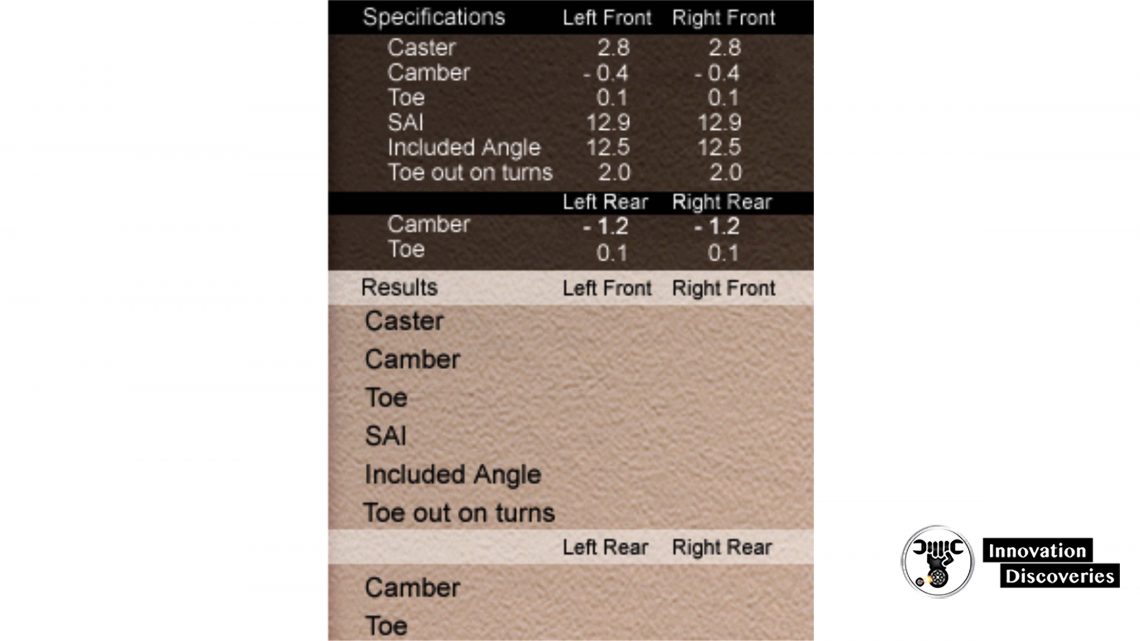
Wheel Alignment
Camber Angle
- Camber is the amount that the centerline of the wheel tilts away from true vertical when viewed from the front of the vehicle
- Camber places the tire tread flat on the road reducing tire wear and improving vehicle handling
- Excessive camber will cause wear on the edge of the tire’s tread
Camber Split
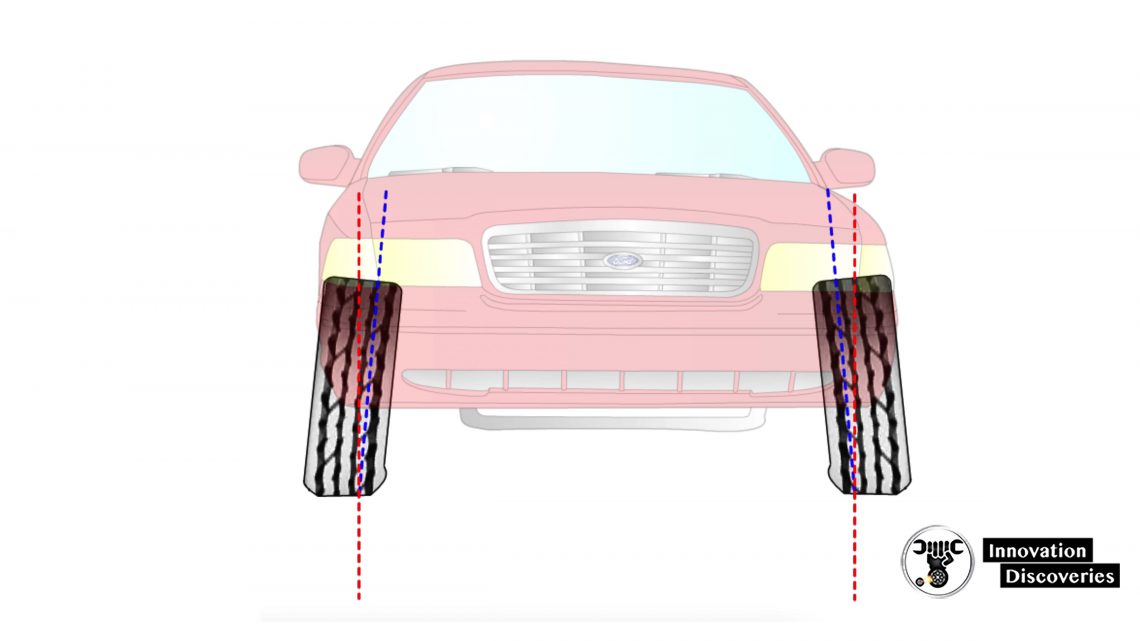
- Camber split is the difference between the left and right camber settings
- Excessive camber split will cause a vehicle to pull to the most positive side
- Camber split should be limited to ½ a degree or less to prevent vehicle pull
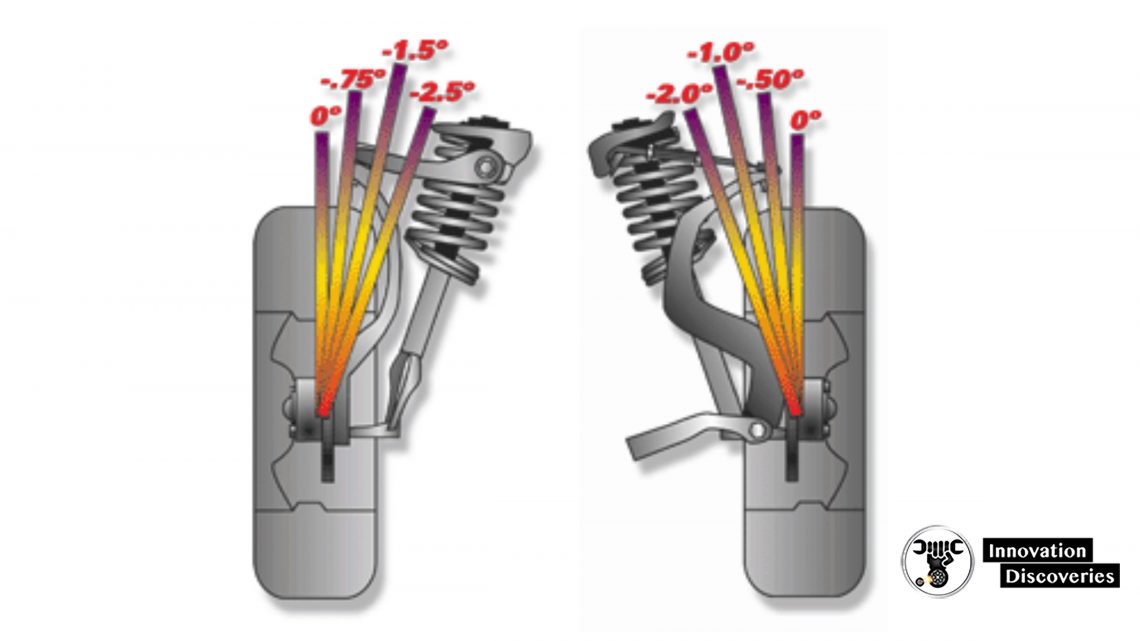
Caster Angle
- Positive caster is the rearward tilt of the steering axis
- Negative caster is the forward tilt of the steering axis
- The vehicle will pull to the least positive side
- Not a tire wear angle
- The caster aids in directional stability and steering wheel return
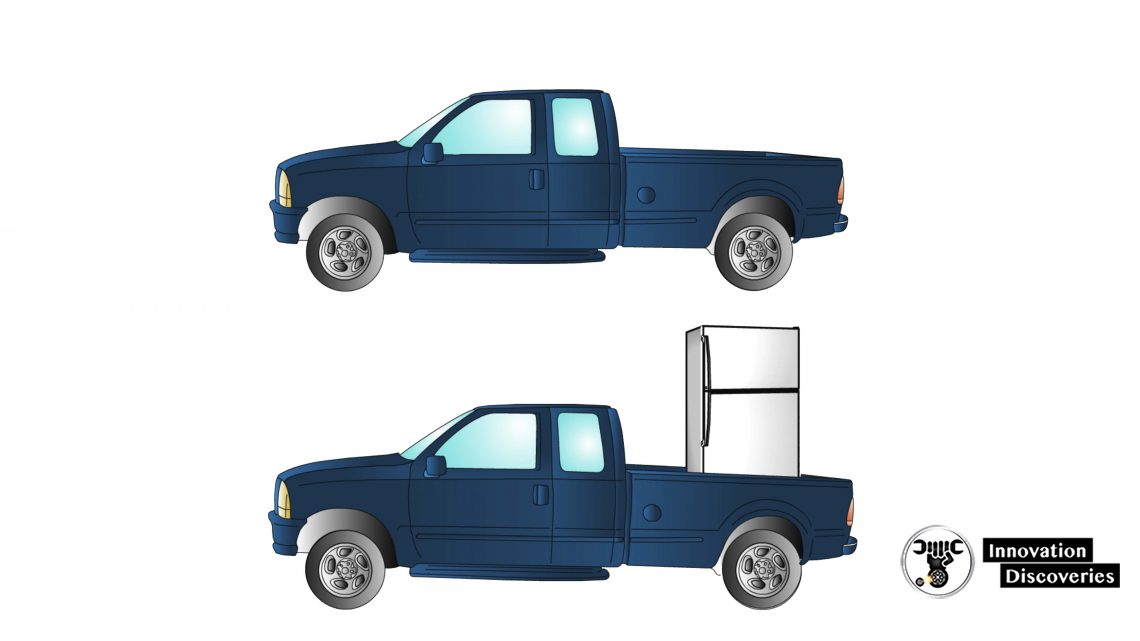
Caster and Ride Height
- It is important to consider normal vehicle loading when performing alignment checks and adjustments
- What effect does loading the truck have on the caster?
