Introduction
Signs Your Throttle Body Is Going Bad, and What to Do
The throttle body is a crucial component of your vehicle’s air intake system, playing a pivotal role in regulating the amount of air entering the engine.
This directly influences your car’s power and performance. When the throttle body malfunctions, it can lead to a range of problems, impacting your vehicle’s drivability and efficiency.
In this article, we’ll discuss the signs of a failing throttle body and provide detailed steps on what to do if you encounter these issues.
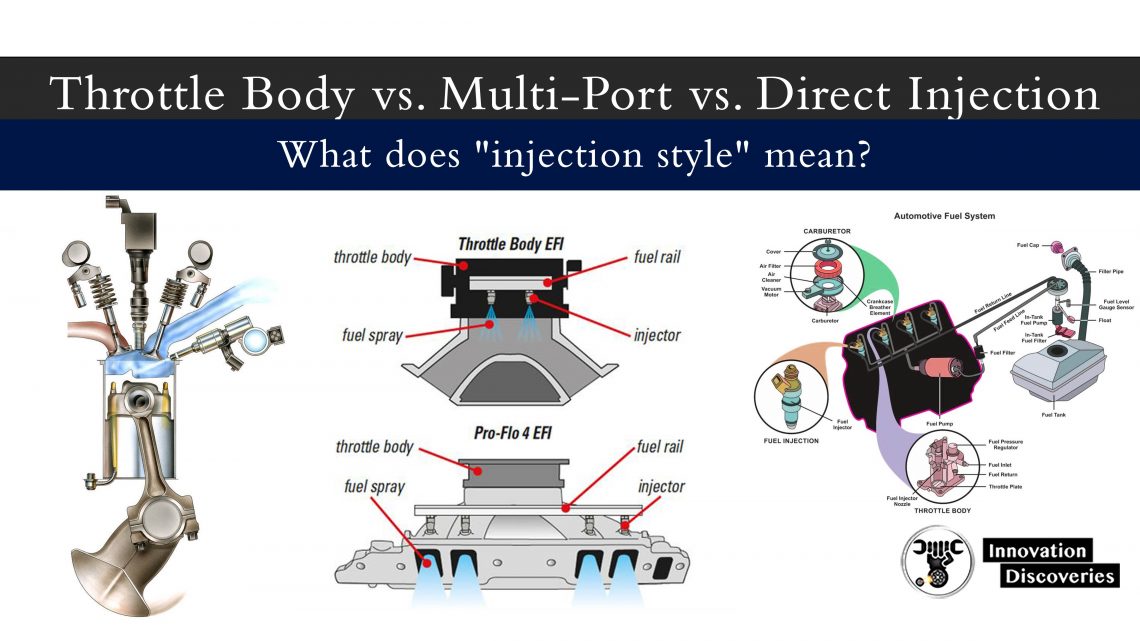
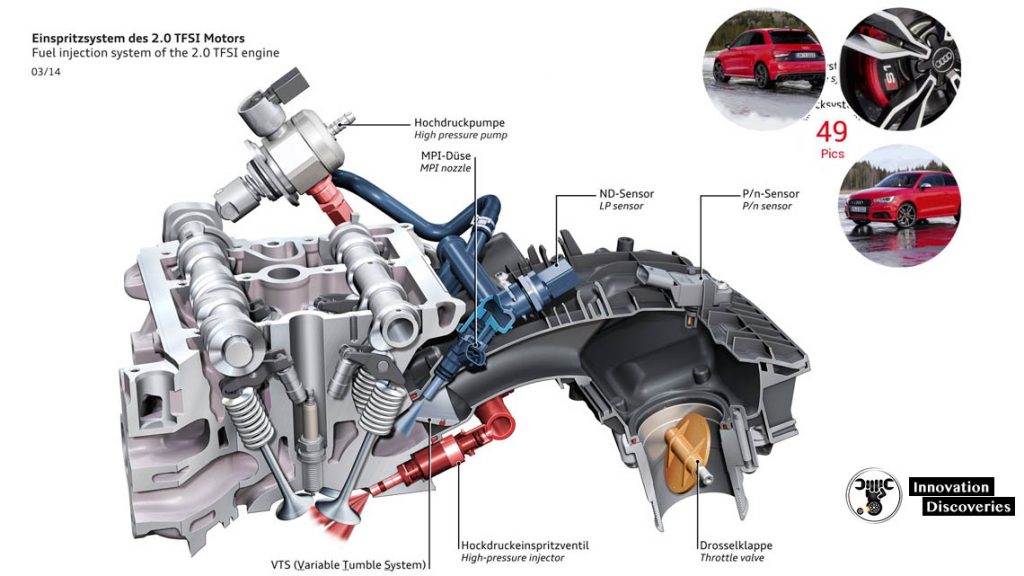
What is a Throttle Body?
