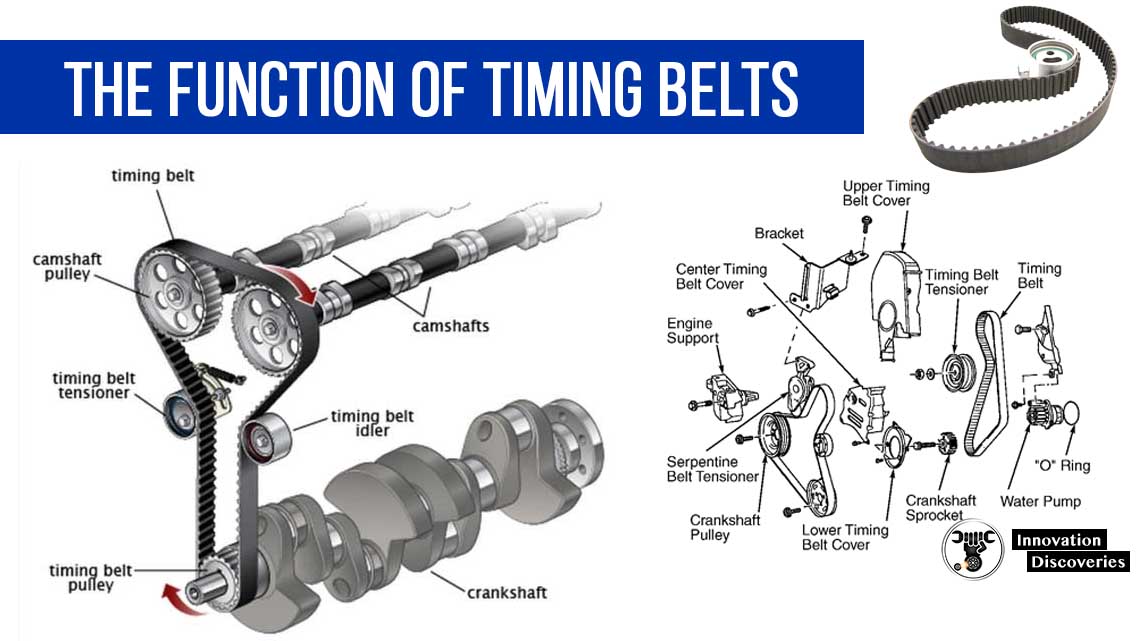
A timing belt is a crucial engine component that ensures your vehicle’s engine operates smoothly and efficiently. Often overlooked, this belt synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and the camshaft, allowing the engine’s valves to open and close at the correct intervals during the four-stroke combustion cycle.
What is a Timing Belt?
A timing belt, also known as a cam belt, is typically made of high-tensile synthetic rubber with embedded fiberglass or Kevlar cords for strength and durability. Its inner surface features precision-molded teeth that mesh with the pulleys on the crankshaft and camshaft(s), ensuring exact synchronization of engine components.
🔧 Key function: It ensures that the engine’s intake and exhaust valves open and close in precise coordination with the movement of the pistons.
How Does a Timing Belt Work?
In internal combustion engines — particularly overhead camshaft (OHC) engines — the crankshaft converts the linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion. The timing belt transfers this rotational force to the camshaft, which then actuates the valves.
In a four-stroke engine, this coordination occurs across four main strokes:
1. Intake Stroke
- The intake valves open.
- Air-fuel mixture enters the combustion chamber.
- The exhaust valves remain closed.
2. Compression Stroke
- All valves remain closed.
- The piston compresses the air-fuel mixture.
3. Power (Combustion) Stroke
- Spark plugs ignite the compressed mixture.
- A controlled explosion drives the piston downward.
- All valves remain closed.
4. Exhaust Stroke
- The exhaust valve opens.
- Combustion gases are expelled from the cylinder.
- The intake valve remains closed.
The timing belt ensures that all these phases occur in precise sequence and timing, typically at a 2:1 ratio between the crankshaft and camshaft rotations.
Read More: HOW ENGINE TIMING WORKS
Why Timing Matters: Valve Timing and Engine Efficiency
The term valve timing refers to the precise timing of valve operation in relation to piston movement. If the timing is off due to a worn or misaligned belt, the valves and pistons can collide — especially in interference engines, leading to catastrophic engine damage.