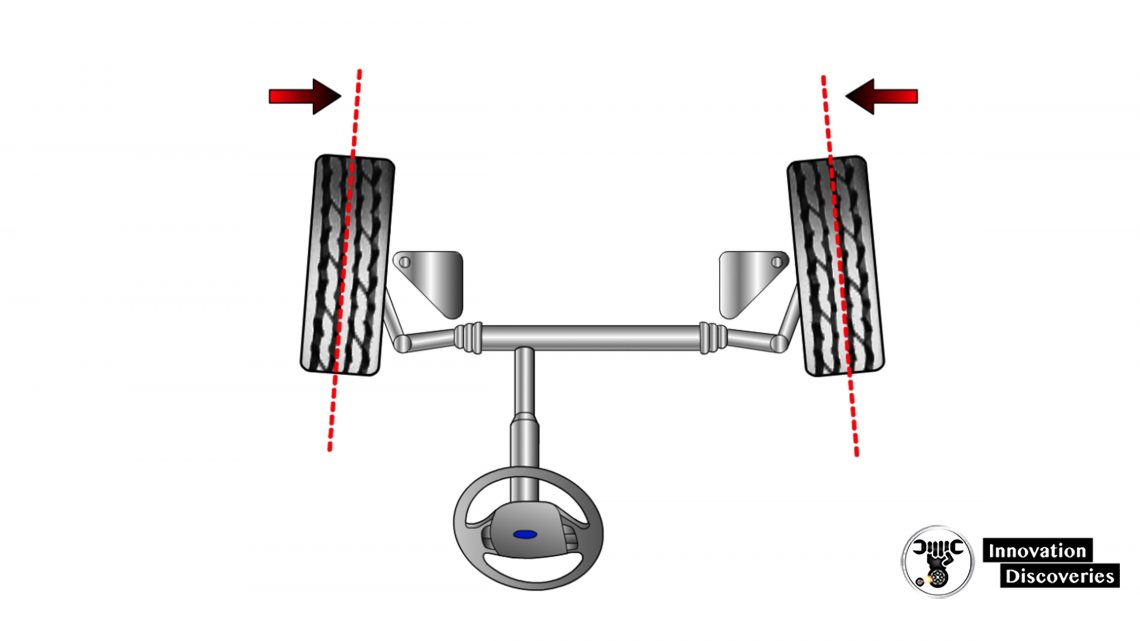
Toe Angle
- Inward or outward variation of tires from a straight-ahead position
- Toe-in is referred to as positive toe
- Toe out is referred to as negative toe
- Not a directional control angle
- Toe is a critical tire wear angle that commonly causes feathered tire tread wear
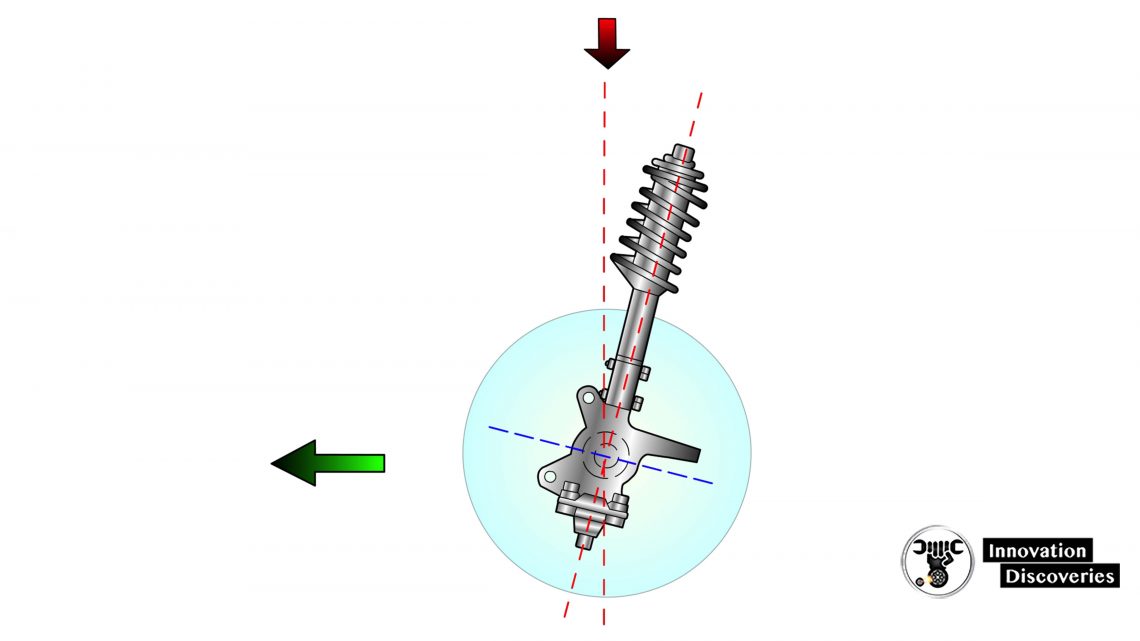
SAI and Included Angle
- SAI – Steering Axis Inclination
- The angle between the steering knuckle pivot points and true vertical
- Included Angle
- Sum of SAI and camber
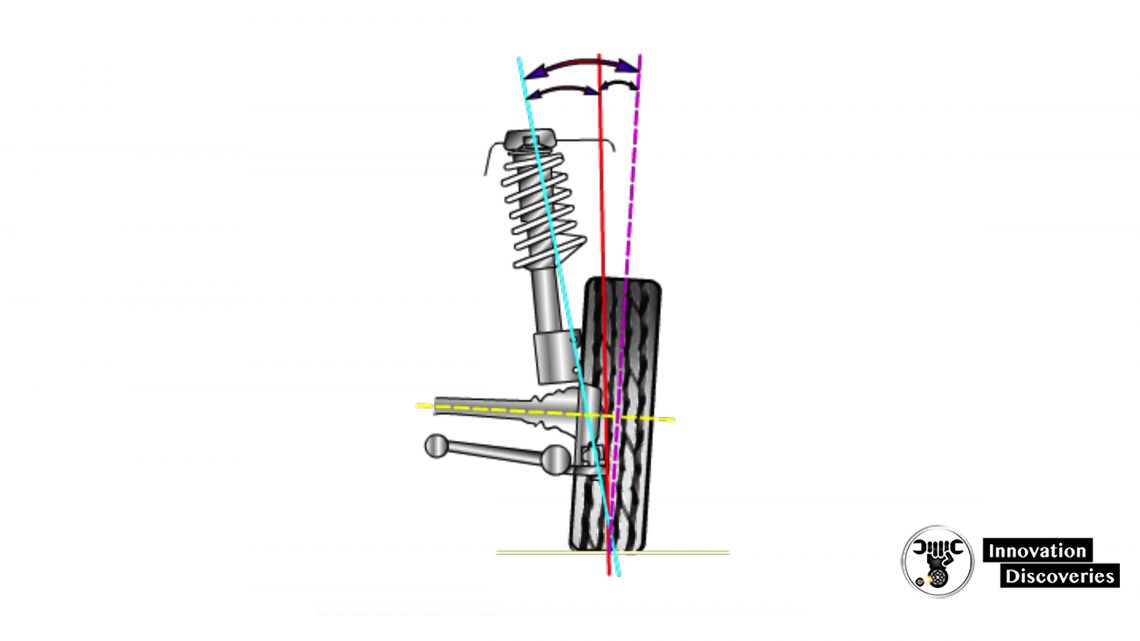
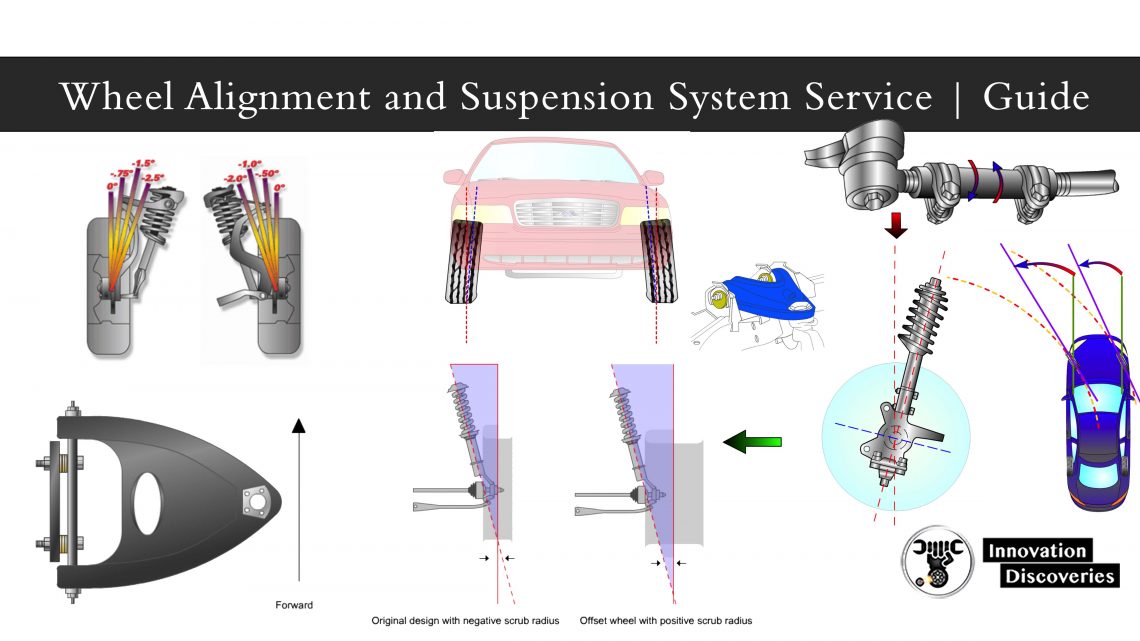
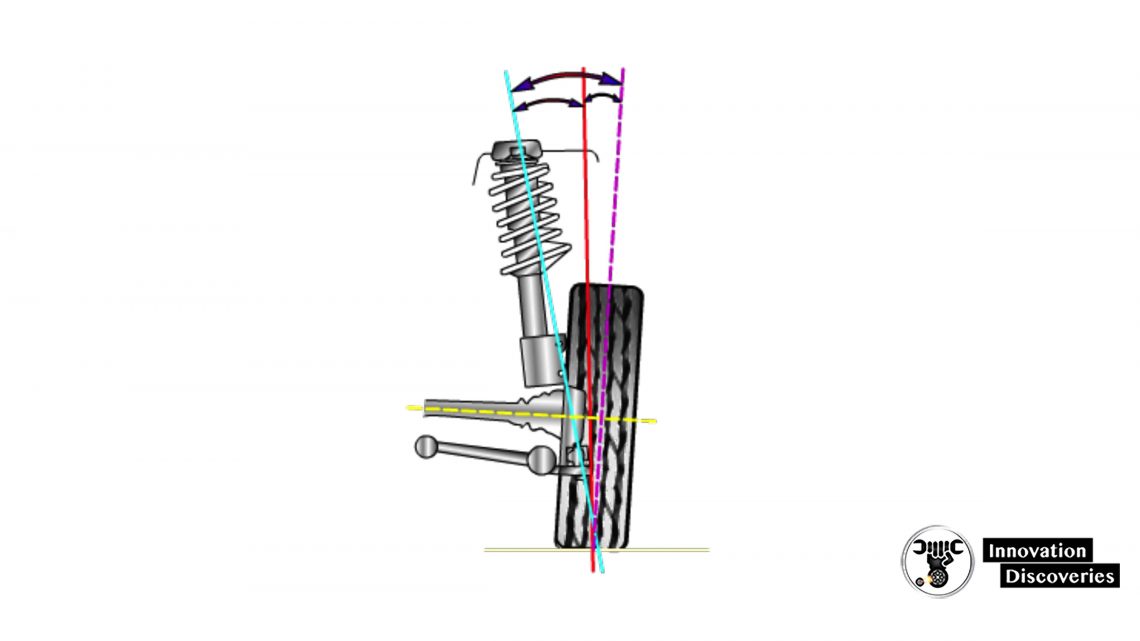
Scrub Radius
- Scrub radius is the distance between the tread centerline and the point where a projection of the steering axis angle would contact the road surface
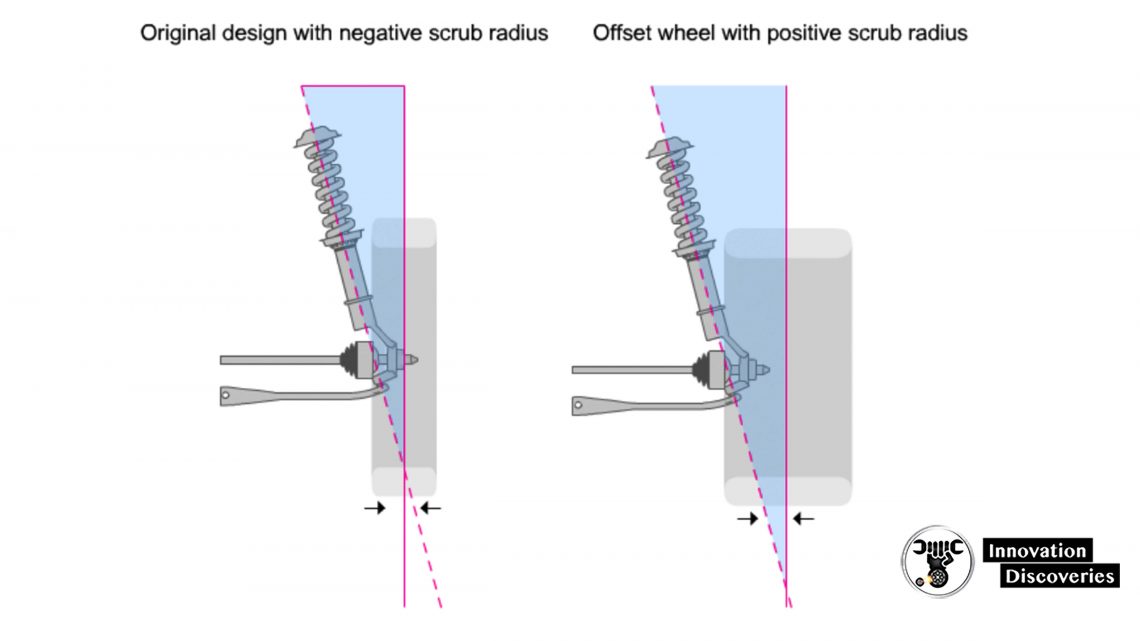
Scrub Radius & Wheel Offset