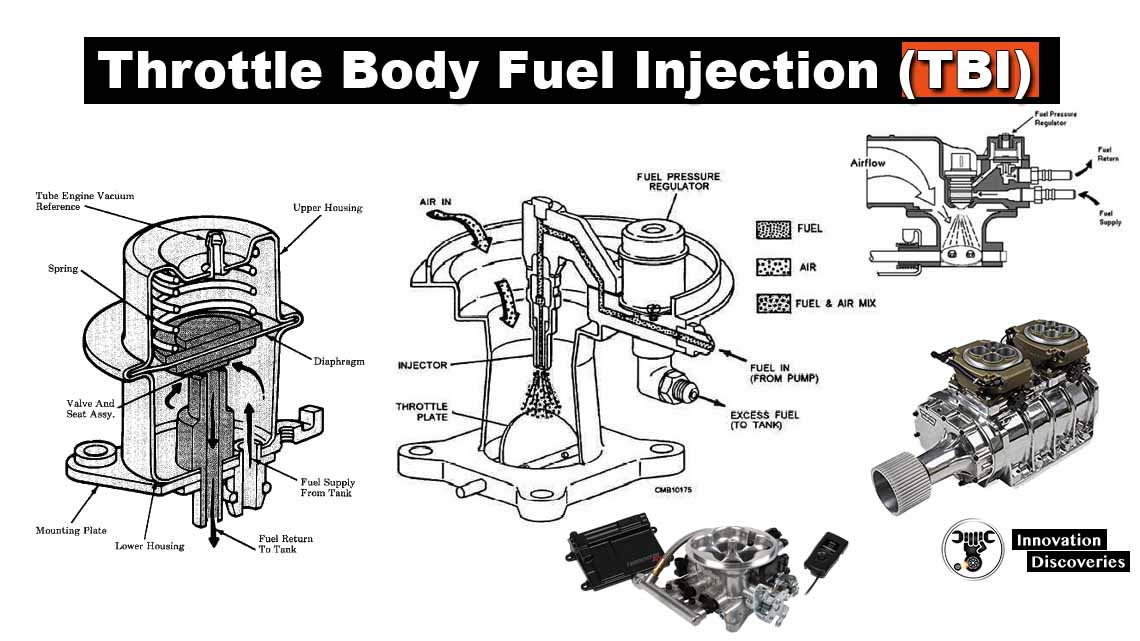
The throttle body is a component located between the air filter and the intake manifold in a fuel-injected engine. It houses the throttle plate, which opens and closes to control the amount of air flowing into the engine.
The throttle body is connected to the accelerator pedal, and its position is monitored by the throttle position sensor (TPS).
Common Signs of a Failing Throttle Body
- Rough Idle
- Symptoms: The engine idles roughly, experiencing irregular RPMs, or feels shaky.
- Cause: Carbon buildup or a malfunctioning throttle plate can restrict air flow, causing the engine to idle poorly.
- Poor Acceleration
- Symptoms: The vehicle hesitates or responds sluggishly when you press the accelerator.
- Cause: A dirty or failing throttle body can limit the air entering the engine, leading to reduced performance.
- Stalling
- Symptoms: The engine stalls unexpectedly, particularly at low speeds or when coming to a stop.
- Cause: Inconsistent air flow due to a faulty throttle body can cause the engine to cut out.
- Check Engine Light
- Symptoms: The Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminates on your dashboard.
- Cause: The vehicle’s computer detects a problem with the throttle body or related components, often storing a specific trouble code.
- Poor Fuel Economy
- Symptoms: A noticeable decrease in fuel efficiency.
- Cause: An imbalanced air-to-fuel ratio due to a malfunctioning throttle body can cause the engine to use more fuel.
- Unresponsive Throttle
- Symptoms: The accelerator pedal feels unresponsive or inconsistent.
- Cause: Issues with the electronic throttle control or mechanical linkage can result in poor throttle response.
Diagnosing Throttle Body Problems
- Visual Inspection
- Check for Carbon Buildup: Remove the air intake hose and inspect the throttle body for dirt and carbon deposits.
- Examine Electrical Connections: Ensure all wiring and connectors are secure and free of corrosion.
- Use an OBD-II Scanner
- Read Trouble Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any stored trouble codes related to the throttle body or TPS.
- Monitor Live Data: Observe throttle position readings and other related parameters to identify abnormalities.
- Manual Testing
- Throttle Plate Movement: Manually move the throttle plate to check for smooth operation and resistance.
- Throttle Position Sensor: Test the TPS with a multimeter to ensure it provides accurate readings.
What to Do if Your Throttle Body is Going Bad
- Clean the Throttle Body
- Tools Needed: Throttle body cleaner, a clean cloth, and basic hand tools.
- Steps:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove the air intake hose.
- Spray the throttle body cleaner on the throttle plate and surrounding area.
- Wipe away carbon deposits with a clean cloth.
- Reassemble and reconnect the battery.
- Replace the Throttle Body
- Symptoms: If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, a replacement may be necessary.
- Steps:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove the air intake hose and any electrical connectors.
- Unbolt the throttle body from the intake manifold.
- Install the new throttle body and reassemble the components.
- Reconnect the battery and perform any required throttle body re-learn procedures.
- Check and Replace the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
- Symptoms: If the TPS is faulty, it can send incorrect signals to the ECU.
- Steps:
- Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove the TPS from the throttle body.
- Install the new TPS and reconnect the wiring.
- Reconnect the battery and clear any stored trouble codes.
Preventative Maintenance Tips
- Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the throttle body to prevent carbon buildup.
- Quality Fuel: Use high-quality fuel to reduce deposits in the intake system.
- Timely Repairs: Address any CEL issues promptly to prevent further damage to the throttle body or other engine components.
Conclusion
A failing throttle body can significantly impact your vehicle’s performance and efficiency. By recognizing the signs early and taking appropriate action, you can maintain your car’s reliability and avoid costly repairs.
Regular maintenance and timely repairs are key to ensuring your throttle body and overall engine remain in good working condition. If you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing a throttle body issue, consult with a professional mechanic to get the best results.
Discover More:
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website