Introduction:
When it comes to power and performance, diesel engines have always held a special place. Known for their exceptional torque output, diesel engines dominate heavy-duty vehicles, ensuring they can handle tough tasks with ease. But have you ever wondered why diesel engines excel in torque production compared to their gasoline counterparts?
In this article, we will delve into the five primary reasons behind the remarkable torque generated by diesel engines.
1. Higher Compression Ratio: Unleashing the Powerhouse
Diesel engines possess a distinct advantage in their ability to achieve higher compression ratios. Unlike gasoline engines, which typically operate within compression ratios of 9:1 to 12:1, diesel engines ramp it up to 15:1 or even higher.
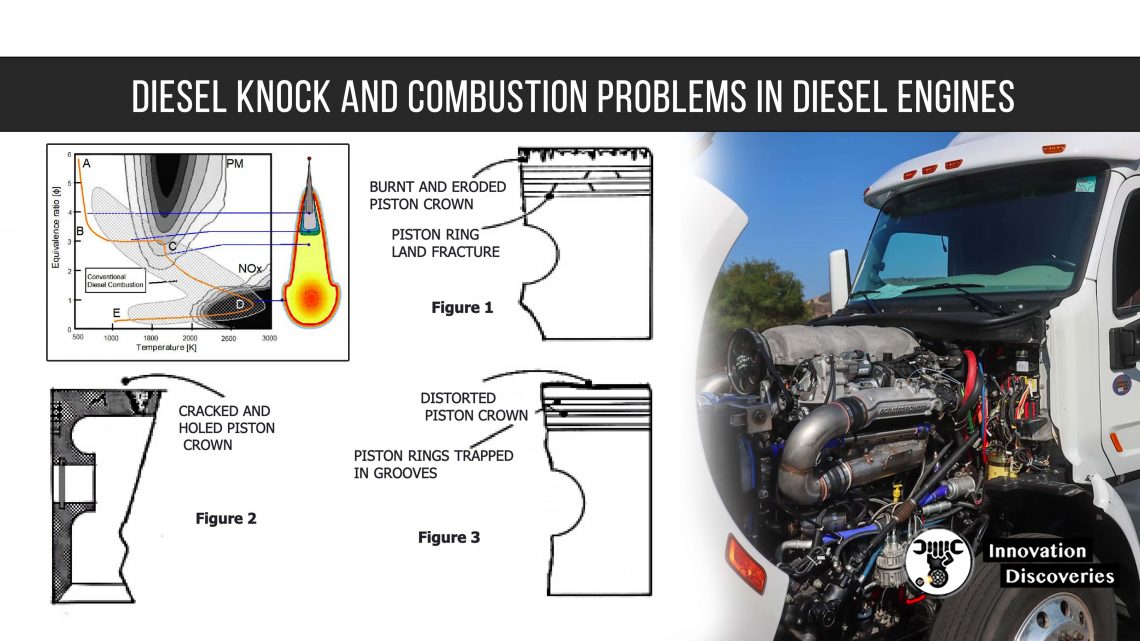
This higher compression ratio allows for a more efficient combustion process and a forceful expansion of the combustion gases. The result? Increased torque production that sets diesel engines apart.

2. Turbocharging: Boosting Performance to New Heights
Turbocharging technology has become a defining feature of modern diesel engines, further amplifying their torque output. By harnessing the energy from the engine’s exhaust gases, a turbocharger drives a turbine, compressing the incoming air.
This process enhances the amount of fuel that can be burned, leading to increased torque production. While turbocharging can be found in some gasoline engines, it is far more prevalent in diesel engines, contributing to their superior torque capabilities.
3. Fuel Properties: The Energy-Dense Elixir
The properties of diesel fuel play a pivotal role in the torque supremacy of diesel engines. Diesel fuel boasts a higher energy density than gasoline, meaning it contains more potential energy per unit volume.
With this higher energy content, diesel engines extract more work from each combustion cycle, resulting in a significant boost in torque output.
Moreover, diesel fuel’s higher flash point and its requirement for higher compression temperatures allow for a controlled and efficient combustion process, further contributing to increased torque.
