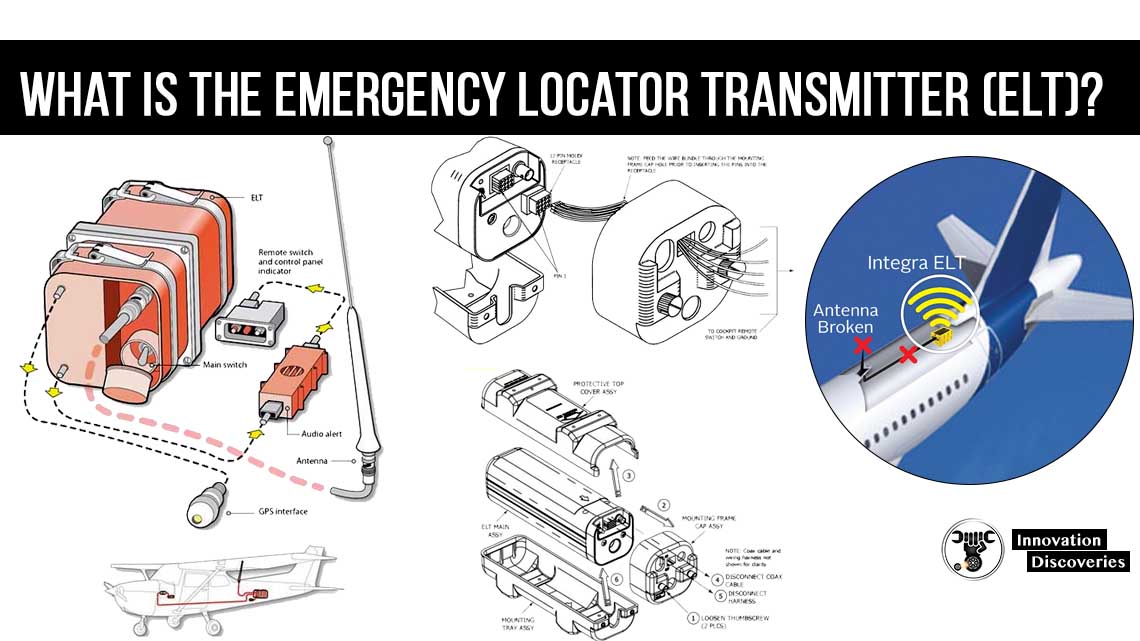
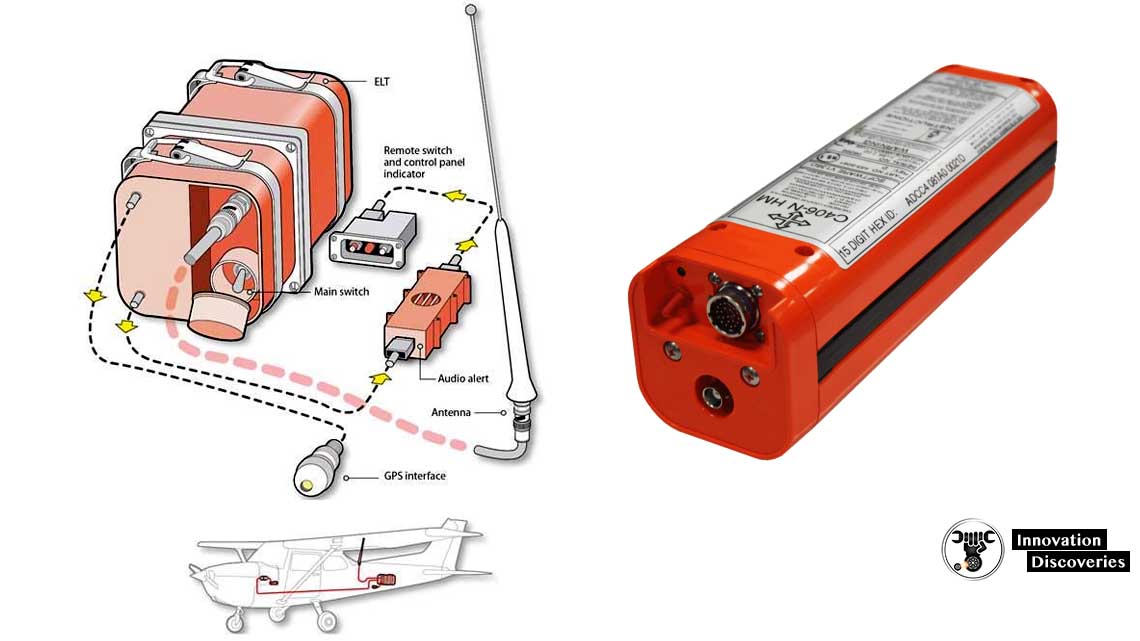
Introduction
The Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) is a critical safety device in aviation, designed to facilitate the swift location and rescue of aircraft in distress.
