Introduction
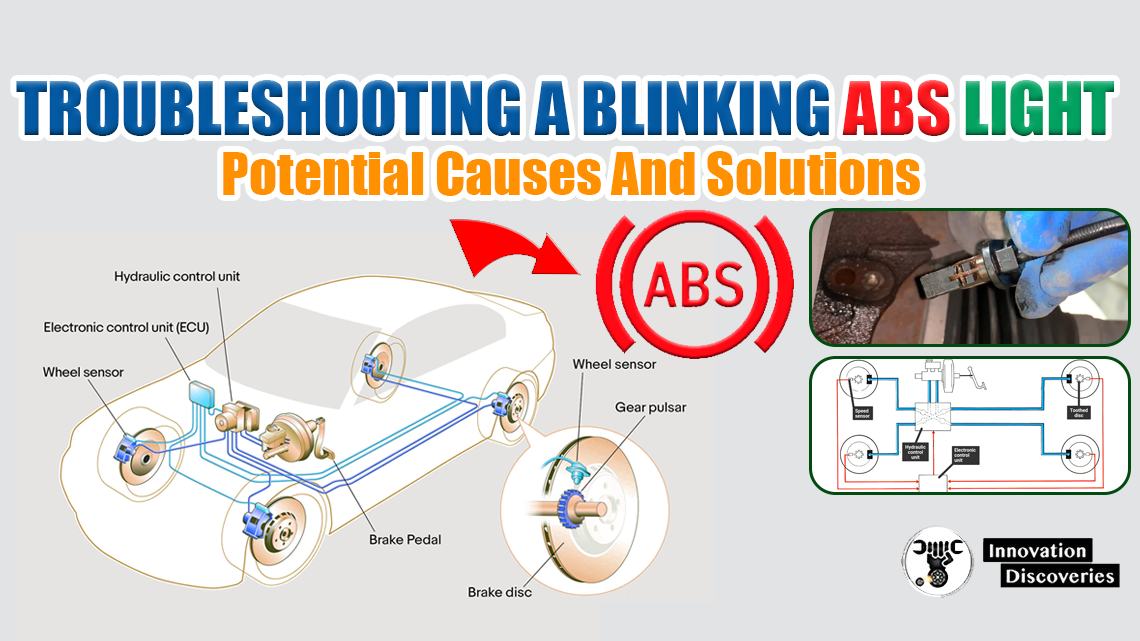
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles, designed to prevent the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby maintaining traction with the road surface.
A critical component of this system is the ABS differential sensor. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into what an ABS differential sensor is, how it works, its importance, common issues, and maintenance tips.
What is an ABS Differential Sensor?
