Why do we use the engines?
The engine converts heat energy to mechanical output.
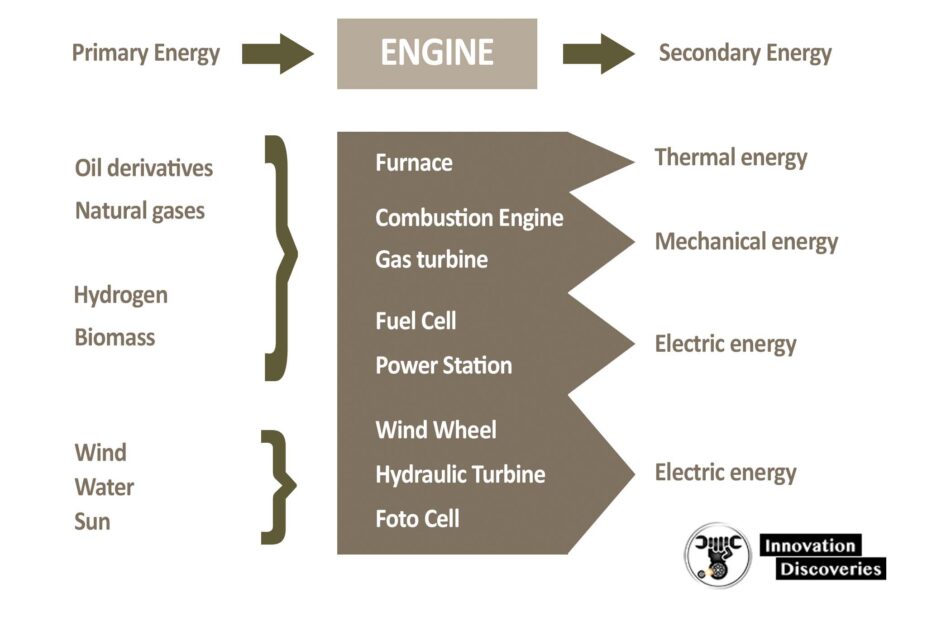
The following diagram describes that primary energy can be converted into secondary energy using an engine.
Engine Types
- Heat engines
- Non-thermal chemically powered motors
- Electric motors
- Physically powered motors
1) Heat engines
The heat engine is,
Is the engine that converts thermal energy into mechanical output.
- Combustion engines
- Non combustion engines
- Combustion engines
Combustion engines are,
Engines that run on heat from a high-temperature chemical reaction between a fuel and atmospheric oxygen (combustion) process,
They are classified as follows.