The disappearance of Malaysia Airlines flight MH370 in 2014, despite having an ELT on board, highlights the importance and limitations of this technology.
This article delves into the intricacies of ELTs, their functionality, installation, and the advancements in this field.
How Does an ELT Work?
An ELT is a self-contained, battery-powered device that activates upon experiencing the significant G-forces associated with a crash.
Upon activation, it transmits a digital distress signal every 50 seconds on a frequency of 406.025 MHz at a power output of 5 watts.
This transmission is designed to last for at least 24 hours, providing a critical window for search and rescue operations.
Signal Transmission and Reception
The distress signal emitted by the ELT is received by the COSPAS-SARSAT satellite system, a global network dedicated to search and rescue. This system consists of two types of satellites:
- Low Earth Orbiting Satellites (LEOSATs): These satellites orbit the Earth at altitudes of approximately 800 to 1,000 kilometers. They offer near-global coverage and can quickly detect ELT signals as they pass overhead.
- Geostationary Satellites (GEOSATs): Positioned at an altitude of about 35,786 kilometers, GEOSATs remain stationary relative to a fixed point on the Earth’s surface. They provide continuous coverage of large areas but rely on LEOSATs for precise location information.
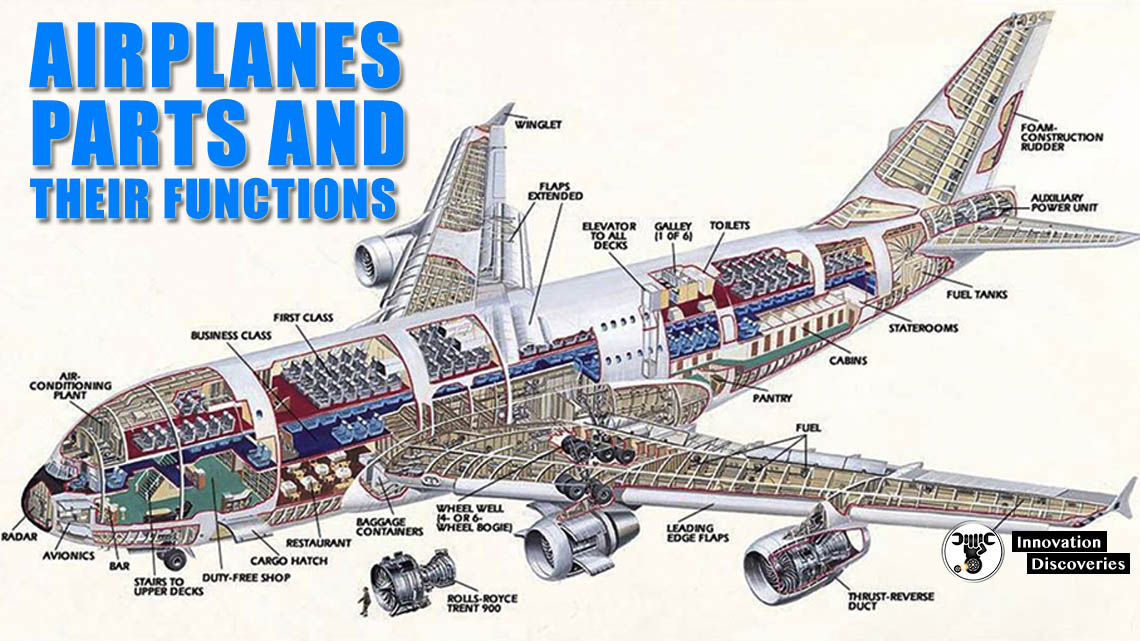
READ MORE: AIRPLANES: PARTS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
Processing and Response
Once the signal is received by the satellites, it is partially processed and stored before being relayed to ground stations known as Local User Terminals (LUTs).