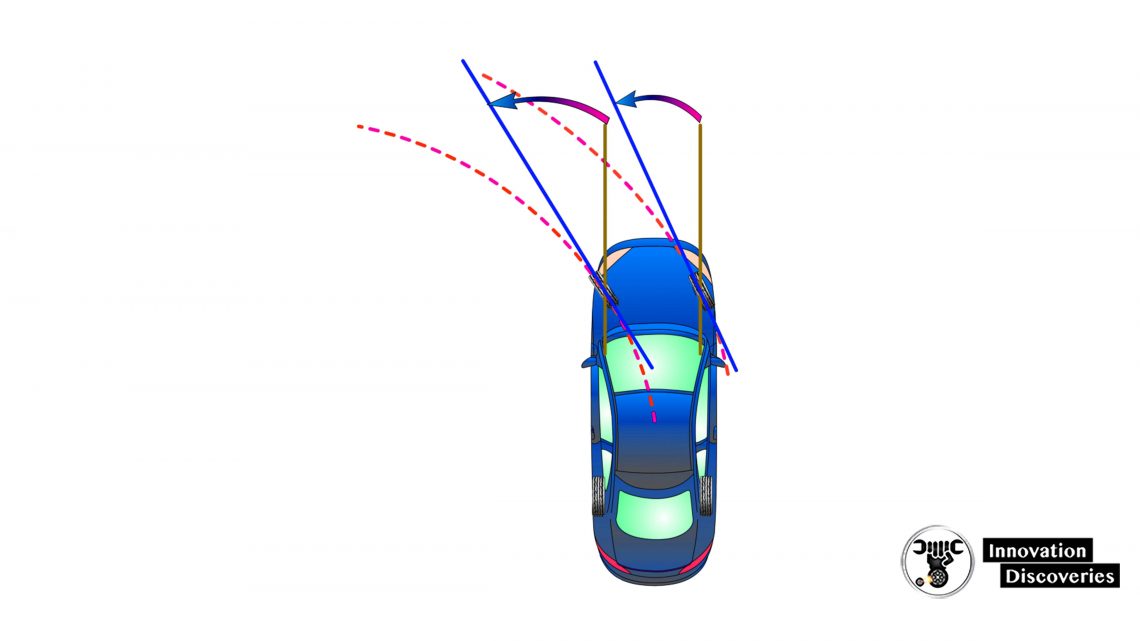
Toe Out On Turns
- Toe out on turns is the difference in turning angles between the two front tires measured at a specific turning angle
- Customer concerns about toe out on turns are usually related to tire squealing during low-speed parking manoeuvres
- Improper toe out on turns is commonly caused by bent or damaged steering linkage and/or steering knuckles
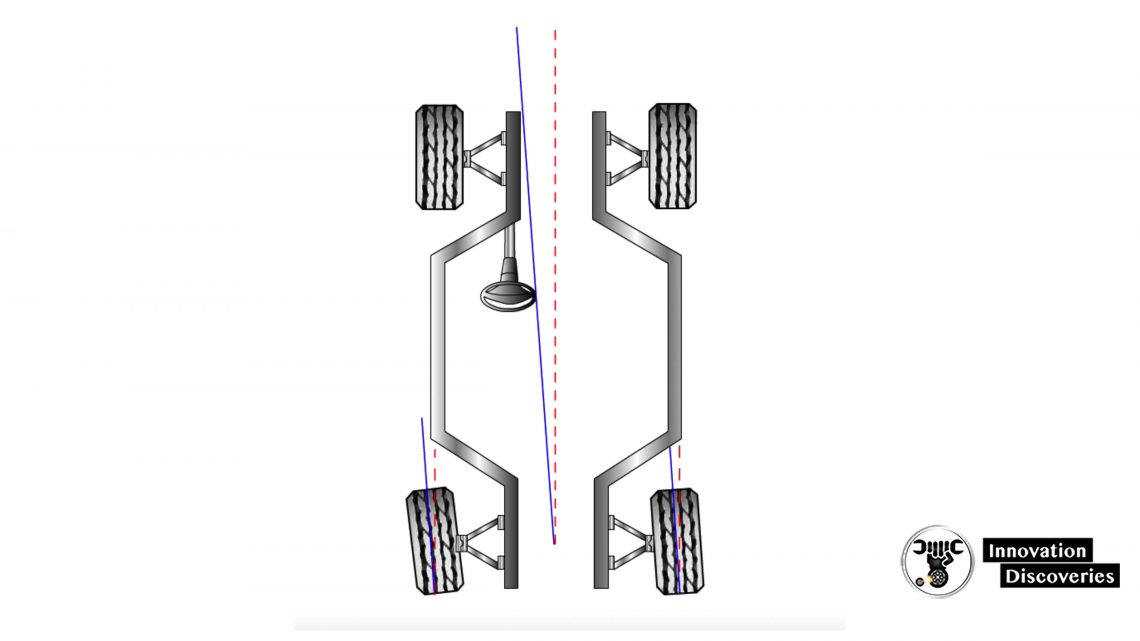
Thrust Angle
- Thrust angle is the difference between the centerline of the vehicle and the thrust line of the rear axle
- Negative – rear wheels point left
- Positive – rear wheels point right
Don’t Miss:
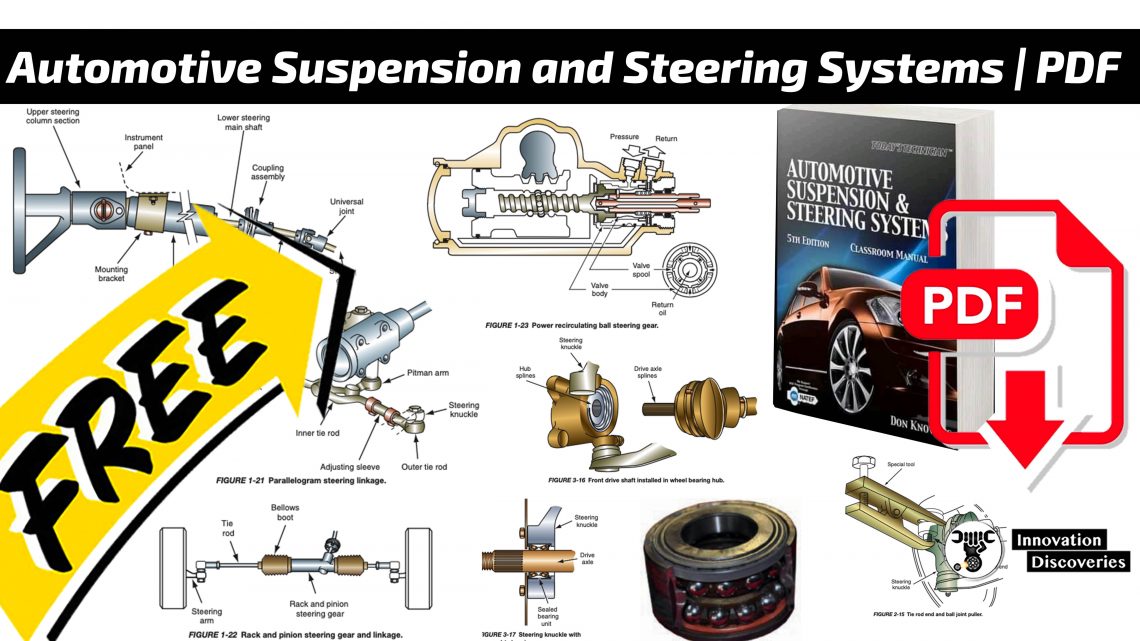
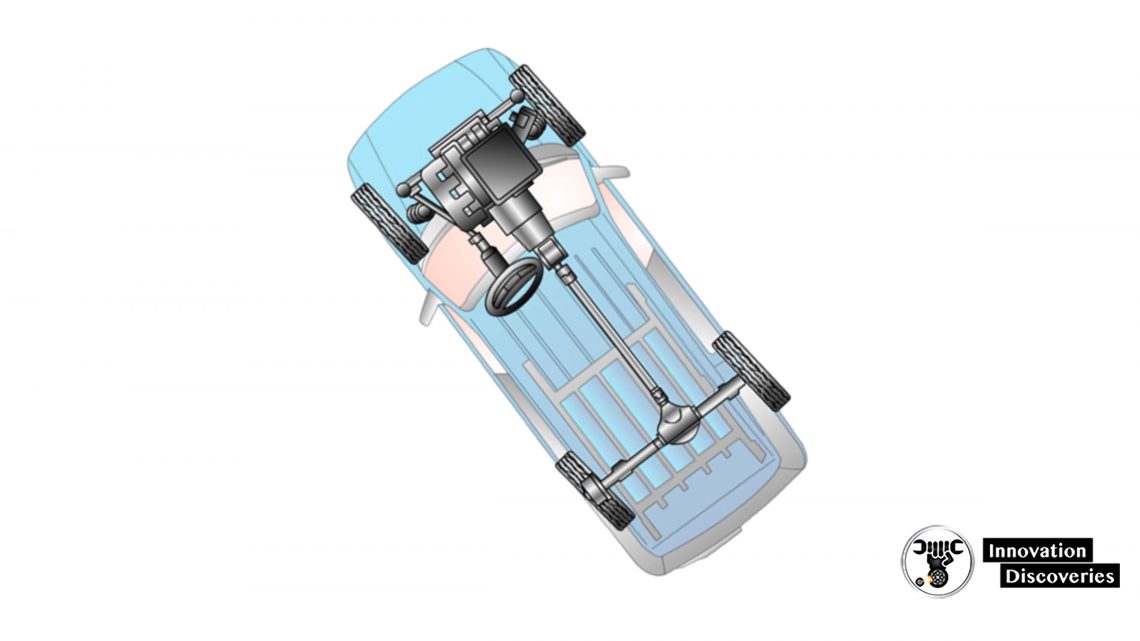
Suspension System
Suspension System Service
- Alignments are often considered part of routine vehicle maintenance