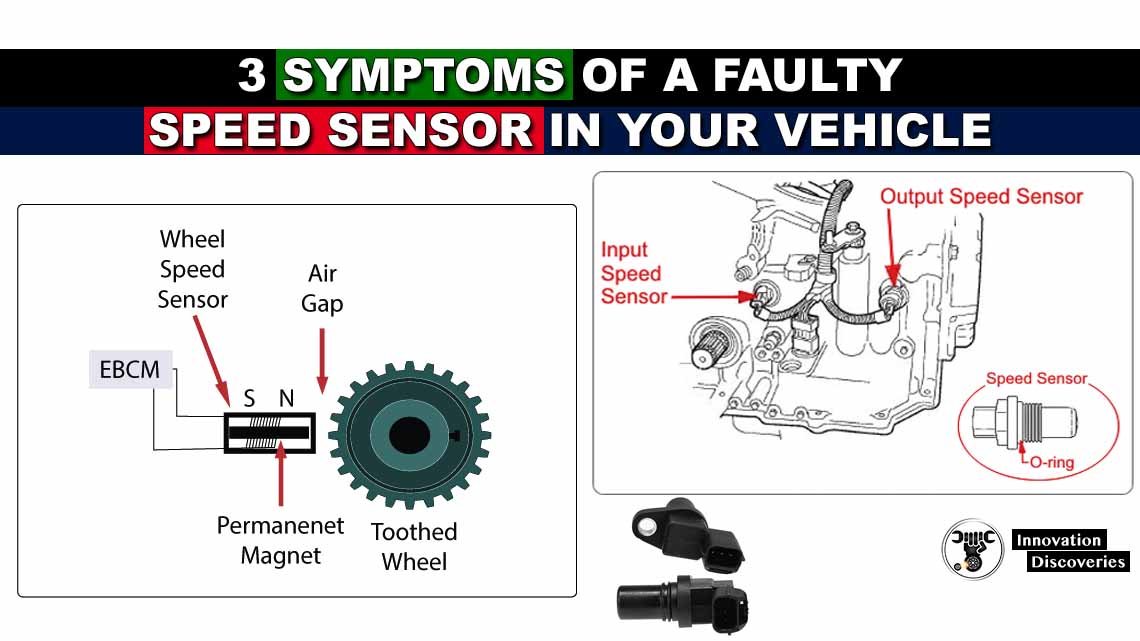
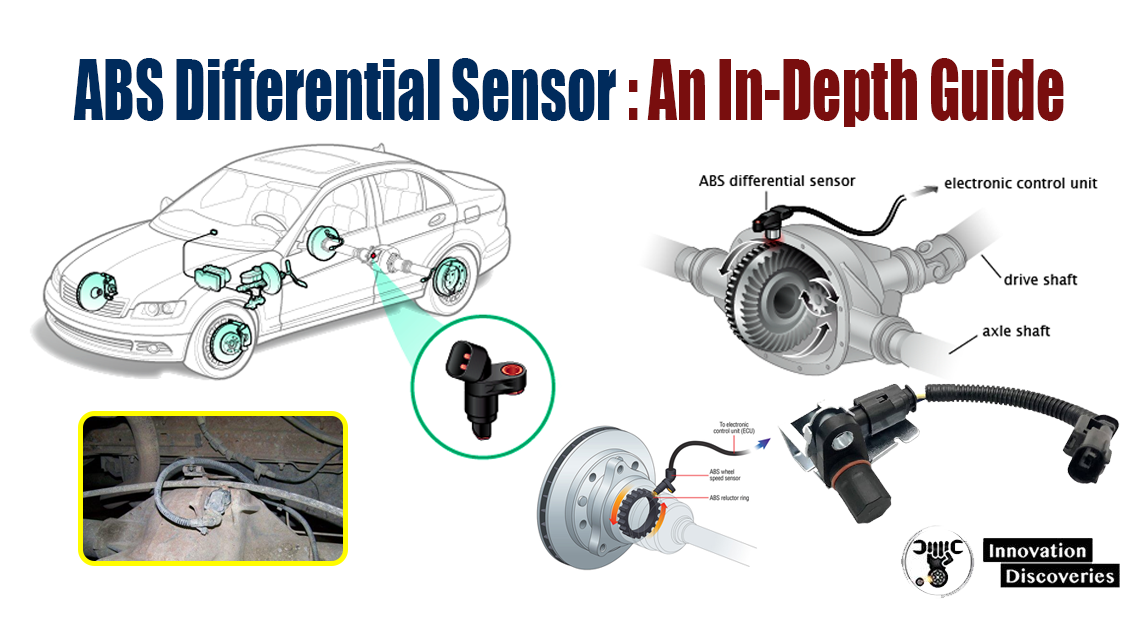
The ABS differential sensor, often referred to as the wheel speed sensor, is a vital part of the ABS system. It monitors the rotational speed of each wheel and sends this information to the ABS control module.
This data is essential for the ABS to determine when a wheel is about to lock up, allowing it to modulate brake pressure and prevent skidding.
How Does the ABS Differential Sensor Work?