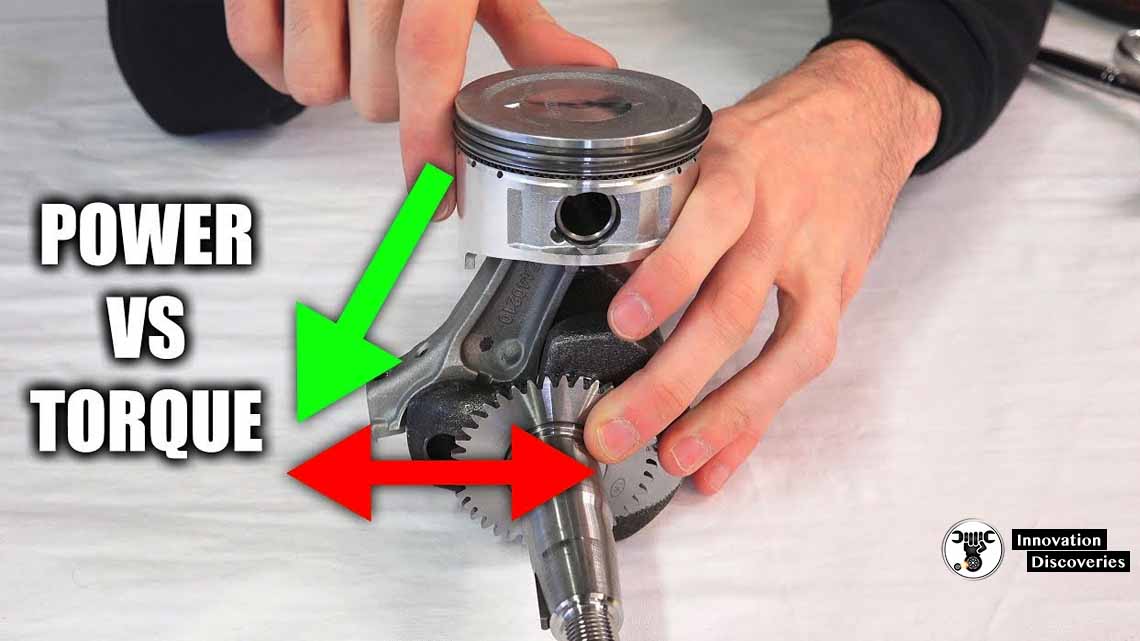
4. Longer Stroke Length: The Journey to Greater Power
Diesel engines flaunt a longer stroke length compared to their gasoline counterparts. Stroke length refers to the distance the piston travels inside the cylinder. With a longer stroke, diesel engines can accommodate a larger displacement, allowing for a greater amount of air-fuel mixture to be combusted.
This design characteristic, when combined with the high compression ratio and turbocharging, propels diesel engines to achieve exceptional torque output.
5. Robust Construction: Engineered for Dominance
Diesel engines are renowned for their sturdy and rugged construction, purpose-built to handle high compression and heavy-duty applications.
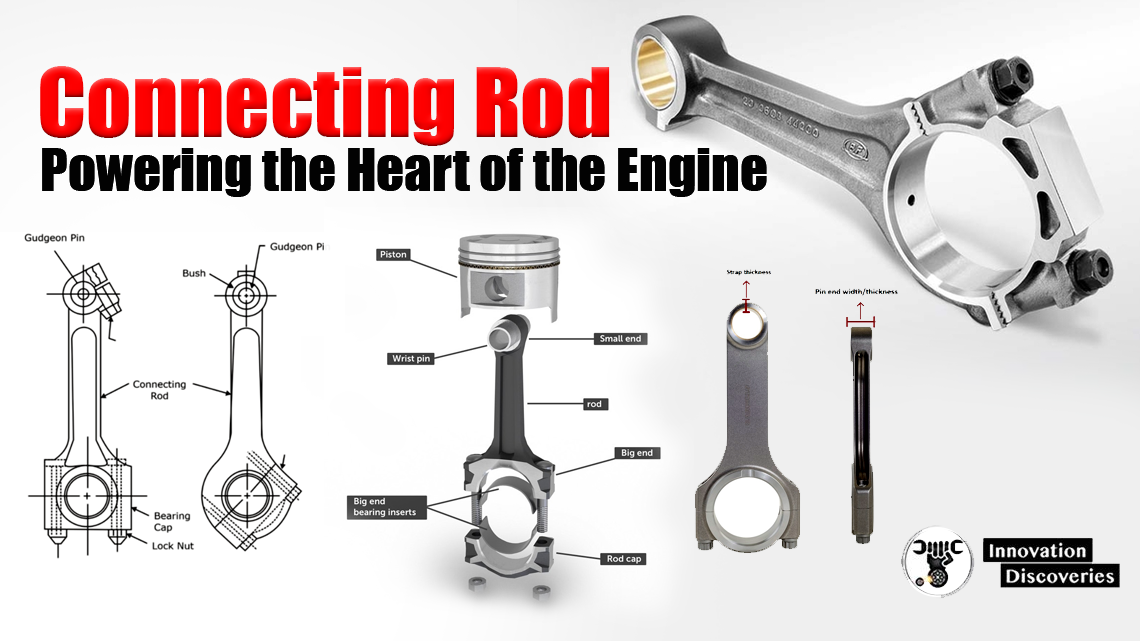
The components of a diesel engine, including the block, pistons, connecting rods, and crankshaft, are engineered to withstand the substantial forces associated with high compression ratios and the increased torque output.
In contrast, gasoline engines are typically designed for lighter loads and lower compression ratios, resulting in comparatively lower torque ratings.
Conclusion:
In the realm of torque production, diesel engines reign supreme for several reasons.
The higher compression ratio, coupled with turbocharging technology, the energy density of diesel fuel, longer stroke length, and robust construction, all contribute to the diesel engine’s remarkable torque capabilities. These factors make diesel engines the go-to choice for heavy-duty applications that require exceptional pulling and hauling capabilities.
However, it’s important to recognize that gasoline engines have their own advantages, such as higher RPM capabilities and smoother operation, which make them more suitable for lighter vehicles and high-performance applications. With this understanding, we can appreciate the power and prowess of diesel engines, propelling them to be the torque kings of the automotive world.
Discover More:
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website