- A vehicle’s alignment should always be checked and adjusted after performing any steering or suspension system service that could impact alignment angles
- Proper wheel alignment affects vehicle handling, control, ride quality and tire life
Alignment Pre-Checks
- Tire pressure and condition
- Evidence of recent collision damage
- Ride height
- Wheel bearings
- Steering linkage
- Suspension components

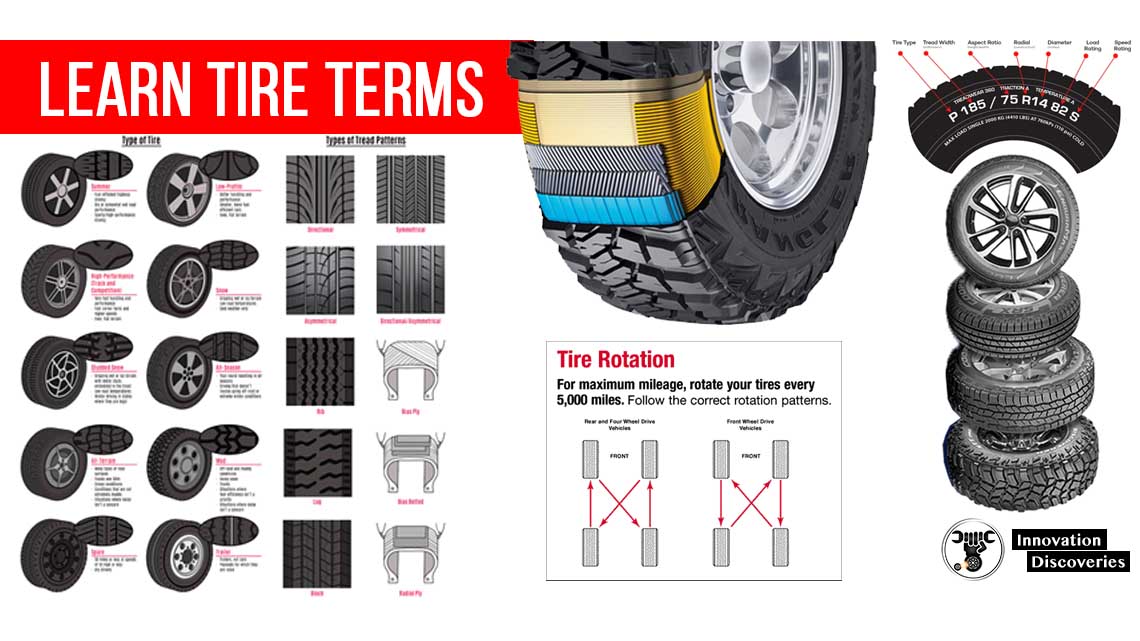
Tire Inspection
- Check and adjust tire pressure to the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications
- Inspect the tires for abnormal wear such as
- Center wear
- Wear on both outer edges
- Wear on one outer edge
- Feathering
- Cupping or damage
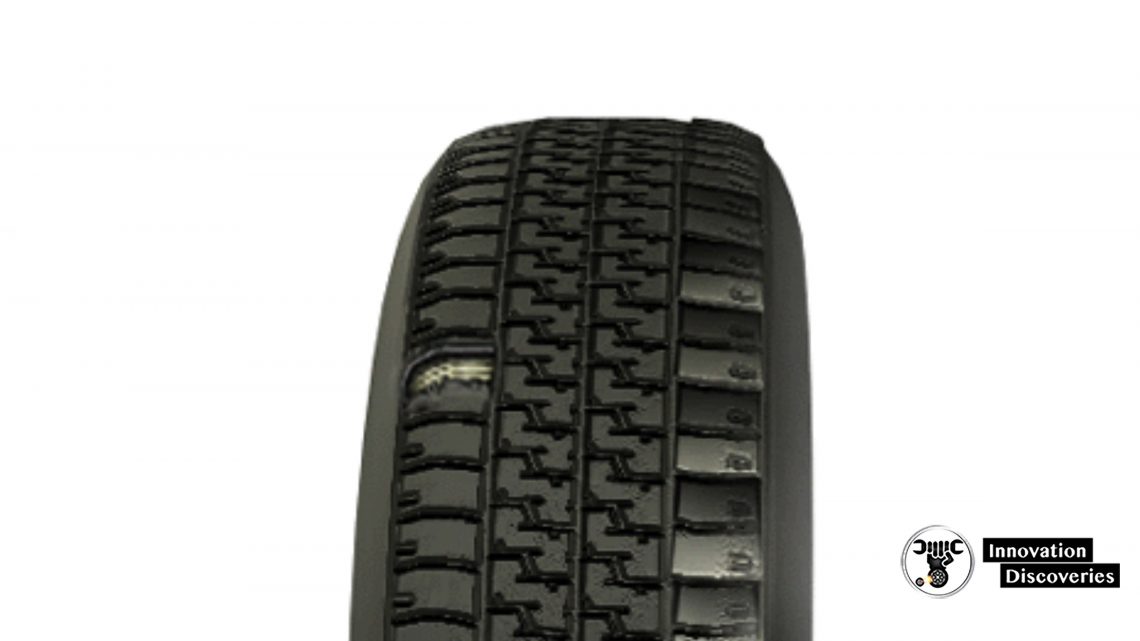

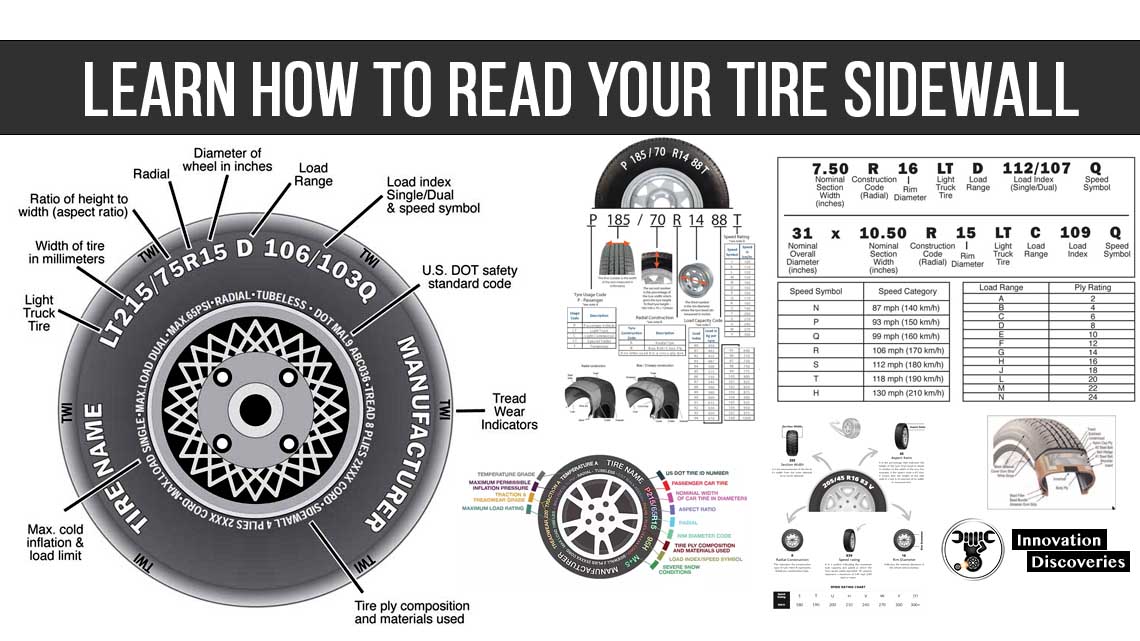
READ: Learn How to Read Your Tire Sidewall
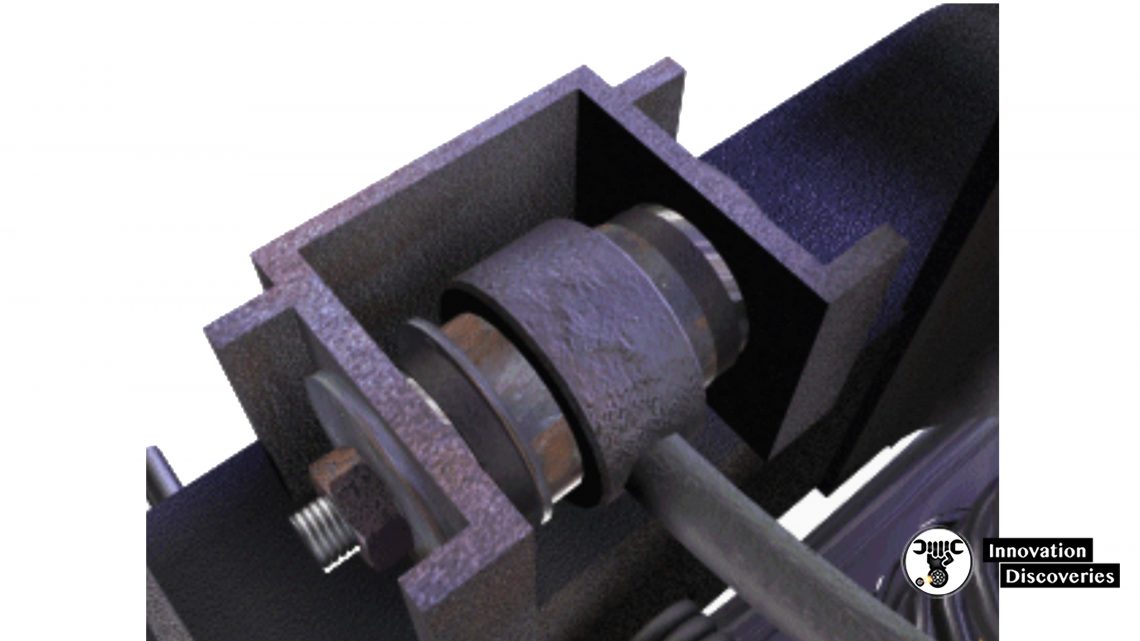
Bearing Adjustment Inspection