The ABS differential sensor operates based on the principles of electromagnetic induction. Here’s a step-by-step look at its working mechanism:
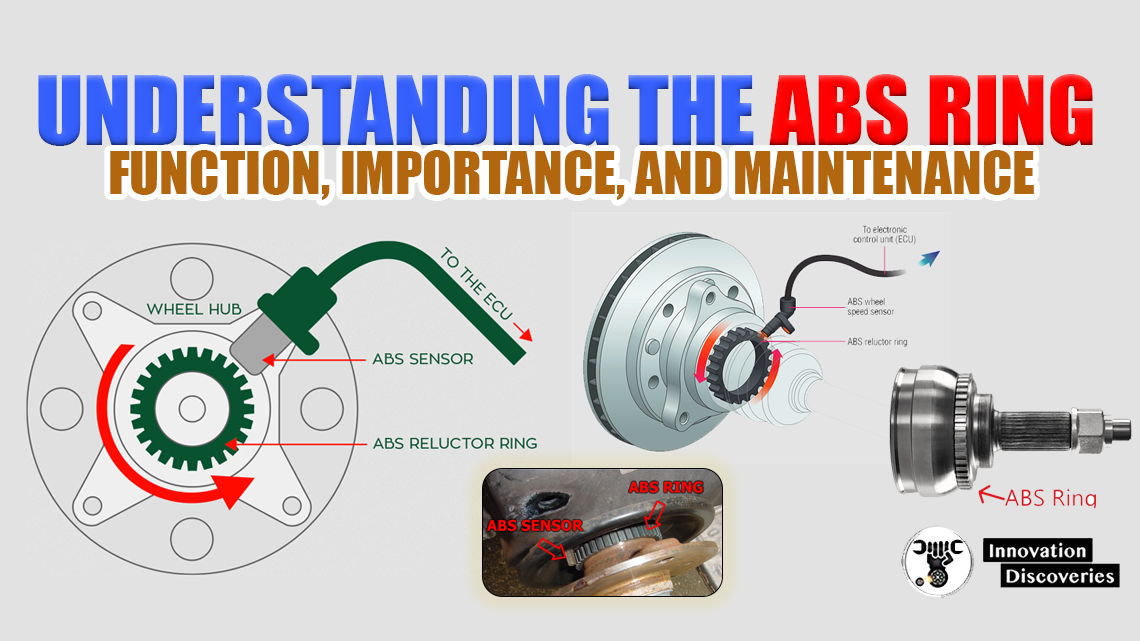
- Sensor Placement: Each wheel has an ABS sensor located near the wheel hub.
- Tone Ring: A toothed ring, known as the tone ring or reluctor ring, is attached to the wheel or axle.
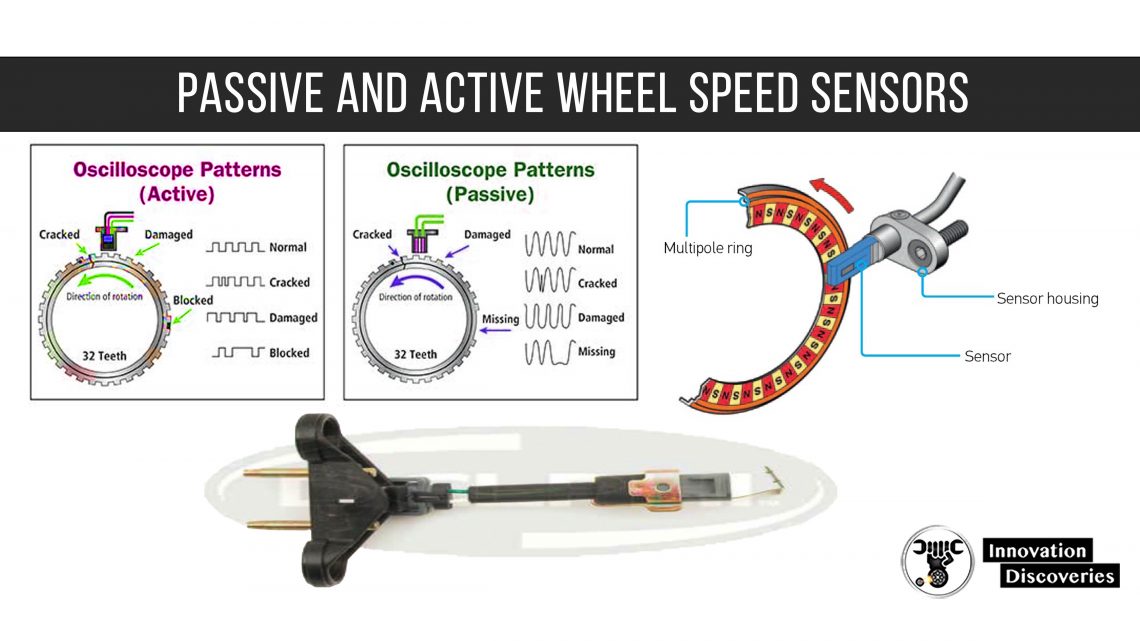
- Electromagnetic Induction: As the wheel rotates, the teeth of the tone ring pass by the magnetic sensor, creating an alternating current (AC) signal.