Related Topic:
HOW VARIABLE VALVE TIMING WORKS, AND HOW IT MAKES YOUR ENGINE BETTER
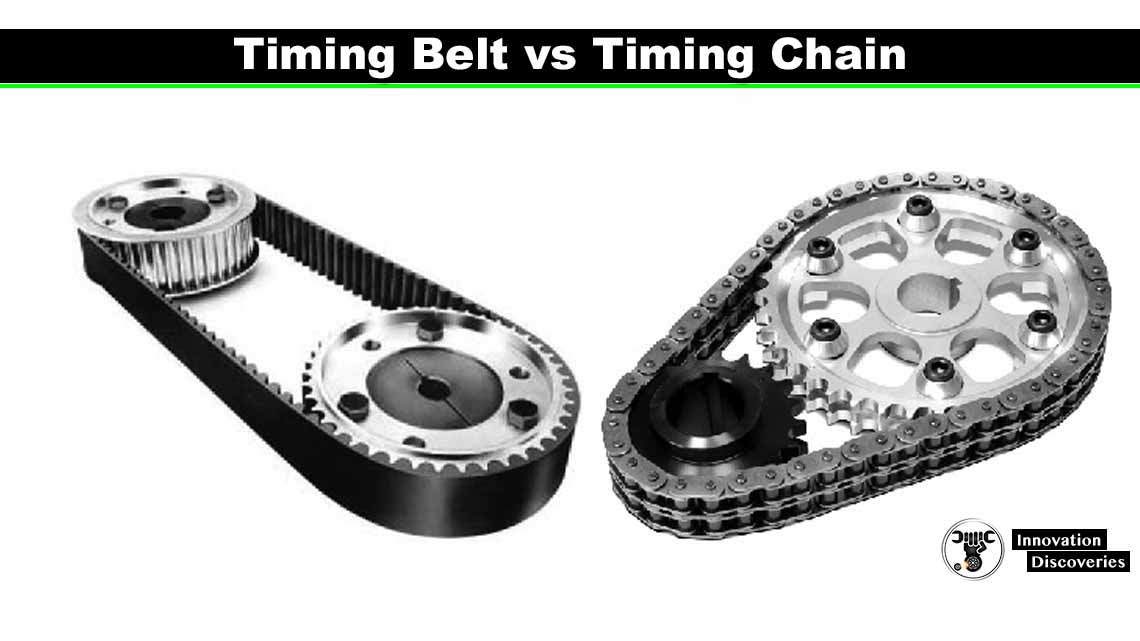
Timing Belt vs. Timing Chain
While timing belts are common in many modern vehicles due to their quieter operation and lighter weight, some engines use a timing chain, which generally lasts longer but is heavier and noisier.
Related Topic:
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CRANKSHAFT AND CAMSHAFT
What Happens if a Timing Belt Fails?
A broken timing belt can cause:
- Complete engine shutdown
- Valve damage from piston collisions
- Bent or broken connecting rods
- Cylinder head or camshaft damage
In interference engines, this failure often requires engine rebuilding or replacement, making preventive maintenance critical.
Read More: WHAT HAPPENS WHEN A TIMING CHAIN BREAKS WHILE DRIVING
When Should You Replace Your Timing Belt?
Most automakers recommend replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles (96,000 to 160,000 km). However, this can vary depending on:
- Manufacturer’s guidelines
- Driving conditions
- Belt material and design
🔍 Tip: Always refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the recommended service interval.
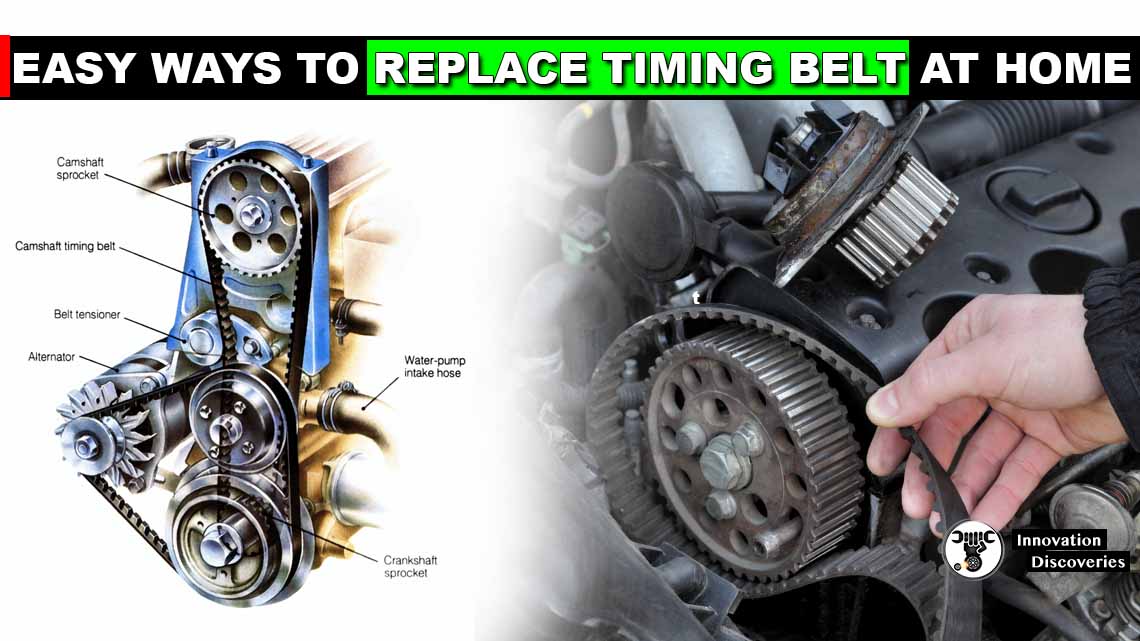
Why Timing Belt Replacement Is Not DIY-Friendly
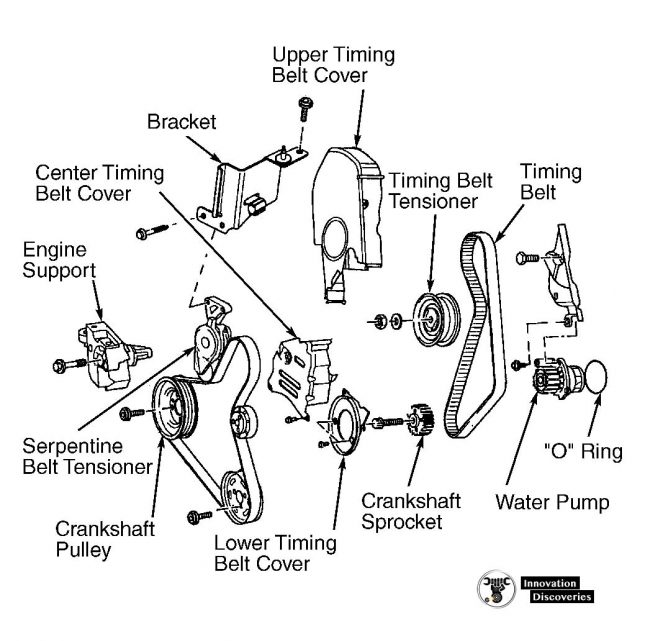
Timing belt replacement is a precision mechanical task that often requires removal of multiple engine components, including:
- Timing covers
- Tensioners and idler pulleys
- Possibly the water pump
After installation, the belt must be tensioned correctly and synchronized precisely with the crankshaft and camshaft using timing marks and, in some cases, specialized tools.
🛠️ Recommendation: Always have a certified technician perform this replacement.
Download: VALVE SELECTION HANDBOOK | PDF
🔧 Why Do You Need to Replace Your Engine’s Timing Belt?
A timing belt failure can result in catastrophic engine damage — especially in interference engines, where the pistons and valves occupy the same space at different times.
Over time, the belt may become worn, brittle, or stretched, which can cause:
- Valve timing misalignment
- Loss of synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft
- Piston-to-valve collisions (in interference engines)