These ground stations further process the signal to verify its authenticity and determine its location. The processed information is then sent to Mission Control Centers (MCCs), which coordinate the appropriate search and rescue operations.
This process ensures that resources are effectively deployed and false alerts are minimized.
Installation and Activation
ELTs are typically installed in the rear section of the aircraft, just forward of the empennage (the tail assembly).
This location is chosen because it is often the least damaged part in a crash, increasing the likelihood that the ELT will remain functional. The built-in G-force sensor is aligned with the longitudinal axis of the aircraft to accurately detect crash forces.
In helicopters, ELTs may be mounted elsewhere on the airframe, depending on the specific design and requirements.
ELTs are equipped with multidirectional activation devices, allowing them to activate regardless of the aircraft’s orientation upon impact. Additionally, many modern ELTs include GPS receivers, which significantly enhance the accuracy of the location data transmitted.
This GPS data can pinpoint the crash site within 100 meters, greatly improving the efficiency of search and rescue operations.
Helicopter ELTs may be located elsewhere on the airframe.
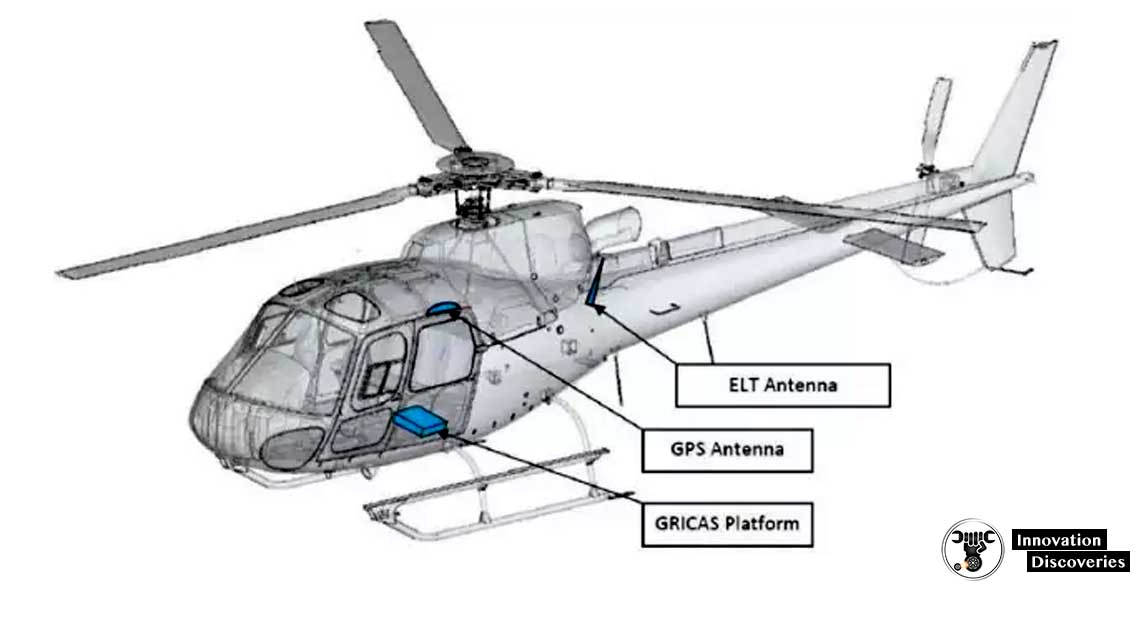
Additional Features and Regulations
- Dual Frequency Transmission: Besides the primary 406 MHz digital signal, ELTs can also transmit on 121.5 MHz, an analog frequency used for homing purposes by nearby aircraft and ground search teams. Although 121.5 MHz was once monitored by satellites, this function has been phased out in favor of the more accurate 406 MHz standard.
