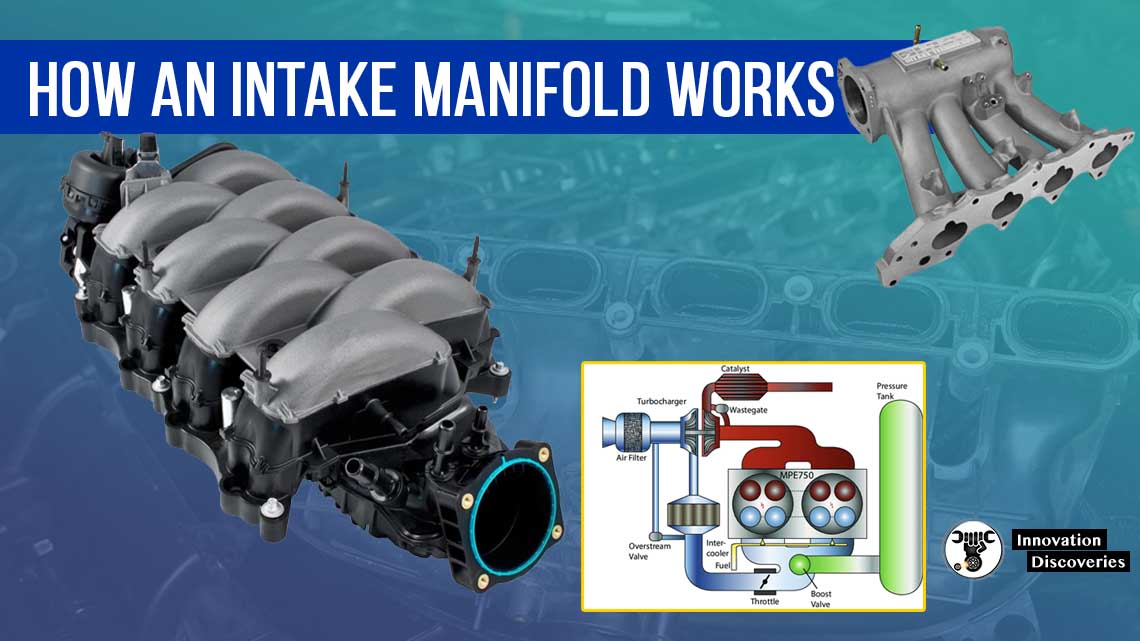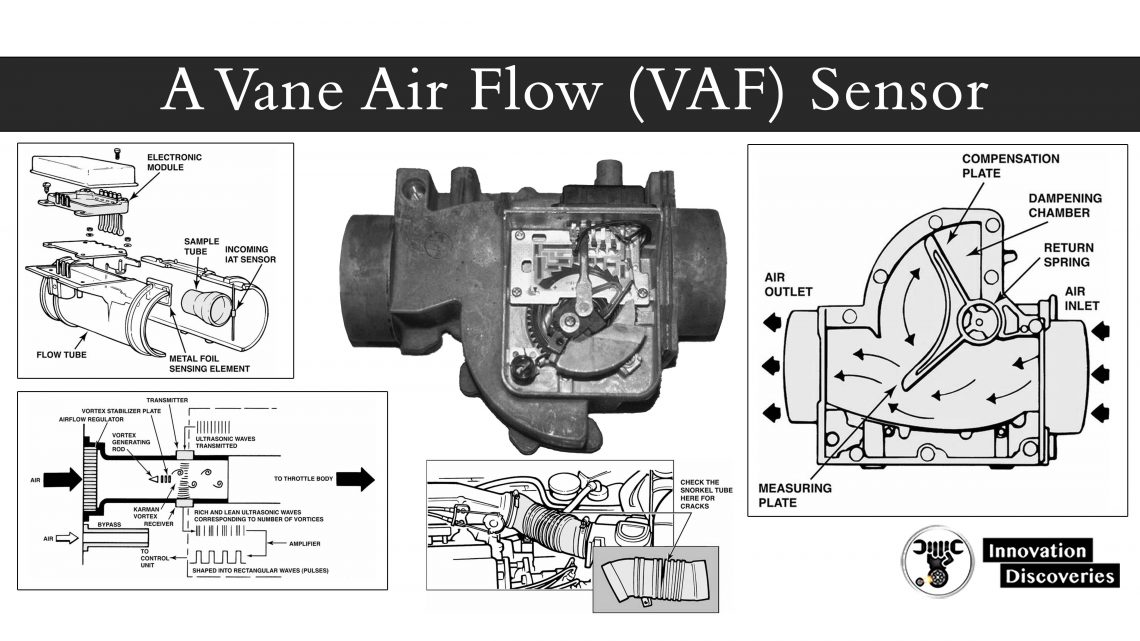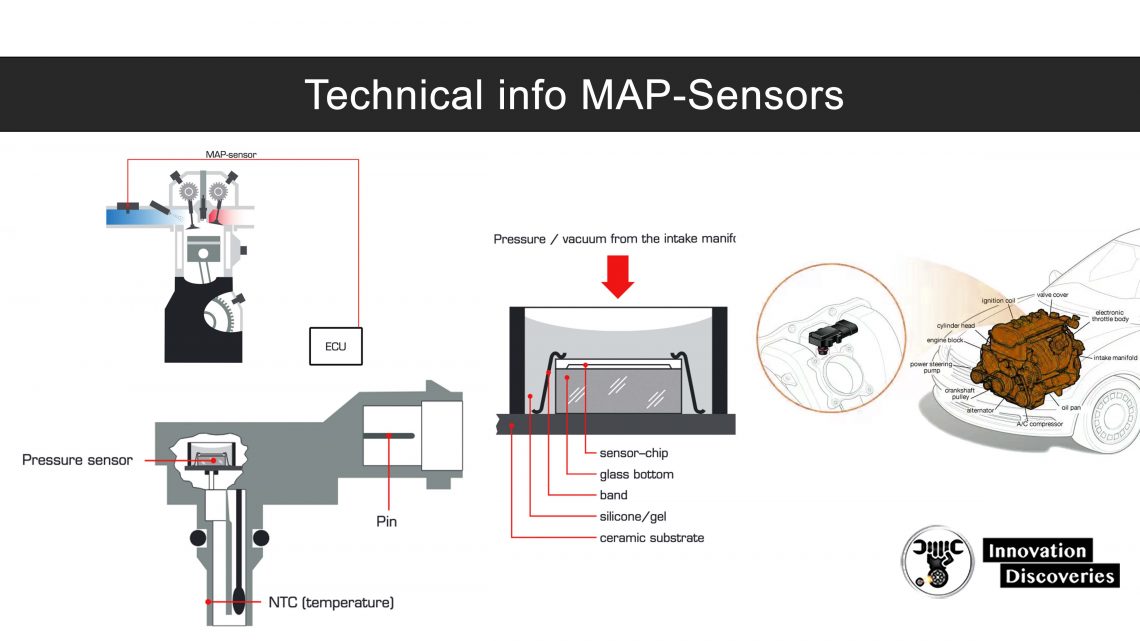
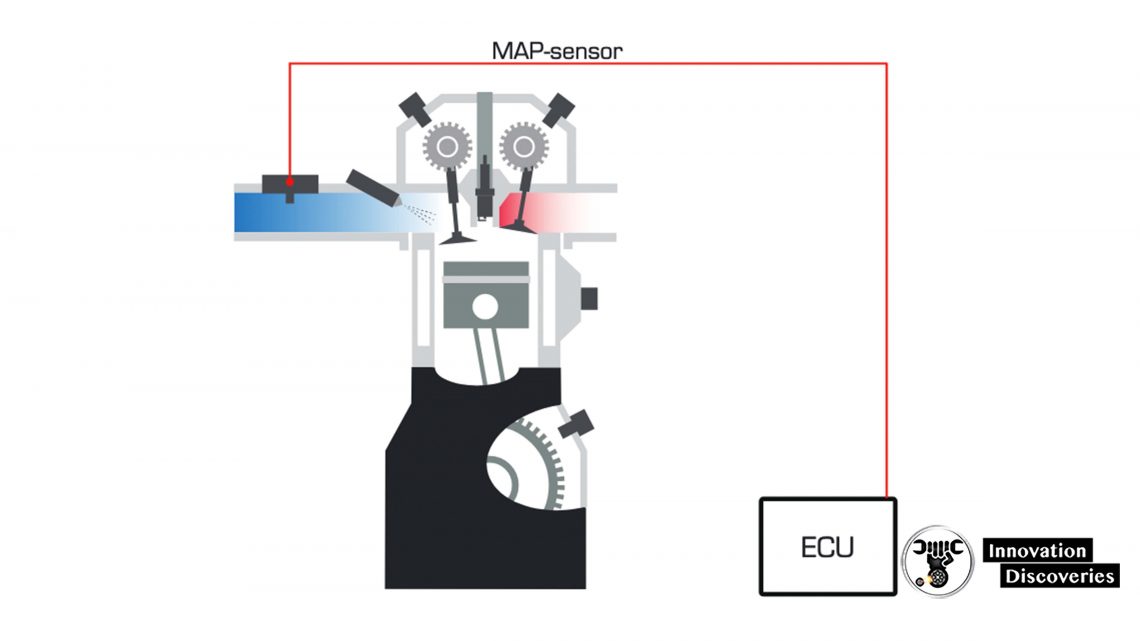
The MAP sensor measures the pressure in the intake manifold for use in the vehicle’s engine control (ECU).
In some cases, the MAP sensor also includes a temperature sensor for measuring the air temperature.