- Signal Transmission: This AC signal, which corresponds to the wheel speed, is transmitted to the ABS control module.
- Data Analysis: The ABS control module analyzes the signals from all four wheels. If it detects a wheel slowing down too quickly (indicating a potential lock-up), it modulates the brake pressure to that wheel, maintaining traction and control.
Importance of ABS Differential Sensors
ABS differential sensors play a critical role in vehicle safety by:
- Preventing Wheel Lock-Up: By continuously monitoring wheel speed, the sensors help prevent the wheels from locking up during hard braking, reducing the risk of skidding.
- Enhancing Control: Maintaining wheel traction allows drivers to steer and control the vehicle more effectively during emergency braking situations.
- Improving Stopping Distance: While ABS systems are primarily designed for control rather than reducing stopping distances, in many situations, they can help achieve shorter and more controlled stops.
- Supporting Stability Systems: Modern vehicles often integrate ABS with other stability control systems like Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control System (TCS), which rely on wheel speed data to function effectively.
Common Issues with ABS Differential Sensors
ABS differential sensors can encounter various issues that affect their performance. Common problems include:
- Sensor Damage: Physical damage to the sensor due to debris, accidents, or wear and tear can impair its functionality.
- Dirty or Damaged Tone Ring: Accumulation of dirt, rust, or damage to the tone ring can disrupt the sensor’s ability to read wheel speed accurately.
- Wiring Problems: Damaged or corroded wiring can interrupt the signal transmission between the sensor and the ABS control module.
- Electrical Interference: External electromagnetic interference can affect the sensor’s signals, leading to erratic ABS performance.
Diagnosing ABS Differential Sensor Issues
Diagnosing problems with ABS sensors typically involves:
- Check for Warning Lights: The ABS warning light on the dashboard indicates a potential issue with the ABS system.
- OBD-II Scanner: Using an On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) scanner can help identify specific fault codes related to ABS sensors.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the sensor and tone ring for visible damage or debris.
- Multimeter Testing: A multimeter can be used to check the sensor’s electrical resistance and continuity.
- Signal Output Test: Monitoring the sensor’s signal output with an oscilloscope can reveal issues with signal generation.
Maintenance and Replacement Tips
To ensure optimal performance of ABS differential sensors:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the sensor and tone ring clean from dirt and debris.
- Periodic Inspections: Regularly inspect the sensor, wiring, and tone ring for signs of damage or wear.
- Timely Replacements: Replace damaged or faulty sensors promptly to maintain ABS functionality.
- Professional Service: Have a professional mechanic diagnose and service ABS-related issues, especially if the ABS warning light is on.
Conclusion
The ABS differential sensor is a key component in maintaining vehicle safety and control during braking. Understanding its function, recognizing common issues, and performing regular maintenance can help ensure your vehicle’s ABS system operates effectively.
Whether you’re a car enthusiast or a professional mechanic, staying informed about ABS sensors can significantly contribute to road safety and vehicle reliability.
By following these guidelines and maintaining your ABS system, you can enjoy enhanced driving confidence and peace of mind on the road.
Discover More:
More About Braking Systems
- Top 5 Causes of Steering Wheel Shakes at Low and High Speeds
- HOW HYDRAULIC BRAKE WORKS?
- AIR BRAKE SYSTEM: COMPONENTS, WORKING PRINCIPLE, AND APPLICATIONS
- HOW DOES REGENERATIVE BRAKING WORK?
- 8 REASONS YOUR CAR IS MAKING GRINDING NOISE WHEN BRAKING
- Regenerative Braking System
- JAKE BRAKE VS. EXHAUST BRAKE: WHICH IS BETTER?
- SQUEALING BRAKES AT LOW SPEED: CAUSES AND SOLUTIONS
- TROUBLESHOOTING A HARD BRAKE PEDAL
- CONVERT DRUM BRAKES TO DISC BRAKES IN 3 STEPS!
- CAUSES OF THE BRAKE WARNING LIGHT COMING ON
– Additional –
This file contains information transposed from the BMW Car Club of Bulgaria forum site (Errors and omissions excluded) –
Visit Forum
Visit Our Friendly Website