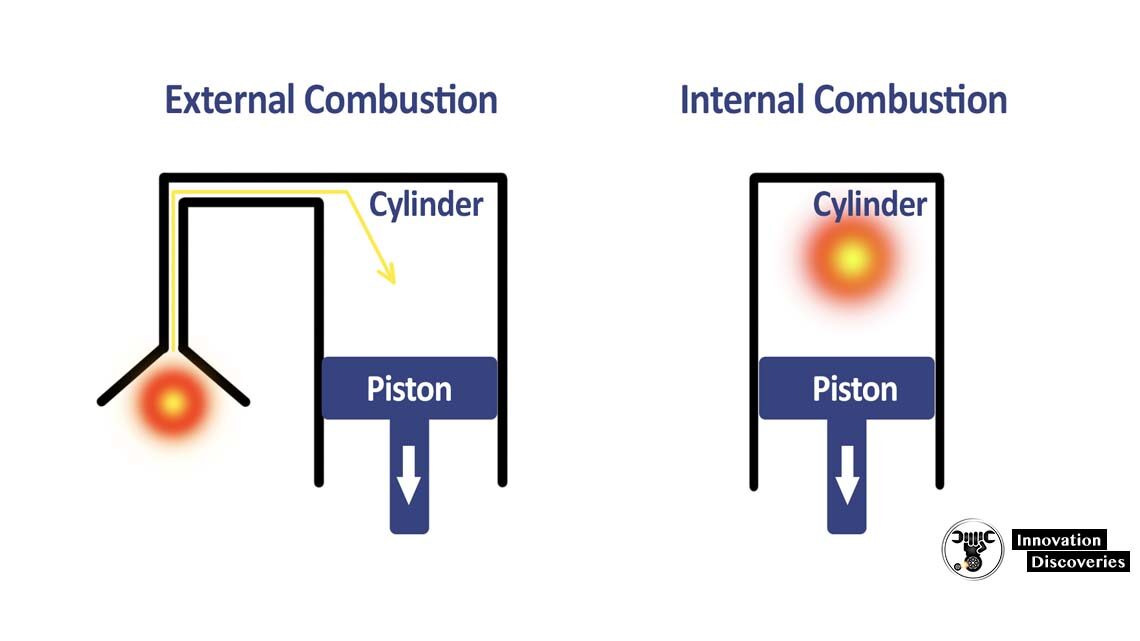
· Internal combustion engines (IC engines)
· External combustion engines (EC engines)
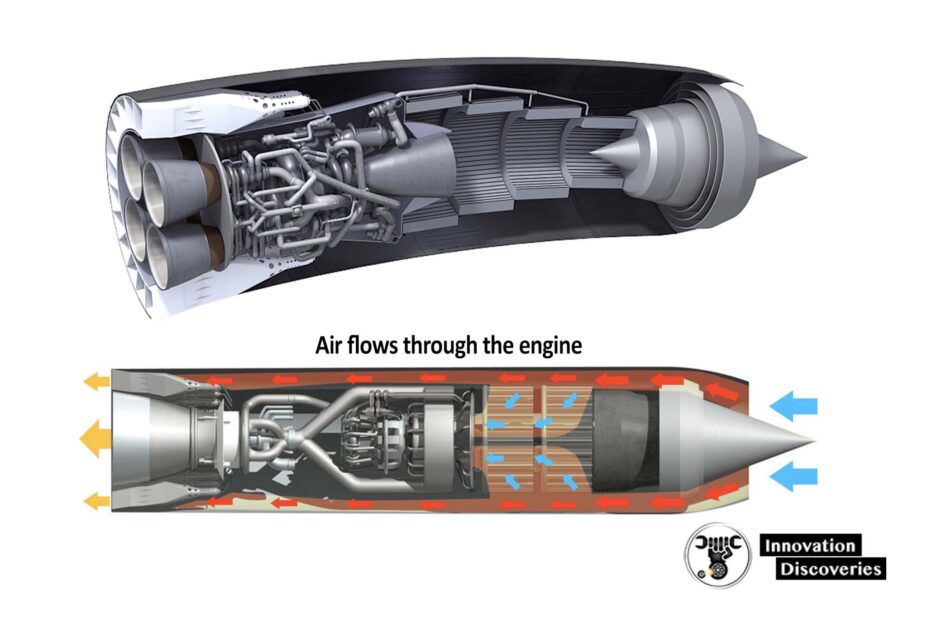
· Air-breathing combustion engines
The representation of extremal and internal combustion
An air-breathing rocket engine
Both EC and IC engines can be divided as,
- Reciprocating engines
- Rotary engines
- Non-combusting engines
There are some engines that convert heat into mechanical work output by the non-combustive process.
These are called non-combusting engines.
Eg:
- Some rocket engines
- Steam engines in nuclear power plants.

2) Non-thermal chemically powered motors
These are usually powered by chemical reactions.