- Wheel bearings should be inspected for proper adjustment or excessive wear
- Attempt to rock the tire from top to bottom
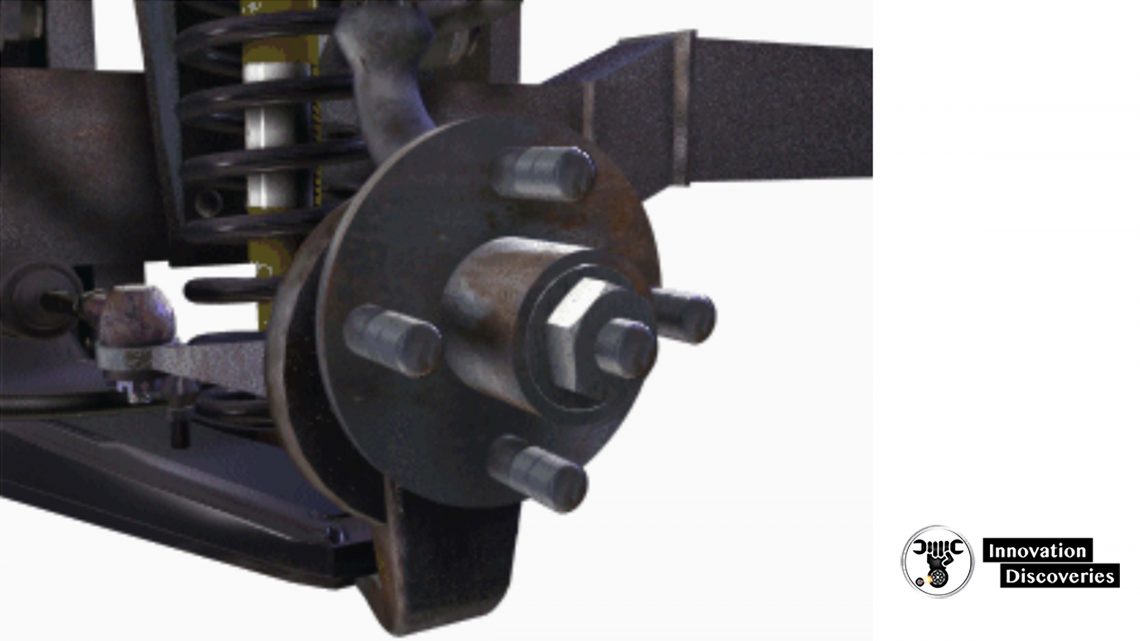

Steering Linkage Inspection
- The steering linkage should be inspected for excessive wear or damage
- Attempt to rock the tire from left to right
- Carefully inspect the linkage for evidence of damage
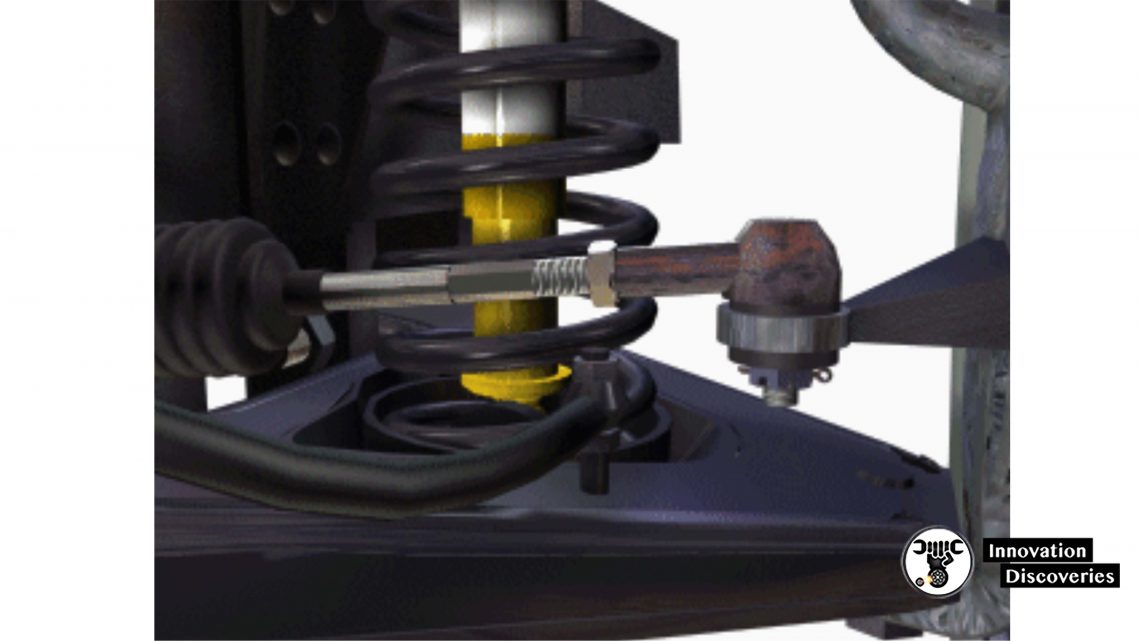

Suspension Inspection
- Inspect all bushings for evidence of damage, cracking and wear
- Inspect control arms, springs, ball joints, etc. for evidence of damage and wear
- Inspect shock absorbers and struts for leakage and damage
Types of Alignments
- Center line alignment
- The vehicle’s front wheels are aligned to the vehicle’s centerline
- Thrust angle alignment
- The vehicle’s front wheels are aligned to match the rear wheel’s thrust angle
