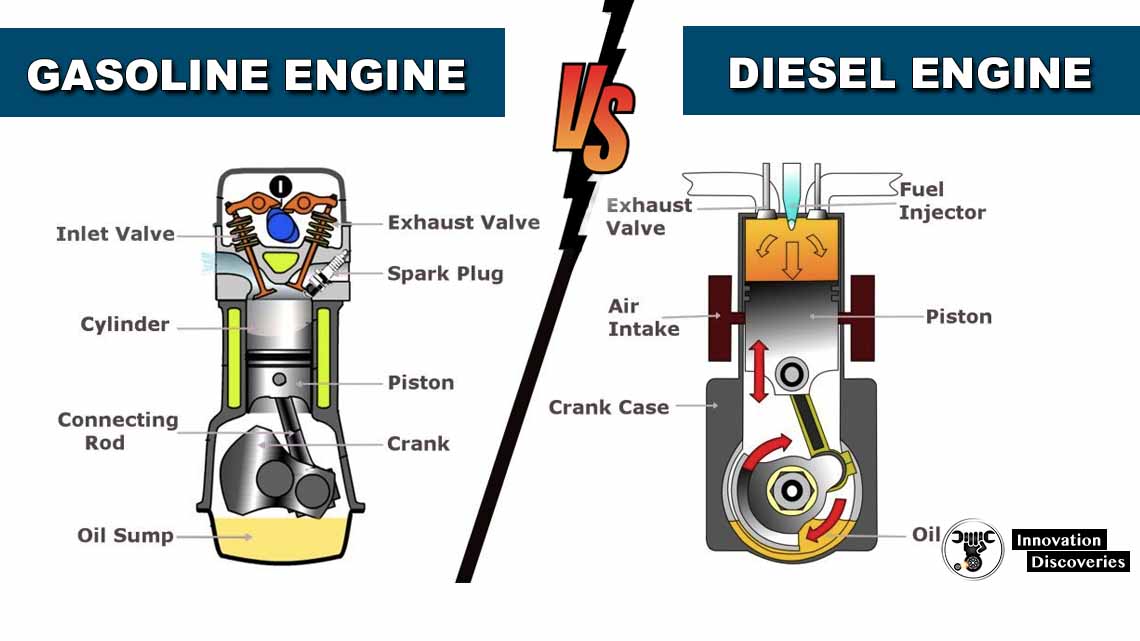
The properties of diesel fuel are at times varied from other fuels such as gasoline.
However, there are also some similarities, such as the fact that they both burn in a fuel cylinder to make the engine work, and it goes without saying that they both power vehicles.
Did You Know? | WONDERING “WHY ARE DIESEL ENGINES NOISY?” THE REASONS
But how different are gasoline and diesel fuel really?
There are several differences between the properties of gasoline and diesel fuel, for example:
- Diesel requires less refining
- It is heavier, thicker, and oilier
- It has an increased evaporation time
- Can be compressed more

Diesel is used to fueling and power a large range of vehicles, including:
- Buses
- Cars
- Boats
- Trains
- Farm equipment, the list goes on!
Also, read:
- HOW DO GASOLINE ENGINES DIFFER FROM DIESEL ENGINES?
- WHY ARE DIESEL ENGINES USED IN HEAVY VEHICLES? EPIC REASONS
- TROUBLESHOOTING AND REPAIRING DIESEL ENGINE
More technical properties of diesel include:
- Centane number: minimum 40 (as of 2000)
- Cloud point: -34 degrees celsius (maximum)
- Water and sediment: 0.02% (maximum volume)
- Microbiological contamination: Bacteria – SRB causes corrosion and sludge development
- Fame content (biopart): approximately 7%
- Density: 0.832 kg/L
- Sulphur content: 500ppm
- CFFP – cold filter plugging point: up to -5 degrees celsius
- Heating (calorific) value: 45.5MJ/kg
- Flash point: 40 degrees celsius (minimum)
- Viscosity: (at 40 degrees celsius) 2.5-3.5mm2/s
- Carbon residue: 0.1% (maximum mass)
- Ash: 0.01% (maximum)
- Oxidation stability: up to 0.025mg/ml
Also, read:
Abstract:
Diesel fuel is a mixture of hydrocarbons obtained by distillation of crude oil.
The important properties which are used to characterize diesel fuel include cetane number (or cetane index), fuel volatility, density, viscosity, cold behavior, and sulfur content.
Diesel fuel specifications differ for various fuel grades and in different countries.
Read More:
- 3 INTAKE MANIFOLD LEAK SYMPTOMS (AND REPLACEMENT COST)
- WHAT ARE THE INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET LEAK SYMPTOMS?
- INTRODUCTION OF ENGINES
- Piston and Piston Rings
Read More:

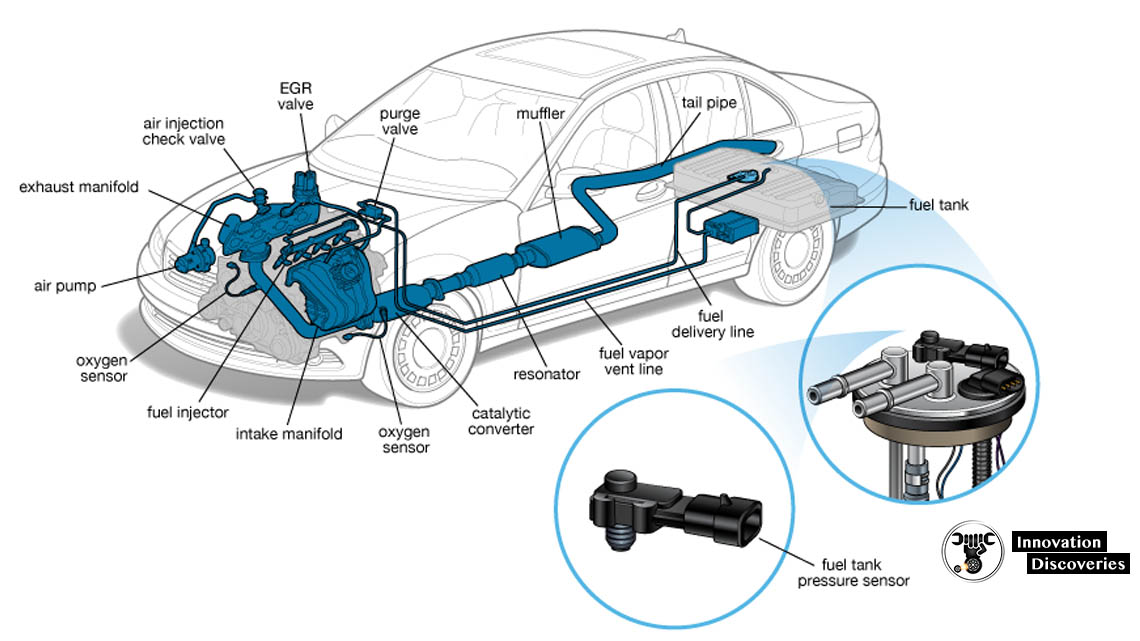
FUEL SYSTEM: COMPONENTS, WORKING PRINCIPLES, SYMPTOMS AND EMISSION CONTROLS
Visit Our Friendly Website