The information is included in the calculation of the load ratio of the engine used to control the amount of fuel and mixture, as well as the ignition timing.
System design
Function
The MAP sensor has a pressure sensor and an electronic circuit that generates a voltage signal that changes with respect to pressure.
The voltage signal is typically between 1 and 5 volts. The output voltage is increased when a vacuum drop is detected that occurs when gas is given.
At idle, where the largest vacuum is detected – about 20 kPa, the voltage is typically between 1.0 and 2.0 volts. Conversely, it is at full throttle between 4.5 and 5.0 volts – about 80 kPa.
The read voltage typically changes by about 1.0 volts when the vacuum is changed by 20 kPa.
For versions with a built-in temperature meter, the measuring range is generally between -40 and 120 ° C. 65kOhm at -40 ° C and 100ohms at 120 ° C.
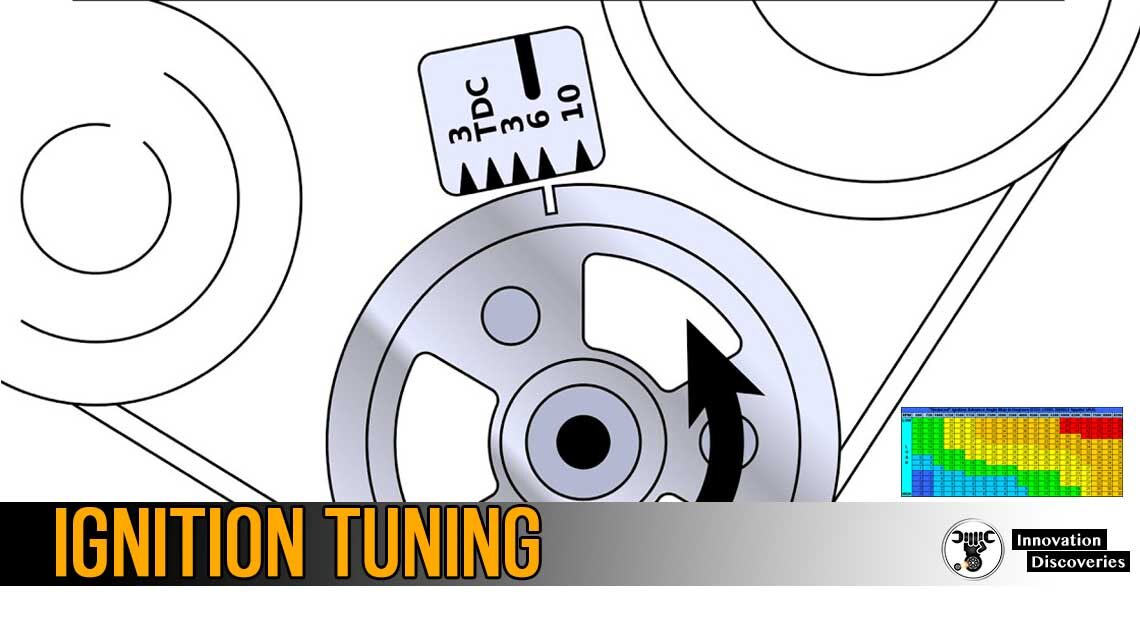
ECU Chip Tune | Ignition Timing | Increase Horsepower
Types
There are mainly two types of MAP sensors:
- 3-poles – without integrated temperature display