- Manual and Automatic Activation: ELTs are designed for both automatic and manual activation. In the event of a crash, the built-in G-force sensor triggers the device automatically. However, the flight deck is also equipped with a panel that allows the pilot to manually activate, test, or arm the ELT. This ensures the device can be activated in scenarios where the automatic trigger might fail.
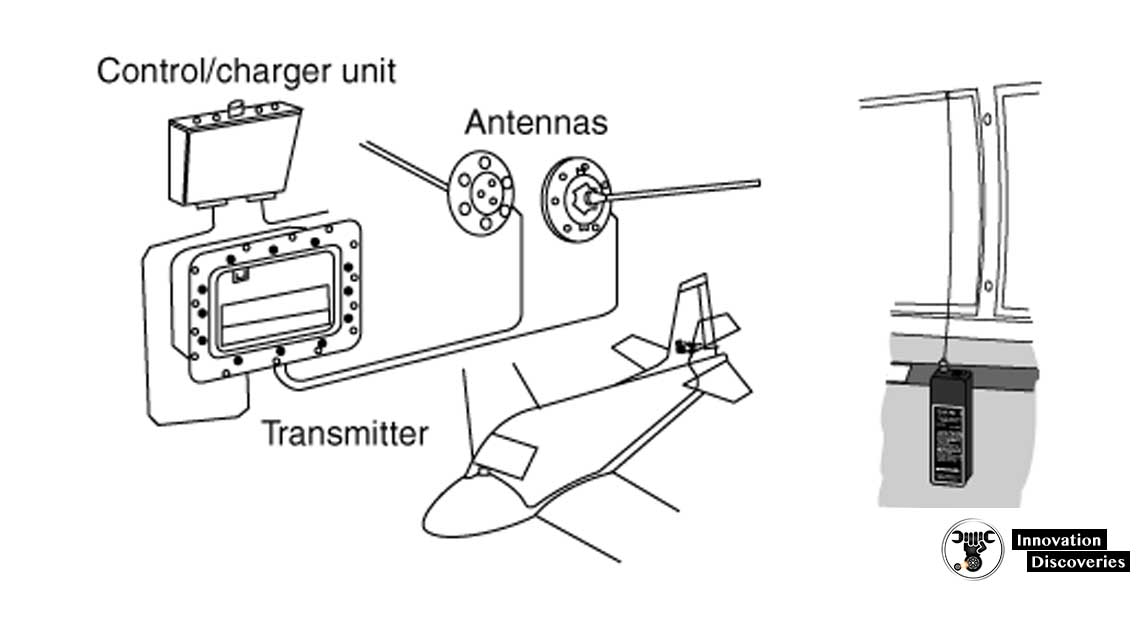
- Portable Usage: Many ELTs are designed to be easily removable from the aircraft and carried by crash survivors. These portable units often include a deployable antenna, enabling continuous transmission of the distress signal even if the survivors move away from the crash site.