- Bent valves, damaged pistons, or even a cracked cylinder head
Even a minor delay in valve timing can result in poor engine performance, misfires, or complete engine failure. That’s why proactive replacement of the timing belt is critical to preventing severe internal damage and costly repairs.
⏱️ When Should You Replace Your Engine’s Timing Belt?
Most manufacturers recommend replacing the timing belt every 60,000 to 100,000 miles (96,000 to 160,000 km). However, this interval may vary based on:
- Vehicle make and model
- Driving conditions (hot climates, stop-and-go traffic, etc.)
- Type of belt material (e.g., reinforced rubber or Kevlar)
🛑 Always consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the specific service interval.
⚙️ Why Timing Belt Replacement Requires a Professional
Replacing a timing belt is not a simple DIY task. It often involves:
- Removing engine accessories like the serpentine belt, engine covers, or even the radiator fan
- Detaching the water pump (in some models, it’s driven by the timing belt)
- Carefully aligning the timing marks on the crankshaft and camshaft(s)
- Properly tensioning the belt to avoid belt slippage or premature wear
After installation, the new belt must be synchronized precisely to maintain optimal valve timing and ensure smooth engine performance.
✅ Pro Tip: It’s often recommended to replace related components such as the tensioner, idler pulleys, and water pump during a timing belt service for maximum reliability.
Final Thoughts
A properly functioning timing belt is essential for engine performance and longevity. Ignoring the replacement schedule can lead to costly repairs or complete engine failure. By understanding the technical role of timing belts and maintaining them properly, you ensure your engine runs smoothly and reliably.
How To Change Timing Belt ( Mitsubishi 4d56 | Pajero | MK1 )
How to Replace Timing Belt 2007 Toyota Hilux Vigo
Also, Read:
Read More:
- Here’s How You Quickly Stop a Runaway Diesel
- The engine – how it drives its ancillary parts
- Water Pump Replacement
- 5 Reasons Behind Car Engine Vibration
- VALVE TRAIN: COMPONENTS, TYPES AND THEIR FUNCTION
- Symptoms of an Exhaust Leak
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website





3 Comments