- 4-poles – with integrated temperature display
Cross-section Illustration of a MAP sensor
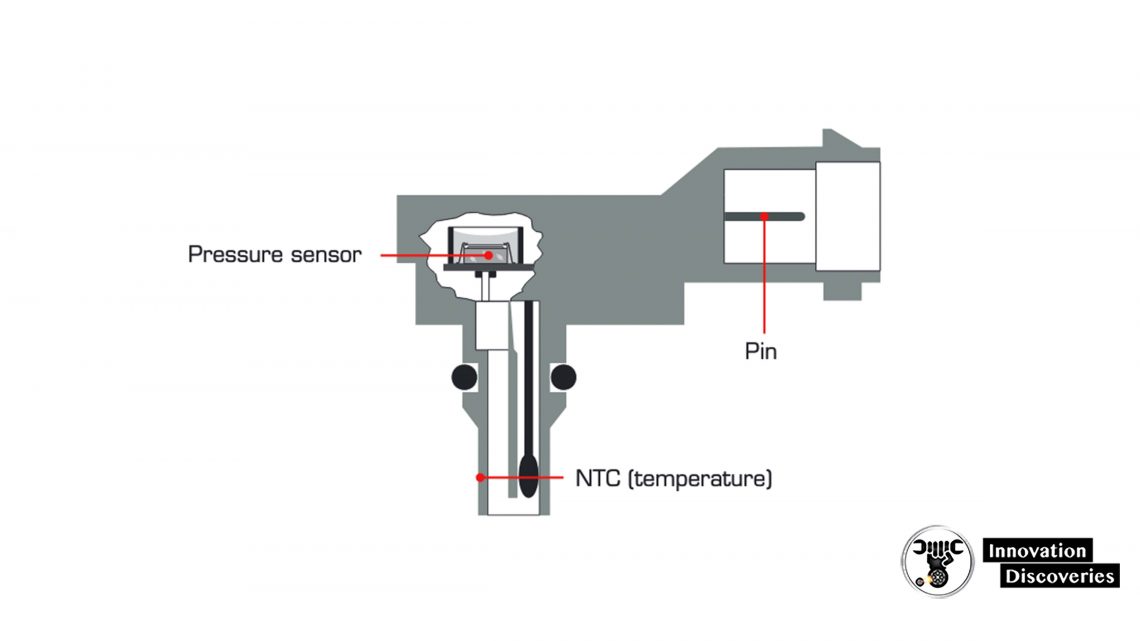
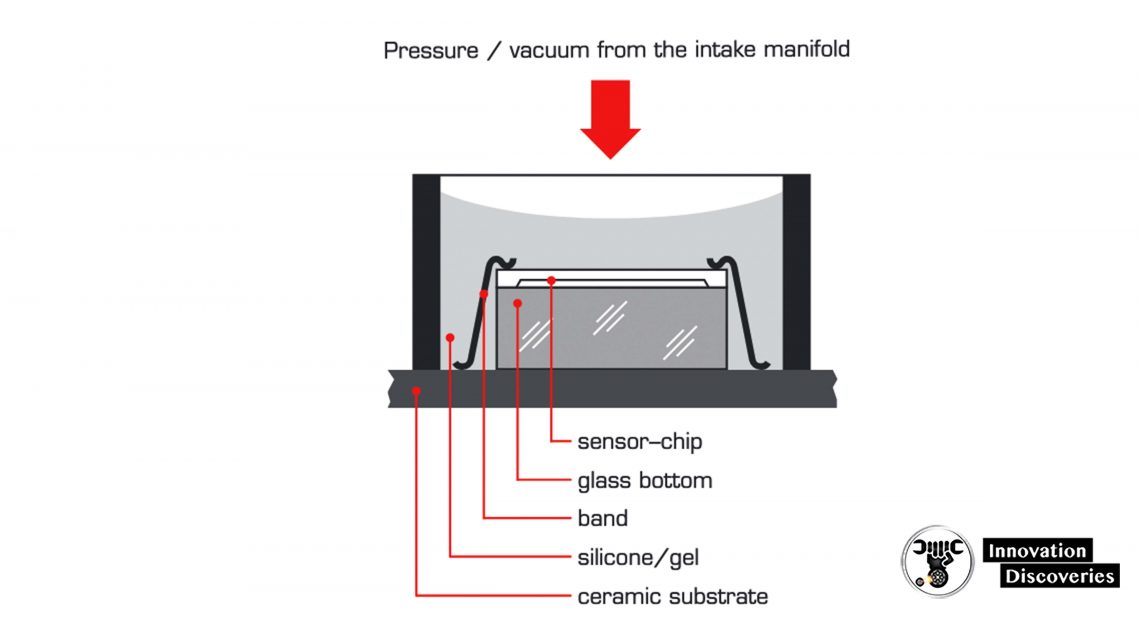
Cross-section Illustration of a pressure sensor
DISCOVER MORE:
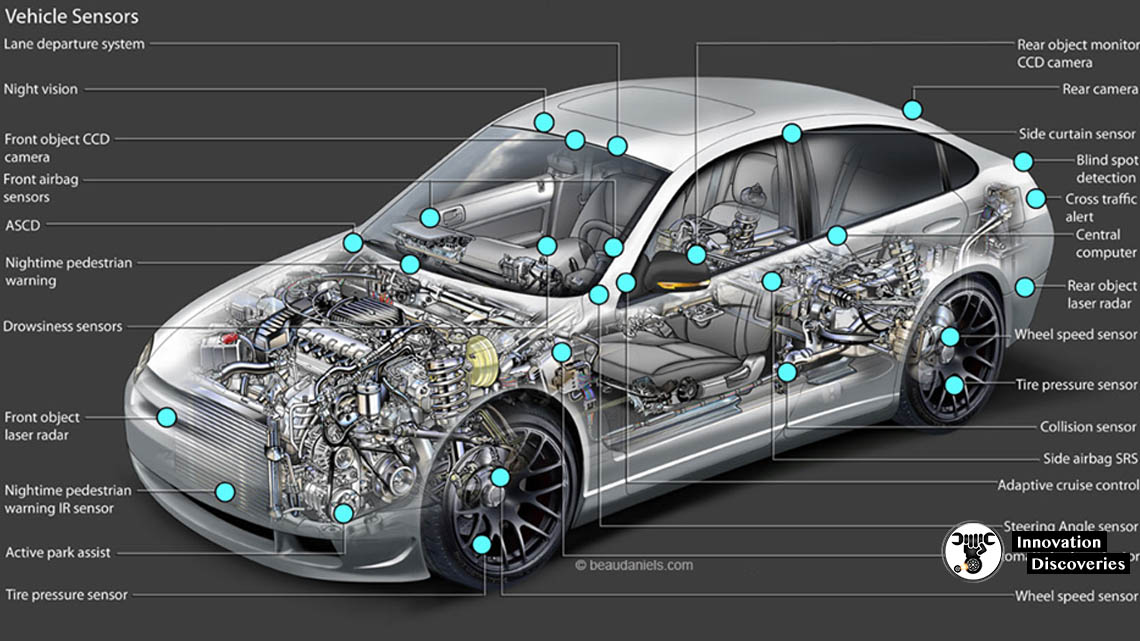
VEHICLE SENSORS: FUNCTIONS AND TYPES
READ MORE

Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website