e.g.: – Molecule motor, synthetic motor
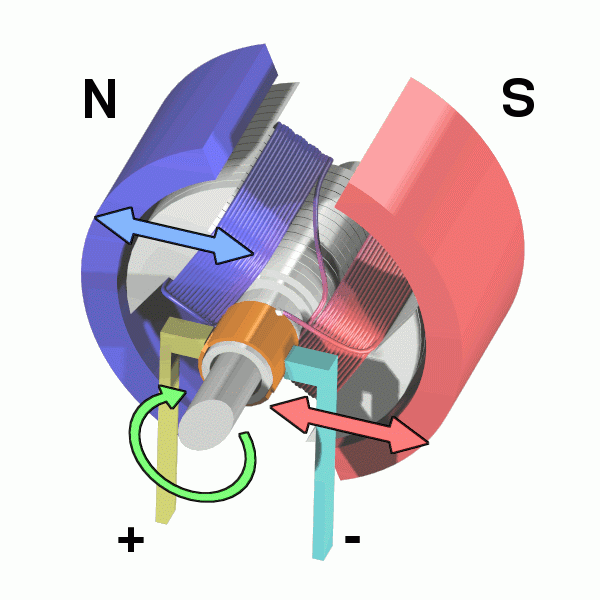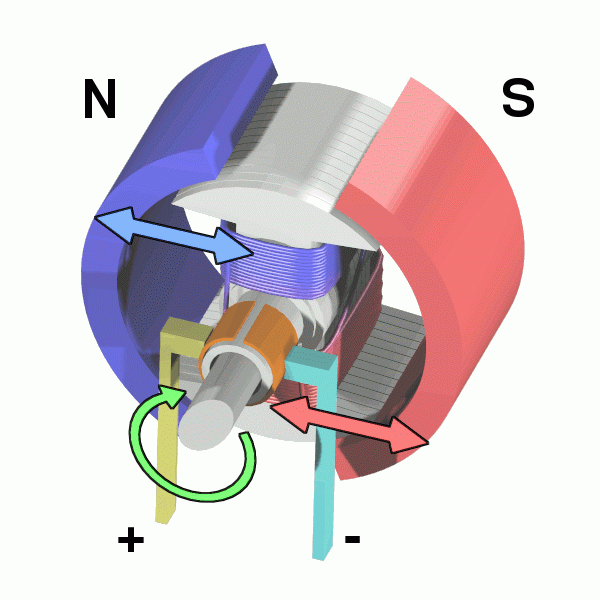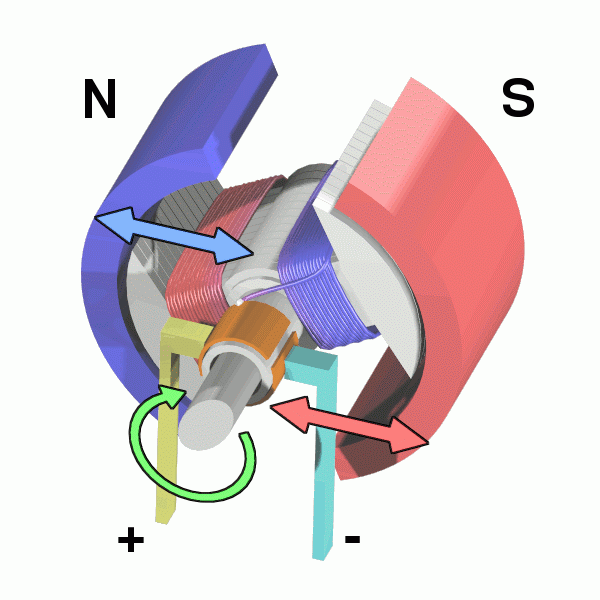
3) Electric motors
Electric motors are can convert electrical energy into mechanical work output by the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductions.
4) Physically powered motors
Physically powered motors,
Are motors powered by potential or kinetic energy
- Pneumatic motors
- Hydraulic motors
What is the most commonly used engine?
Heat engines are the most commonly used engines late 19th century,
Internal combustion engines are the most common type of heat engine.
The following diagrams show some of the common components of internal combustion engines.
Automobile engines can be divided by using the criteria of the configuration of the cylinder-piston system.