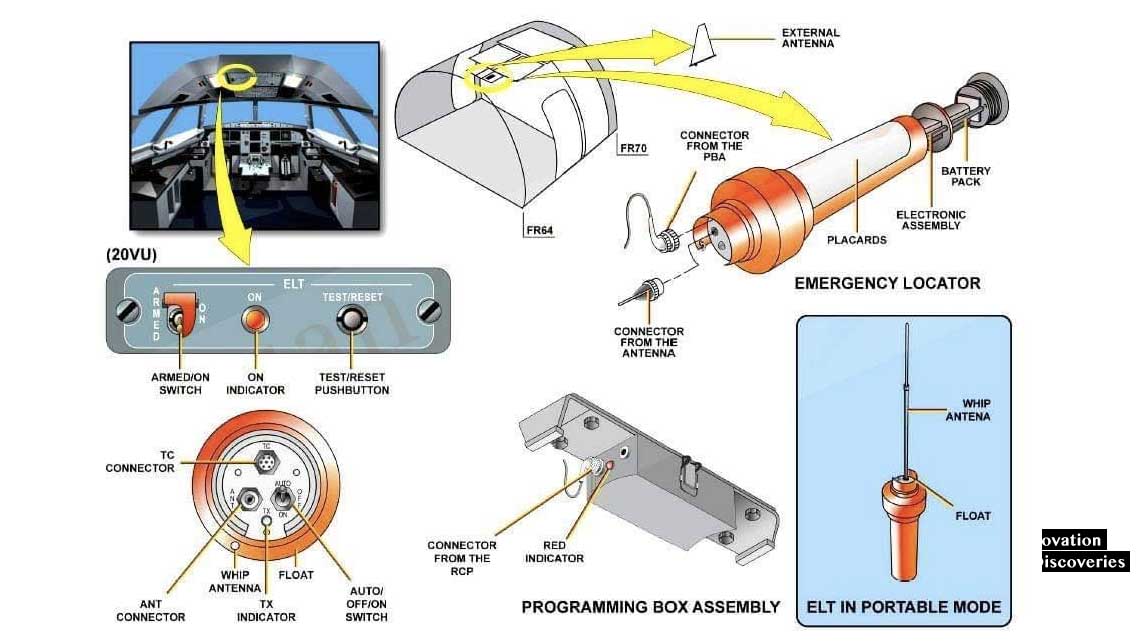
Testing and Maintenance
Regular testing and maintenance are crucial to ensuring the reliability of ELTs. Technicians are required to perform an inspection and test of 121.5 MHz ELTs within 12 months of the previous check.
This inspection ensures the integrity and functionality of the device. For older ELTs, which often lack built-in test circuitry, a true operational test may involve activating the signal. This is done by removing the antenna and installing a dummy load to prevent unnecessary alerts.
Testing must be conducted at specific times—only at the top of each hour and within the first five minutes—to avoid confusion with actual distress signals. The duration of activation during testing must not exceed three audible sweeps.
Additionally, it is recommended to contact the local control tower or flight service station before conducting any tests to inform them of the procedure and prevent any false alarms.
Transition to Digital ELTs
The aviation industry is progressively transitioning from older analog ELTs to modern digital units certified to TSO C-126 standards. These advanced digital ELTs offer several significant improvements over their analog predecessors:
- Enhanced Coverage: The 406 MHz signal is monitored by a global network of satellites, providing comprehensive coverage and ensuring that distress signals are detected regardless of the aircraft’s location.
- Improved Accuracy: The inclusion of GPS data in the digital signal allows for precise location determination, often within 100 meters. This reduces search times and increases the chances of a successful rescue.
- Faster Response: Digital signals are processed more efficiently, leading to quicker identification and validation of genuine distress alerts. This rapid response can be critical in life-threatening situations.
- Reduction of False Alerts: Digital ELTs have mechanisms to minimize false alerts, ensuring that search and rescue resources are not deployed needlessly.
Conclusion
The Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) is a vital component of aviation safety, providing a reliable means of locating and rescuing aircraft in distress.
Despite technological advancements, incidents like the disappearance of flight MH370 highlight the ongoing need for rigorous testing, maintenance, and development of ELT technology.