- Four wheel alignment
- All four wheels are aligned to the vehicle’s centerline
Alignment Procedure
- Perform alignment pre-checks
- Set up the alignment computer as per the equipment manufacturer’s instructions
- Mount and compensate the alignment sensor heads
- Measure caster
Alignment Adjustments
- Compare the alignment specifications to the vehicle’s actual settings and adjust in the following order
- Rear camber
- Rear toe
- Front caster
- Front camber
- Front toe
Camber and Caster Adjustment
- Camber is adjusted by moving the top of the tire inward or outward
- The caster is adjusted by moving the upper steering pivot point forward or backwards
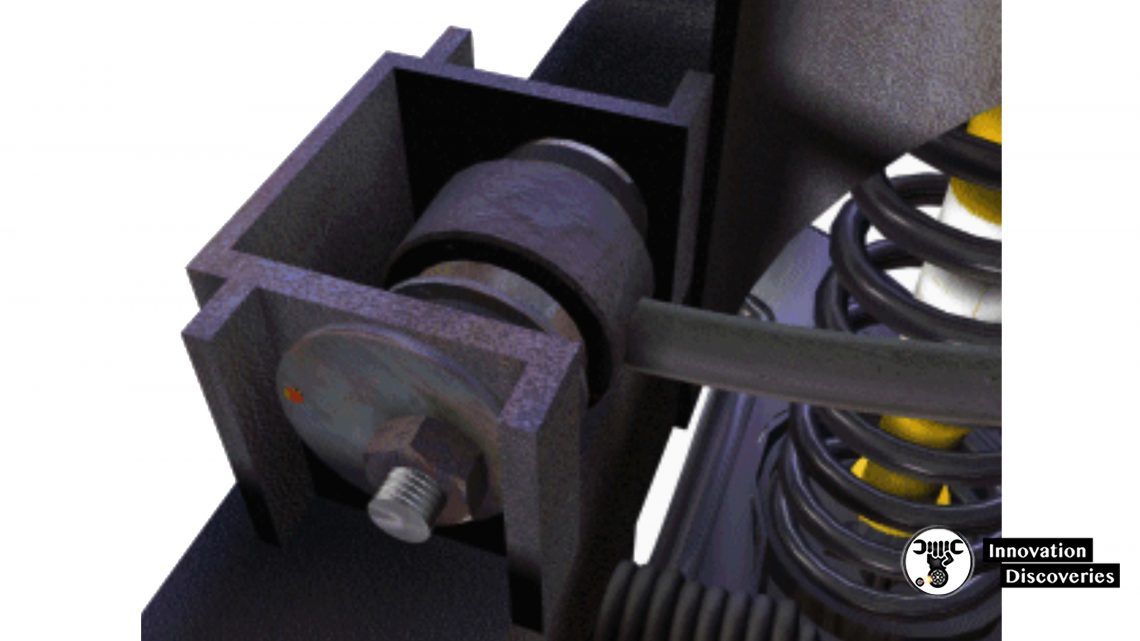

Control Arm Shims
- Adding shims between the control arm and frame as shown moves the upper ball joint inward
- Changing the shim pack dimensions allows the technician to change the caster and camber