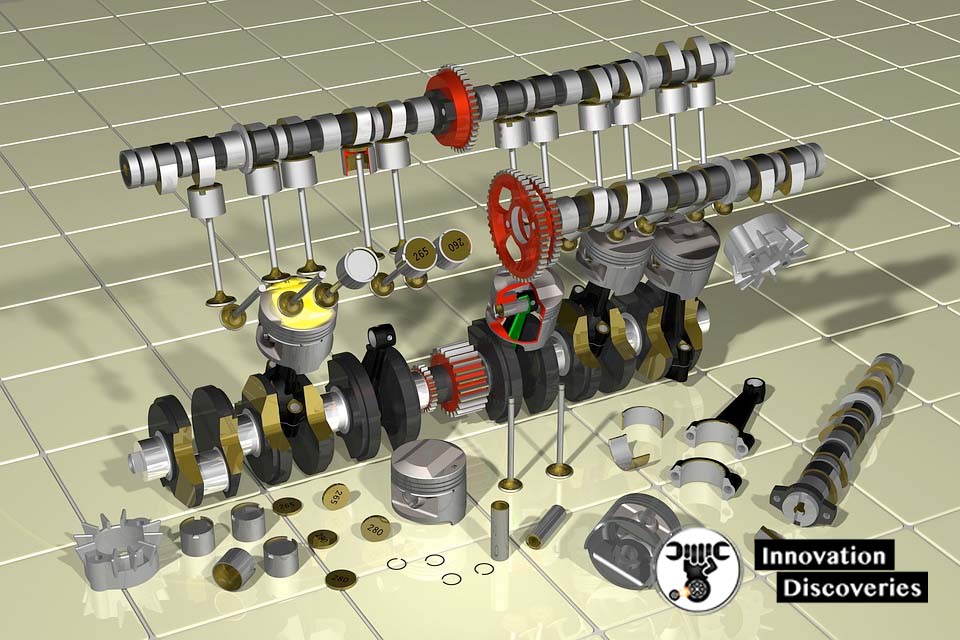
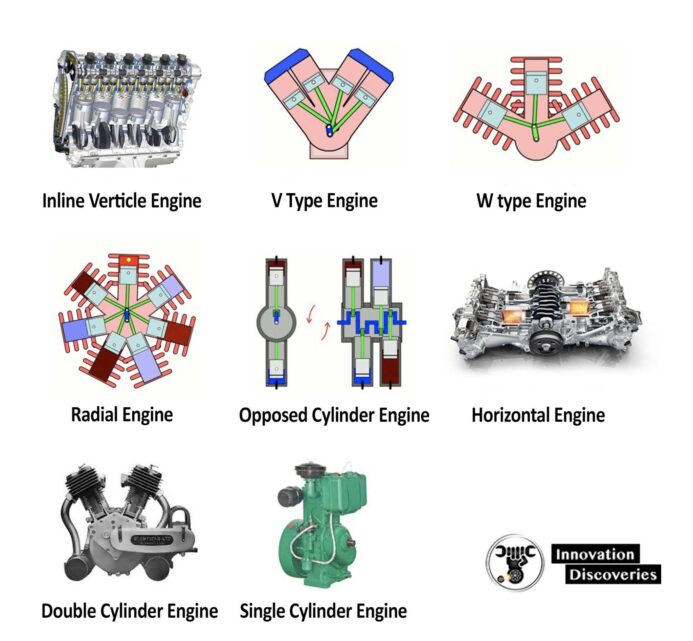
Those are as follows,
- In-line engine
- V-engine
- Radial engine
- Flat engine
- Dual-piston engine
- Opposed piston engine
- Manufacturing of engines
The engine body is made by casting.
By welding, other parts of an engine are made,
Forging: a lump of iron is heated red hot and then formed into parts by using a stumping machine.
Casting: pouring molten iron into a mold that is made by sand.
What are the materials used to manufacture the engine?
- Alloyed and structural steel
- Cast iron
- Aluminum alloys
- Aluminum
- Nickel
- Copper alloys
- Magnesium alloys
- Titanium and its alloys
- Cobalt base alloys
- Conclusion
The engine is the heart of an automobile or any other type of vehicle.
Read More:
- Troubleshooting and Repairing Diesel Engine
- What Is A Wankel Engine And How Does It Work?
- Crank Mechanism Construction
- Vehicle Exhaust Gases
- Kinetic Energy Recovery System (KERS)
- Engine Testing Theory and Practice | PDF





One Comment