuel atomization, resulting in more efficient combustion and improved fuel efficiency.
2. Enhanced Engine Performance:
Properly functioning injectors ensure a consistent and optimal fuel-air mixture, leading to smoother engine operation and increased power.
3. Reduced Emissions:
Clean fuel injectors help minimize harmful emissions by promoting complete combustion, reducing the environmental impact of your vehicle.
Symptoms of Dirty Fuel Injectors
Identifying the symptoms of dirty fuel injectors is crucial for timely maintenance. Here are common signs that your fuel injectors may need cleaning:
1. Rough Idling:
If your vehicle’s engine idles roughly or has irregular RPMs when stationary, it may indicate dirty injectors.
2. Poor Acceleration:
Reduced engine performance during acceleration or a sluggish response to throttle input can be a sign of clogged injectors.
3. Misfires and Hesitation:
Dirty injectors may lead to engine misfires, hesitation, or stumbling, especially under heavy load or during acceleration.
4. Decreased Fuel Efficiency:
A noticeable drop in fuel efficiency could be attributed to inefficient fuel injection caused by dirty injectors.
Cleaning Options
Several methods are available to clean fuel injectors, ranging from DIY solutions to professional services. Here are some cleaning options:
1. Fuel Additives:
Fuel injector cleaning additives can be added to the fuel tank. These detergents help break down deposits over time. Follow the product instructions for proper usage.
2. Ultrasonic Cleaning:
Professional mechanics often use ultrasonic cleaning machines to clean fuel injectors thoroughly. This method involves removing the injectors and subjecting them to ultrasonic vibrations to dislodge deposits.
3. Injector Cleaning Kits:
DIY cleaning kits are available, featuring specialized cleaning solutions and attachments that connect to the fuel rail. These kits are designed for at-home use but should be used cautiously following the provided instructions.
4. Professional Cleaning Services:
Taking your vehicle to a professional service center for fuel injector cleaning is a reliable option. Mechanics can use advanced equipment to clean injectors and ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance of fuel injectors is vital for preserving your vehicle’s fuel efficiency and overall engine performance. By understanding the importance of clean fuel injectors, recognizing symptoms of contamination, and exploring cleaning options, you can ensure that your vehicle operates at its best.
Whether you choose DIY methods or seek professional assistance, a clean set of fuel injectors will contribute to a smoother and more efficient driving experience.
DOWNLOAD
CLICK TO READ:
Discover More:
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website