As the industry continues to adopt modern digital ELTs, the improvements in coverage, accuracy, and response times promise to enhance overall aviation safety and rescue operations.
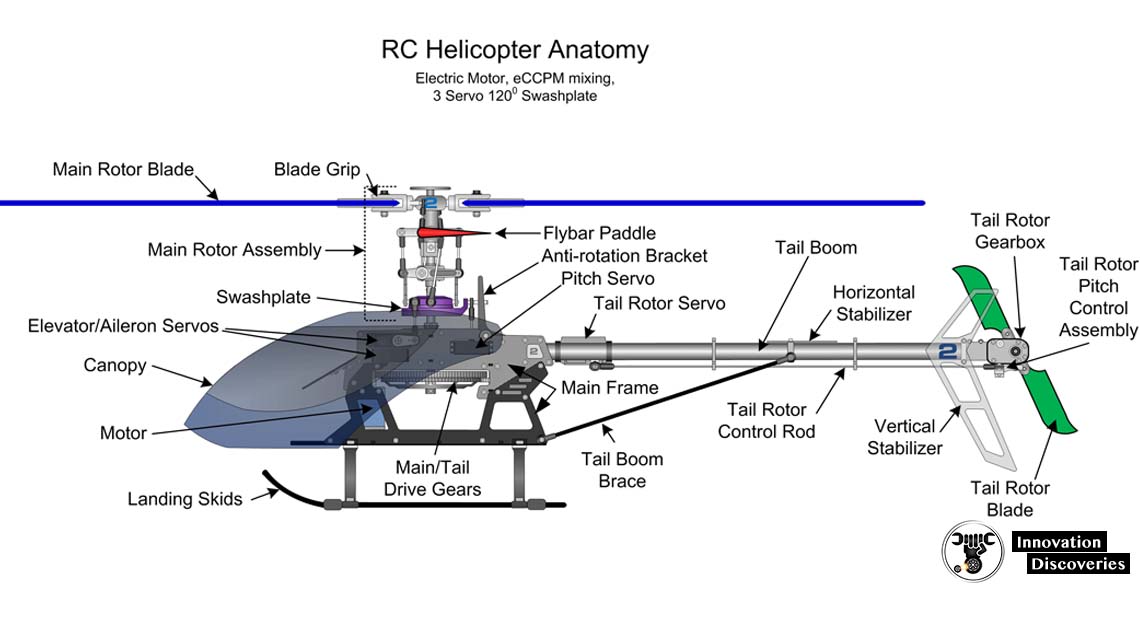
READ MORE: HOW A HELICOPTER FLY AND CONSTRUCTED?
How Do Airplanes Fly? Components
ALSO, READ:
- HOW DO AIRPLANES FLY? COMPONENTS
- WHY ALL AIRPLANE WINDOWS ROUND NOT SQUARE OR RECTANGLE?
- WHAT ARE THE COMPONENTS OF THE LANDING GEAR?
- AIRCRAFT WEIGHT AND BALANCE TERMINOLOGY – EMPTY WEIGHT
- HOW DOES A JET ENGINE WORK? | INNOVATION DISCOVERIES
- WHY ARE AIRPLANES PAINTED WHITE?
- GUY MAKES A HUGE PAPER AIRPLANE AND THROWS IT OFF A HUGE MOUNTAIN
- WHAT IS A SOLAR POWERED AIRPLANE?
- STANDARD WEIGHTS USED FOR AIRCRAFT WEIGHT AND BALANCE
- TAIL WHEEL GEAR CONFIGURATION
- HOW A PROPELLER GENERATES THRUST
- IF ALL THE AIRCRAFT’S ENGINES FAIL, WILL THE PLANE STILL FLY OR WILL IT FALL OUT OF THE SKY?
DOWNLOAD: ENGINEERING VIBRATION

WIRING DIAGRAMS AND WIRE TYPES

Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website