- Some vehicles use shims to move the control arm outward
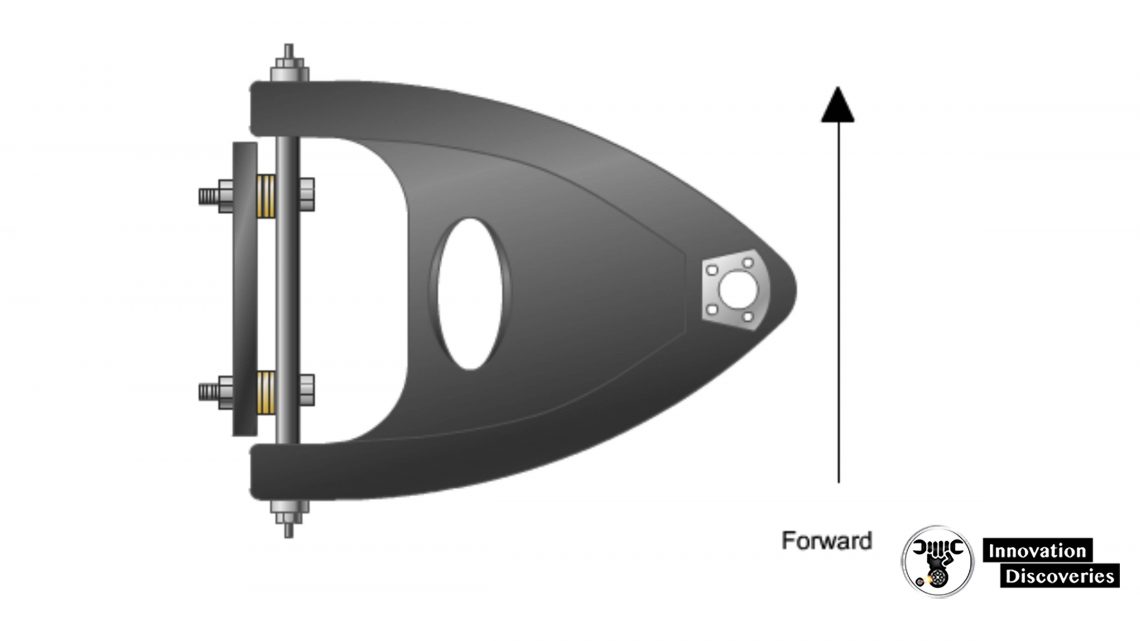
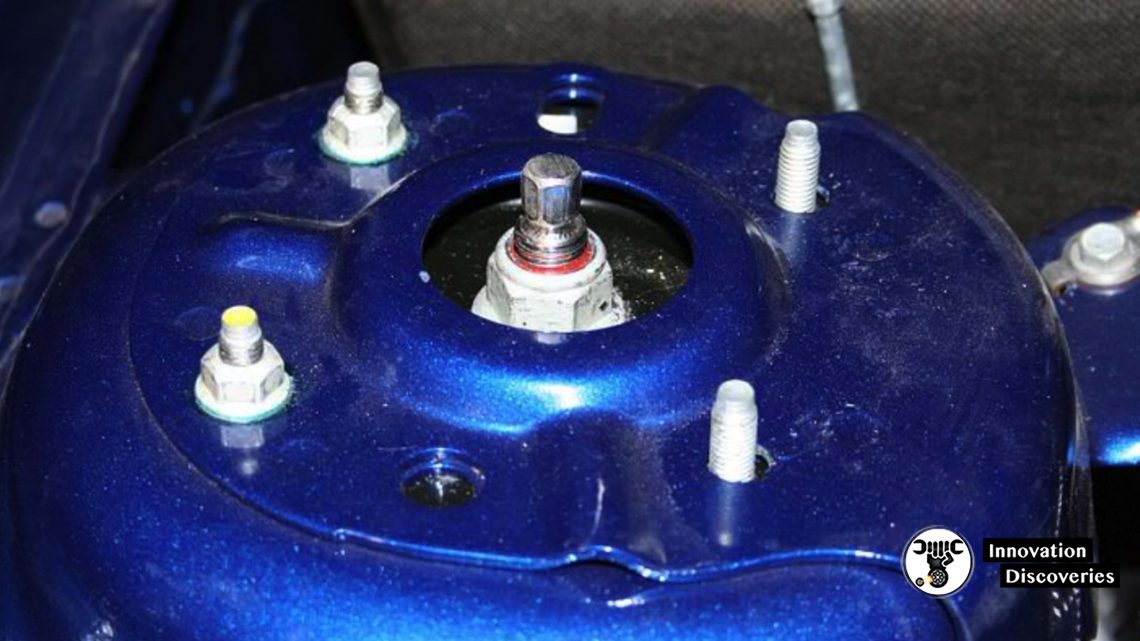
Moveable MacPherson Strut
- Elongated strut mounting holes may allow the strut to be moved to change the caster and/or camber
- Some vehicles require you to rotate the strut in mount holes to make changes in the caster and/or camber

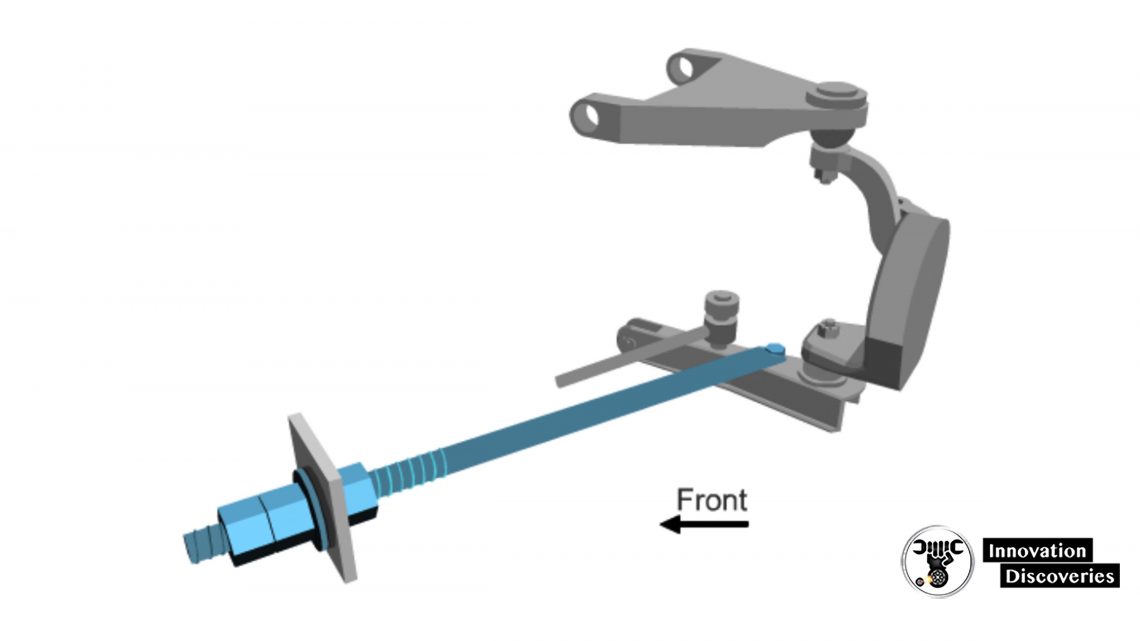
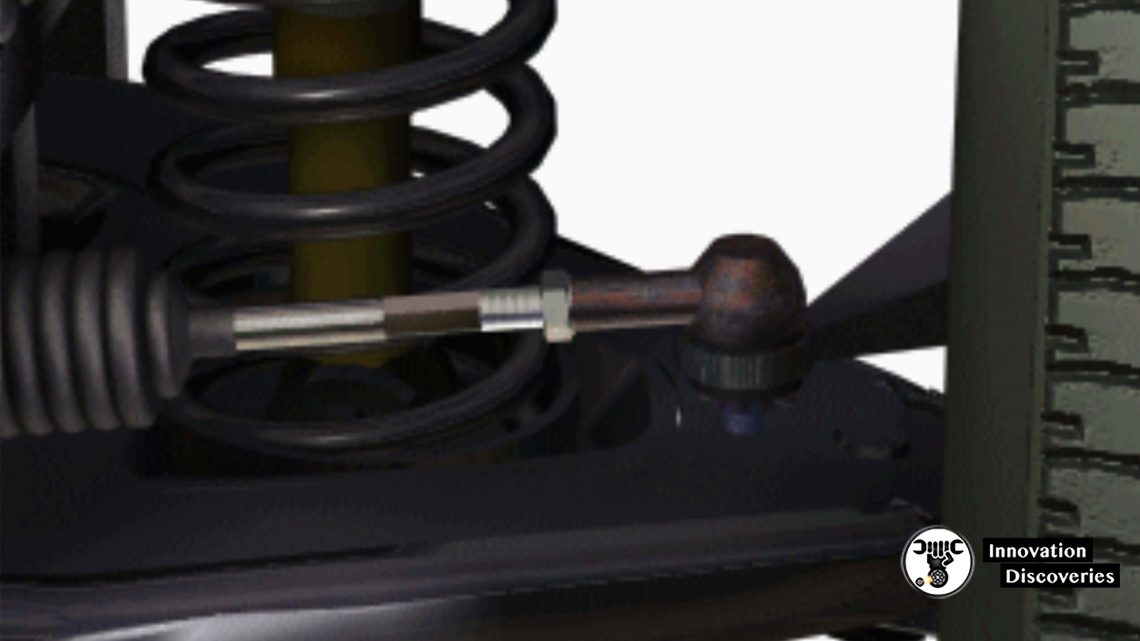
Adjustable Strut Rod
- Change strut rod length moves the lower ball joint to be shifted forward and rearward
- Moving the lower ball joint forward increases the caster
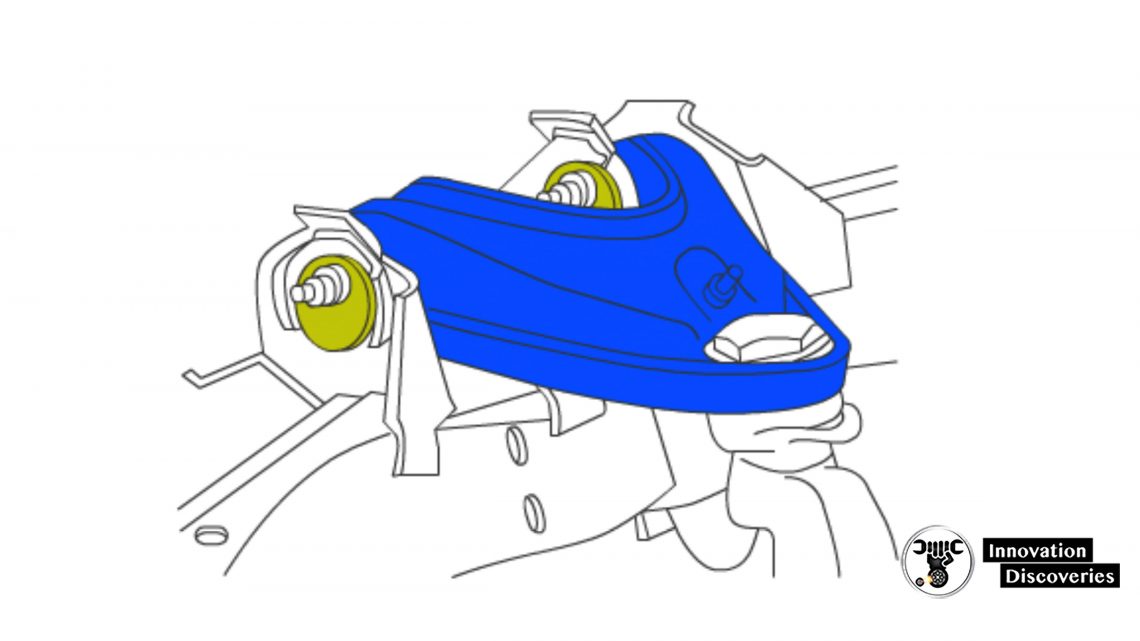
Control Arm Cams
- Eccentric cams allow the technician to move the upper ball joint in and out
- Moving both eccentrics equally changes only camber
- Moving one cam in and the other cam out an equal amount changes only the caster
Toe Adjustment
- Toe is adjusted to set the tires parallel to one another while the vehicle is moving
- Toe is adjusted by increasing or decreasing the tie rod length

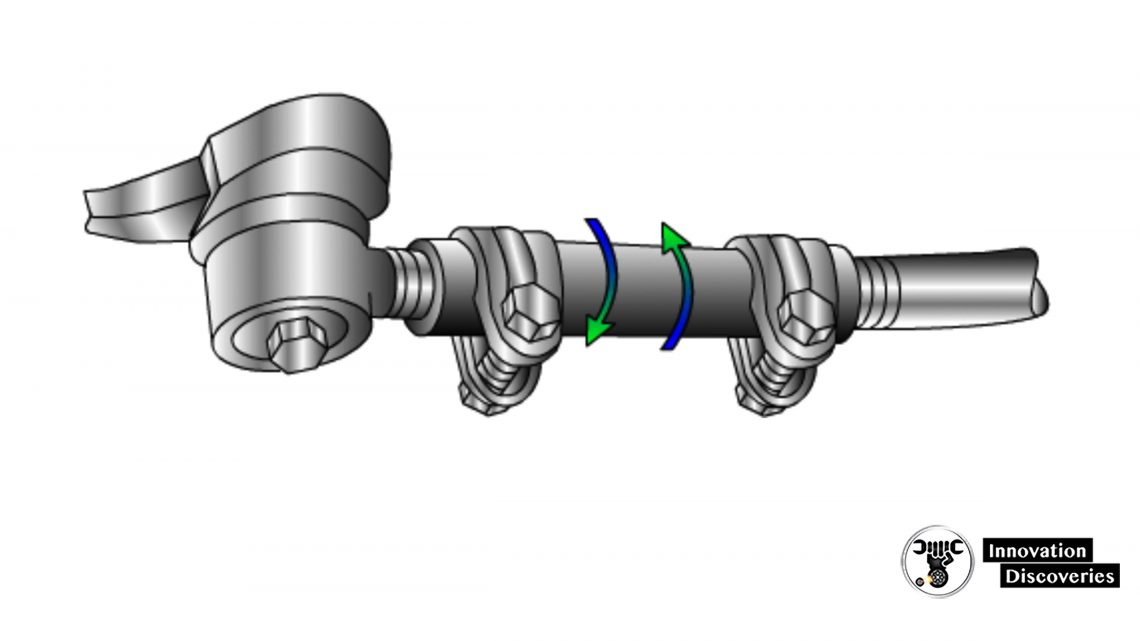
Toe Adjustment Procedure
- Set the steering wheel straight ahead and lock the wheel
- Parallelogram
- Loosen the clamps
- Rotate the adjuster sleeve
- Tighten the clamps
- Rack and pinion
- Loosen the tie rod end lock nut
- Rotate tie rod
- Tighten tie rod end lock nut
DISCOVER MORE:
READ MORE:
- A QUICK GUIDE TO DIAGNOSING 10 COMMON STEERING ISSUES
- 5 WARNING SIGNS OF BAD INTERMEDIATE STEERING SHAFTS
- 3 COMMON SYMPTOMS OF LOW POWER STEERING FLUID
- ELECTRIC VS HYDRAULIC POWER STEERING
- HOW POWER STEERING WORKS?
- STEERING SYSTEM: REQUIREMENTS, TYPES, POWER STEER

Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website